Heat Exhaustion
... index, and also to remember that the heat index is even higher when you are standing in full sunshine. If you live in an urban area, you may be especially prone to develop heat exhaustion during a prolonged heat wave, particularly if there are stagnant atmospheric conditions and poor air quality. In ...
... index, and also to remember that the heat index is even higher when you are standing in full sunshine. If you live in an urban area, you may be especially prone to develop heat exhaustion during a prolonged heat wave, particularly if there are stagnant atmospheric conditions and poor air quality. In ...
ExamView - sample-Questions-ch10-11-12
... of linear expansion of 11 106/C. Give its change in length as the temperature changes from 10C to 45C. a. 0.65 cm b. 1.8 cm c. 5.8 cm d. 12 cm 4. Heat flow occurs between two bodies in thermal contact when they differ in what property? a. mass b. specific heat c. density d. temperature ...
... of linear expansion of 11 106/C. Give its change in length as the temperature changes from 10C to 45C. a. 0.65 cm b. 1.8 cm c. 5.8 cm d. 12 cm 4. Heat flow occurs between two bodies in thermal contact when they differ in what property? a. mass b. specific heat c. density d. temperature ...
electrically conductive grease 57000
... AOS CONDUCTIVE GREASE is a NON-SILICONE-based, chemically inert heat sink compound that is thermally stable and nonflammable. This advanced grease offers premium electrical and thermal conductivity. ...
... AOS CONDUCTIVE GREASE is a NON-SILICONE-based, chemically inert heat sink compound that is thermally stable and nonflammable. This advanced grease offers premium electrical and thermal conductivity. ...
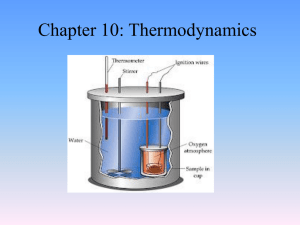
Chapter 10: Thermodynamics
... • Adiabatic process: a thermodynamic process during which heat energy is transferred to or from the system. ex: usually a fast process like filling a tank • Isobaric process: a process that takes place at a constant pressure. ex: heating an open pot of water ...
... • Adiabatic process: a thermodynamic process during which heat energy is transferred to or from the system. ex: usually a fast process like filling a tank • Isobaric process: a process that takes place at a constant pressure. ex: heating an open pot of water ...
chapter 13 (Homework) - Tutor
... (1) Type your answer for physical states using the format of g for gas, l for liquid, and s for solid. If more than one physical state is present, enter the physical states separated by a comma. (2) Type your answer for trends using the format of increase, decrease, remains constant. (3) Type your ...
... (1) Type your answer for physical states using the format of g for gas, l for liquid, and s for solid. If more than one physical state is present, enter the physical states separated by a comma. (2) Type your answer for trends using the format of increase, decrease, remains constant. (3) Type your ...
Virtual Lab: Determining the Formula of a Hydrate handout
... 1. The first frame shows an evaporating dish with crystals of copper II sulfate, in hydrated form. Click on the right arrow. 2. Write down the chemical reaction for the heating of the hydrated form of copper II sulfate. The triangle is the symbol for "heat added". 3. Note the initial mass of the rea ...
... 1. The first frame shows an evaporating dish with crystals of copper II sulfate, in hydrated form. Click on the right arrow. 2. Write down the chemical reaction for the heating of the hydrated form of copper II sulfate. The triangle is the symbol for "heat added". 3. Note the initial mass of the rea ...
Heat Transfer - Concord Consortium
... Conduction is the transfer of heat through solid materials. Thermal conductivity is the measure of how fast a material conducts heat. The opposite of conductivity is resistivity, or insulating value. Metals, like aluminum or iron, conduct very well, that is, they are good conductors and poor insulat ...
... Conduction is the transfer of heat through solid materials. Thermal conductivity is the measure of how fast a material conducts heat. The opposite of conductivity is resistivity, or insulating value. Metals, like aluminum or iron, conduct very well, that is, they are good conductors and poor insulat ...
Practice Problems in Physics (set 1) - Physics2
... 1. A steel beam in a bridge extends 25m across a small stream. What is the change in length from the winter, when its temperature is -20oC, to the summer, when it is 38oC? The coefficient of linear expansion of steel is 12 x 10-6/oC. (ans. 1.7cm) 2. The aluminum lid of a jar of pickles is stuck to t ...
