389H_NO_02_review_I
... (refers to force, not to mass) • specific gravity = ratio of weight of volume of liquid to same volume of water at std. conditions (usually 60 °F or 20 °C and 1 atm) ...
... (refers to force, not to mass) • specific gravity = ratio of weight of volume of liquid to same volume of water at std. conditions (usually 60 °F or 20 °C and 1 atm) ...
Chapter 9 and 10
... Conductors allow heat/electricity to easily flow through them because they have loosely held electrons. Insulators do not allow heat or electricity to easily flow through them because their electrons are tightly held to the molecule. 9. Explain why the water at the beach is cooler than the sand on t ...
... Conductors allow heat/electricity to easily flow through them because they have loosely held electrons. Insulators do not allow heat or electricity to easily flow through them because their electrons are tightly held to the molecule. 9. Explain why the water at the beach is cooler than the sand on t ...
specific heat
... Heat capacity of a body is the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of the body by 1oC. The specific heat of a substance is the heat capacity per unit mass. Thus, heat capacity = mass x specific heat. The specific heat is essentially a measure of how thermally insensitive a substance i ...
... Heat capacity of a body is the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of the body by 1oC. The specific heat of a substance is the heat capacity per unit mass. Thus, heat capacity = mass x specific heat. The specific heat is essentially a measure of how thermally insensitive a substance i ...
Thermochemistry 2 Matching Match each item with the correct
... Match each item with the correct statement below. a. heat of reaction d. heat of fusion b. heat of formation e. heat of solution c. Hess's law of heat summation ____ ...
... Match each item with the correct statement below. a. heat of reaction d. heat of fusion b. heat of formation e. heat of solution c. Hess's law of heat summation ____ ...
Calorimetry Lab
... masses of water, one “hot” and one “cold”. If the coffee cups were perfect insulators, the final temperature of the combined mass of water would be midway between the hot and cold temperatures, assuming equal masses were used. Because the cups are not perfect insulators, the hot water will lose slig ...
... masses of water, one “hot” and one “cold”. If the coffee cups were perfect insulators, the final temperature of the combined mass of water would be midway between the hot and cold temperatures, assuming equal masses were used. Because the cups are not perfect insulators, the hot water will lose slig ...
Calorimetry Lab
... masses of water, one “hot” and one “cold”. If the coffee cups were perfect insulators, the final temperature of the combined mass of water would be midway between the hot and cold temperatures, assuming equal masses were used. Because the cups are not perfect insulators, the hot water will lose slig ...
... masses of water, one “hot” and one “cold”. If the coffee cups were perfect insulators, the final temperature of the combined mass of water would be midway between the hot and cold temperatures, assuming equal masses were used. Because the cups are not perfect insulators, the hot water will lose slig ...
(C, ° F ) u = internal energy (J/kg, Btu
... surroundings when a force acts through a distance • ft∙lbf or N∙m (note units of energy) ...
... surroundings when a force acts through a distance • ft∙lbf or N∙m (note units of energy) ...
Electronics Cooling MEP 635
... 1. To establish fundamental understanding of heat transfer in electronic equipment. 2. To select a suitable cooling processes for electronic components and systems. 3. To increase the capabilities of post-graduate students in design and analysis of cooling of electronic packages. 4. To analysis the ...
... 1. To establish fundamental understanding of heat transfer in electronic equipment. 2. To select a suitable cooling processes for electronic components and systems. 3. To increase the capabilities of post-graduate students in design and analysis of cooling of electronic packages. 4. To analysis the ...
Word
... The energy gained by the water is the Ematch = 4180 J.kg-1.K-1 m T. This is the energy supplied by the match. A bath tub contains around 300 l or 0.3 m3 which is around 300 kg of water. A nice hot bath is around 50oC, and tap water is typically at around 20oC, so you need a temperature change o ...
... The energy gained by the water is the Ematch = 4180 J.kg-1.K-1 m T. This is the energy supplied by the match. A bath tub contains around 300 l or 0.3 m3 which is around 300 kg of water. A nice hot bath is around 50oC, and tap water is typically at around 20oC, so you need a temperature change o ...
Joule`s Law and Heat Transfer Name
... To do this we need to measure the amount of electrical energy we supply and the amount of heat energy the water, calorimeter-cup, and heater gains. Then neglecting heat loss to the room, we could find the relationship between calorie and Joule. Electrical energy, E is given by: E = I V t; where I = ...
... To do this we need to measure the amount of electrical energy we supply and the amount of heat energy the water, calorimeter-cup, and heater gains. Then neglecting heat loss to the room, we could find the relationship between calorie and Joule. Electrical energy, E is given by: E = I V t; where I = ...
BUOYANCY-DRIVEN TURBULENT CONVECTION IN A BUNDLE
... Buoyant, turbulent convective heat transfer around cylindrical rods arranged in bundles is a technically relevant heat transfer configuration which finds application in steam generators, cooling of reactor core fuel assemblies and heat exchangers in general. Most of the research performed so far con ...
... Buoyant, turbulent convective heat transfer around cylindrical rods arranged in bundles is a technically relevant heat transfer configuration which finds application in steam generators, cooling of reactor core fuel assemblies and heat exchangers in general. Most of the research performed so far con ...
