What Can Changes Inside Earth Communicate? Pre/Post Test 1
... They tell the absolute age of the rock in which they occur. They tell the ages of many different rock layers. They tell the age of the rock at one location only. They tell the relative age of the rock in which they occur. ...
... They tell the absolute age of the rock in which they occur. They tell the ages of many different rock layers. They tell the age of the rock at one location only. They tell the relative age of the rock in which they occur. ...
Introduction to Atmospheric Science, PHSC 3223
... – Rain, snow, hail, sleet, accumulation, melt ...
... – Rain, snow, hail, sleet, accumulation, melt ...
1. Glass is chemically related to what mineral? Fluorite Quartz Pyrite
... 8. In karst regions, caves are carved by the flow of water through limestone bedrock. How do the stalagmites and stalactites in the caves develop? They are carbonate deposits formed by dripping water in air-filled cavities. They are granite intrusions that remain behind after water dissolves the su ...
... 8. In karst regions, caves are carved by the flow of water through limestone bedrock. How do the stalagmites and stalactites in the caves develop? They are carbonate deposits formed by dripping water in air-filled cavities. They are granite intrusions that remain behind after water dissolves the su ...
Unit 3 Review
... • Color- color of the mineral • Streak- color of the powdered form of the mineral. (Remember: that if a scientist draws on a white tile with the mineral, this is how the streak is found.) • Luster- way a surface reflects light • Cleavage and Fracture- The way the mineral breaks/splits • Density- mea ...
... • Color- color of the mineral • Streak- color of the powdered form of the mineral. (Remember: that if a scientist draws on a white tile with the mineral, this is how the streak is found.) • Luster- way a surface reflects light • Cleavage and Fracture- The way the mineral breaks/splits • Density- mea ...
Constructive and Destructive Forces Unit
... the tearing down of the Earth’s surface including weathering, erosion, impact of organisms, earthquakes, and volcanoes ...
... the tearing down of the Earth’s surface including weathering, erosion, impact of organisms, earthquakes, and volcanoes ...
2.2 Notes
... Colliding and Spreading Plates • One way that mountain ranges form is in a process called subduction, when a sea plate collides with and dives beneath a continental plate. • Continents grow in a process called accretion, when pieces of the earth’s crust come together slowly as a sea plate slides un ...
... Colliding and Spreading Plates • One way that mountain ranges form is in a process called subduction, when a sea plate collides with and dives beneath a continental plate. • Continents grow in a process called accretion, when pieces of the earth’s crust come together slowly as a sea plate slides un ...
Core - RCSD
... • Upper mantle melts rocks, forming a substance called ______________ which flows like a thick liquid ASTHENOSPHERE: • The mechanically weak _____________ region of the ___________ mantle that is ________________ & ____________________ due to extreme ___________________________ & ___________________ ...
... • Upper mantle melts rocks, forming a substance called ______________ which flows like a thick liquid ASTHENOSPHERE: • The mechanically weak _____________ region of the ___________ mantle that is ________________ & ____________________ due to extreme ___________________________ & ___________________ ...
Geology Jeopardy Key - The Earth Science Explorer
... I form either inside or outside of the volcano.—IGNEOUS ROCK I am the only rock type that has fossils.—SEDIMENTARY ROCK I am found deep down in the earth but I never melt (I do turn to gum though.)—METAMORPHIC ROCK I am formed when sediment (mud, sand, silt) builds up over millions of years.—SEDIMEN ...
... I form either inside or outside of the volcano.—IGNEOUS ROCK I am the only rock type that has fossils.—SEDIMENTARY ROCK I am found deep down in the earth but I never melt (I do turn to gum though.)—METAMORPHIC ROCK I am formed when sediment (mud, sand, silt) builds up over millions of years.—SEDIMEN ...
Document
... Recognize that lithospheric plates on the scale of continents and oceans continually move at rates of centimeters per year. SPI 0707.7.6 Describe the relationship between plate movements and earthquakes, mountain building, volcanoes, and sea floor spreading. ...