... 1. A steel beam in a bridge extends 25m across a small stream. What is the change in length from the winter, when its temperature is -20oC, to the summer, when it is 38oC? The coefficient of linear expansion of steel is 12 x 10-6/oC. (ans. 1.7cm) 2. The aluminum lid of a jar of pickles is stuck to t ...
now
... Two major consequences of thermal bridging As you would expect there are a significant number of balconies throughout the development and this means the risk of thermal bridging at the many cantilever balcony connections. There are two major consequences of this. One is local heat loss, resulting in ...
... Two major consequences of thermal bridging As you would expect there are a significant number of balconies throughout the development and this means the risk of thermal bridging at the many cantilever balcony connections. There are two major consequences of this. One is local heat loss, resulting in ...
Worksheet- Calculations involving Specific Heat
... Worksheet- Calculations involving Specific Heat 1. For q= m ●c ● Δ T : identify each variables by name & the units associated with it. q = amount of heat (J) m = mass (grams) c = specific heat (J/g°C) ΔT = change in temperature (°C) 2. Heat is not the same as temperature, yet they are related. Expla ...
... Worksheet- Calculations involving Specific Heat 1. For q= m ●c ● Δ T : identify each variables by name & the units associated with it. q = amount of heat (J) m = mass (grams) c = specific heat (J/g°C) ΔT = change in temperature (°C) 2. Heat is not the same as temperature, yet they are related. Expla ...
3-30 An exposed hot surface of an industrial natural gas furnace is
... 3-41C An interface acts like a very thin layer of insulation, and thus the thermal contact resistance has significance only for highly conducting materials like metals. Therefore, the thermal contact resistance can be ignored for two layers of insulation pressed against each other. 3-42C An interfac ...
... 3-41C An interface acts like a very thin layer of insulation, and thus the thermal contact resistance has significance only for highly conducting materials like metals. Therefore, the thermal contact resistance can be ignored for two layers of insulation pressed against each other. 3-42C An interfac ...
Nats 101 S00 #8
... atoms vibrate with large amplitudes and bump into their neighbors and thus increase their vibrations. This is the major way that heat loss occurs in buildings. Air inside the house is warmer than outside. The boundary is the walls and windows. The molecules of air are moving faster inside than outsi ...
... atoms vibrate with large amplitudes and bump into their neighbors and thus increase their vibrations. This is the major way that heat loss occurs in buildings. Air inside the house is warmer than outside. The boundary is the walls and windows. The molecules of air are moving faster inside than outsi ...
Radiant Barrier Training 7-2013 - Fi-Foil
... Air Conditioning (A/C) run time increases and in peak loads cannot maintain internal temperature set points – comfort is compromised. ...
... Air Conditioning (A/C) run time increases and in peak loads cannot maintain internal temperature set points – comfort is compromised. ...
Student Notes Page
... – _________________ (objects must be in contact) – _________________ (fluid motion of currents like warm air rising) – _________________ (electromagnetic waves such as the sun or a microwave oven) Heat is a form of energy associated with the ___________________________ of an object. • Heat is differ ...
... – _________________ (objects must be in contact) – _________________ (fluid motion of currents like warm air rising) – _________________ (electromagnetic waves such as the sun or a microwave oven) Heat is a form of energy associated with the ___________________________ of an object. • Heat is differ ...
P340_2011_week2
... Consider two systems that are isolated from the universe, and each other, but then we allow them to exchange heat (i.e. energy exchange with no work done by either one on the other). What does the 2nd law tell us about this situation, and how might we analyse the relevant physics quantitatively? The ...
... Consider two systems that are isolated from the universe, and each other, but then we allow them to exchange heat (i.e. energy exchange with no work done by either one on the other). What does the 2nd law tell us about this situation, and how might we analyse the relevant physics quantitatively? The ...
CH3080_reportsample_formaterrors
... vapor pressure not too high or low over the operating temperature range high latent heat high thermal conductivity low liquid and vapor viscosities high surface tension acceptable freezing or pour point In the operating temperature range (260-300K), the most efficient among the several p ...
... vapor pressure not too high or low over the operating temperature range high latent heat high thermal conductivity low liquid and vapor viscosities high surface tension acceptable freezing or pour point In the operating temperature range (260-300K), the most efficient among the several p ...