Energy: Conservation and Interconversion Demonstration:
... and work are processes or interactions between the system and the surroundings. Heat and work depend on the way the process is carried out. They “depend on the path”. Note that positive heat absorbed by the system results in an increase in the internal energy of the system. Similarly, the surroundin ...
... and work are processes or interactions between the system and the surroundings. Heat and work depend on the way the process is carried out. They “depend on the path”. Note that positive heat absorbed by the system results in an increase in the internal energy of the system. Similarly, the surroundin ...
Implimenting a Simple Heat Exchanger Unit with
... Traditional heat exchangers are complex units comprised of compressors, radiators, and phase changes involving chemical refrigerants. These systems have several points for failure and are expensive to build, making them impractical for applications requiring small amounts of cooling in a portable en ...
... Traditional heat exchangers are complex units comprised of compressors, radiators, and phase changes involving chemical refrigerants. These systems have several points for failure and are expensive to build, making them impractical for applications requiring small amounts of cooling in a portable en ...
lecture21
... Reversible and Irreversible Processes A process is said to be reversible if both the system and the surroundings can be restored to their respective initial states, by reversing the direction of the process. A reversible process is a process that can be reversed without leaving a trace on the surro ...
... Reversible and Irreversible Processes A process is said to be reversible if both the system and the surroundings can be restored to their respective initial states, by reversing the direction of the process. A reversible process is a process that can be reversed without leaving a trace on the surro ...
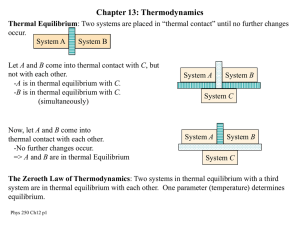
p250c13
... Example: A heat pump is used to maintain an inside temperature of 20 ºC when the outside temperature is 10ºC. What is the theoretical maximum cp for this heat pump? If the pump is to deliver heat at a rate of 15 kW, how much power must be supplied to run the pump? ...
... Example: A heat pump is used to maintain an inside temperature of 20 ºC when the outside temperature is 10ºC. What is the theoretical maximum cp for this heat pump? If the pump is to deliver heat at a rate of 15 kW, how much power must be supplied to run the pump? ...
Chapter 8 Thermochemistry: Chemical Energy
... temperature thermal equilibrium When not Heat transfer to surrounding = exothermic (you feel the heat) hot metal!! Heat transfer to system = endothermic (you feel cold) cold metal!! ...
... temperature thermal equilibrium When not Heat transfer to surrounding = exothermic (you feel the heat) hot metal!! Heat transfer to system = endothermic (you feel cold) cold metal!! ...
Chapter 7 Thermal and Energy Systems
... • Heat can also be transferred by a fluid that is in motion; that process is known as convection. • The cooling system of an automobile engine, for instance, operates by pumping a mixture of water and antifreeze through passageways inside the engine’s block. • Excess heat is removed from the engine, ...
... • Heat can also be transferred by a fluid that is in motion; that process is known as convection. • The cooling system of an automobile engine, for instance, operates by pumping a mixture of water and antifreeze through passageways inside the engine’s block. • Excess heat is removed from the engine, ...
Full PDF
... are favorable, reproductive activity expresses its full potential. Favourable conditions must include adequate photoperiod, thermo-neutral conditions, food availability in quantity and quality and a low stress environment. The body temperature of most domestic animals is considerably higher than the ...
... are favorable, reproductive activity expresses its full potential. Favourable conditions must include adequate photoperiod, thermo-neutral conditions, food availability in quantity and quality and a low stress environment. The body temperature of most domestic animals is considerably higher than the ...
here - UFL MAE - University of Florida
... thermal analysis. Students will learn to apply the conservation of energy to control volumes and express the conservation of energy through mathematical formulations, including both steady state and transient analyses, with emphasis on the fundamental physics and underlying mathematics associated wi ...
... thermal analysis. Students will learn to apply the conservation of energy to control volumes and express the conservation of energy through mathematical formulations, including both steady state and transient analyses, with emphasis on the fundamental physics and underlying mathematics associated wi ...
Energy Transformations
... Heat, represented by q, is energy that transfers from one object to another because of a temperature difference between them. Heat always flows from a warmer object to a cooler object. ...
... Heat, represented by q, is energy that transfers from one object to another because of a temperature difference between them. Heat always flows from a warmer object to a cooler object. ...
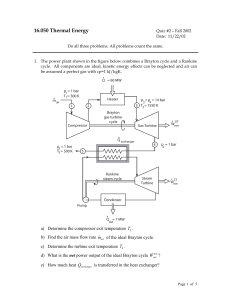
More Carnot Cycle March 4, 2010 Efficiency = W/Qin = Qin
... Heat Transfer occurs only between regions that are at different temperatures, and the direction of heat flow is always from higher to the lower temperature. The diagram shows a rod of a conducting material with cross sectional area A and length L. The left end of the rod is kept at constant temperat ...
... Heat Transfer occurs only between regions that are at different temperatures, and the direction of heat flow is always from higher to the lower temperature. The diagram shows a rod of a conducting material with cross sectional area A and length L. The left end of the rod is kept at constant temperat ...