Phase Changes
... their particle size. Therefore, gases volume is negligible. And gases are easily compressed. 0 Gases do not have attractive or repulsive forces between molecules. 0 Collisions between molecules can transfer energy but the total energy of the system is constant. This is called an ...
... their particle size. Therefore, gases volume is negligible. And gases are easily compressed. 0 Gases do not have attractive or repulsive forces between molecules. 0 Collisions between molecules can transfer energy but the total energy of the system is constant. This is called an ...
Final Exam Review- no solutions
... 8. Assign oxidation states to each element in the following compounds. a. SO3 b. PO4 3c. Cr2O7 2d. HClO2 9. Use the changes in oxidation numbers to determine which elements are oxidized and which are reduced in these reactions. (Note: it is not necessary to use balanced equations) a. C + H2SO4 CO2 ...
... 8. Assign oxidation states to each element in the following compounds. a. SO3 b. PO4 3c. Cr2O7 2d. HClO2 9. Use the changes in oxidation numbers to determine which elements are oxidized and which are reduced in these reactions. (Note: it is not necessary to use balanced equations) a. C + H2SO4 CO2 ...
floor level coverage charts
... FLOOR LEVEL COVERAGE CHARTS The important factors in designing an infrared heating system are: Satisfying the building heat loss (the most important factor in achieving the desired inside design temperature). For detailed information, refer to the Application Section, Section IV, Heat Loss Calcula ...
... FLOOR LEVEL COVERAGE CHARTS The important factors in designing an infrared heating system are: Satisfying the building heat loss (the most important factor in achieving the desired inside design temperature). For detailed information, refer to the Application Section, Section IV, Heat Loss Calcula ...
Heat, Temperature and Atmospheric Circulations
... different parts may be different temperatures ...
... different parts may be different temperatures ...
Introduction - HCC Learning Web
... **NOTE: Use instructions provide by the instructor – DO NOT USE INSTRUCTIONS IN CHEMLAB! To remove the instructions on the screen, and free-up more working area, perform the following operation: click on the OPTIONS tab; then click on LAB ONLY. The instructions “disappear” and all of the area is now ...
... **NOTE: Use instructions provide by the instructor – DO NOT USE INSTRUCTIONS IN CHEMLAB! To remove the instructions on the screen, and free-up more working area, perform the following operation: click on the OPTIONS tab; then click on LAB ONLY. The instructions “disappear” and all of the area is now ...
Thermal Energy - St. Thomas the Apostle School
... • Gases such as air usually make better insulators than liquids or solids • A vacuum layer in a thermos is a good insulator because it contains almost no matter to allow conduction or convection to occur. ...
... • Gases such as air usually make better insulators than liquids or solids • A vacuum layer in a thermos is a good insulator because it contains almost no matter to allow conduction or convection to occur. ...
Chapters 12-15 Thermodynamics
... • The volume of ice decreases (it melts) and the pressure and volume of the balloon decrease • They come to a final state of thermal equilibrium which must be characterized by a new physical property called temperature T • In thermal equilibrium: Tice = Tballoon 3 ...
... • The volume of ice decreases (it melts) and the pressure and volume of the balloon decrease • They come to a final state of thermal equilibrium which must be characterized by a new physical property called temperature T • In thermal equilibrium: Tice = Tballoon 3 ...
module 7
... Two basic flow arrangements are as shown in Figure 7.2. Parallel and counter flow provide alternative arrangements for certain specialized applications. In parallel flow both the hot and cold streams enter the heat exchanger at the same end and travel to the opposite end in parallel streams. Energy ...
... Two basic flow arrangements are as shown in Figure 7.2. Parallel and counter flow provide alternative arrangements for certain specialized applications. In parallel flow both the hot and cold streams enter the heat exchanger at the same end and travel to the opposite end in parallel streams. Energy ...
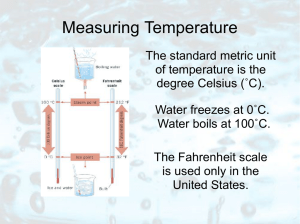
Measuring Temperature
... physical process cannot decrease during that process, but it can increase. That's not to say that you can't create a little more order in some part of your world, but the price you pay is to create more disorder somewhere else. ...
... physical process cannot decrease during that process, but it can increase. That's not to say that you can't create a little more order in some part of your world, but the price you pay is to create more disorder somewhere else. ...