... Recognize that lithospheric plates on the scale of continents and oceans continually move at rates of centimeters per year. SPI 0707.7.6 Describe the relationship between plate movements and earthquakes, mountain building, volcanoes, and sea floor spreading. ...
Researchers find oldest rocks on Earth
... composition of the rare earth elements neodymium and samarium in the rocks, O'Neil and Carlson determined that the rock samples range from 3.8 to 4.28 billion years old. The oldest dates came from rocks termed "faux amphibolite," which the researchers interpret to be ancient volcanic ...
... composition of the rare earth elements neodymium and samarium in the rocks, O'Neil and Carlson determined that the rock samples range from 3.8 to 4.28 billion years old. The oldest dates came from rocks termed "faux amphibolite," which the researchers interpret to be ancient volcanic ...
Science Study Guide What is the hot molten rock
... What is the central opening in a volcanic area through which magma can escape called? ...
... What is the central opening in a volcanic area through which magma can escape called? ...
Chapter 8
... solid; has a characteristic (recognizable) crystal structure and chemical composition. ...
... solid; has a characteristic (recognizable) crystal structure and chemical composition. ...
Ch 7 Changes to the Earth`s Surface
... • A mountain made of lava, ash, or other materials from eruptions that occur at an opening in Earth’s crust. ...
... • A mountain made of lava, ash, or other materials from eruptions that occur at an opening in Earth’s crust. ...
Chapter 4 Lesson 1 Plate Tectonics
... Geologist – person that studies rocks Thought of by Alfred Wegener in 1915. Continents "drifted" to their present positions. ...
... Geologist – person that studies rocks Thought of by Alfred Wegener in 1915. Continents "drifted" to their present positions. ...
Document
... 1. Compare and contrast uniformitarianism and catastrophism 2. Diagram the four basic internal structures of the earth. Describe the characteristics of each layer in terms of thickness, composition, and whether the layers are solid ,liquid or plastic. 3. What percent of the earth's mass does the cru ...
... 1. Compare and contrast uniformitarianism and catastrophism 2. Diagram the four basic internal structures of the earth. Describe the characteristics of each layer in terms of thickness, composition, and whether the layers are solid ,liquid or plastic. 3. What percent of the earth's mass does the cru ...
File
... S__________ because of the immense amount of pressure that it is under. 9. A C_______________ C_______________ occurs when hot rock in the mantle R__________ toward the crust, C__________ and then F__________ in a continuous motion. 10. At a D_______________ B_______________ plates move A___________ ...
... S__________ because of the immense amount of pressure that it is under. 9. A C_______________ C_______________ occurs when hot rock in the mantle R__________ toward the crust, C__________ and then F__________ in a continuous motion. 10. At a D_______________ B_______________ plates move A___________ ...
EES Geology Vocabulary Review Name___________________
... Focus- the location inside the crust where an earthquake begins Epicenter- the location on the surface directly above the focus Magnitude- the strength of an earthquake Intensity- a description of the effects of an earthquake Richter Scale- a measure of the magnitude of an earthquake Modified Mercal ...
... Focus- the location inside the crust where an earthquake begins Epicenter- the location on the surface directly above the focus Magnitude- the strength of an earthquake Intensity- a description of the effects of an earthquake Richter Scale- a measure of the magnitude of an earthquake Modified Mercal ...
Determining the Relative Age of Rocks
... flat plain into landforms such as anticlines and synclines, folded mountains, fault-block mountains, and plateaus. A fold in rock that bends upward into an arch is an anticline. A fold in rock that bends downward to form a valley is a syncline. Anticlines and synclines are found on many parts of the ...
... flat plain into landforms such as anticlines and synclines, folded mountains, fault-block mountains, and plateaus. A fold in rock that bends upward into an arch is an anticline. A fold in rock that bends downward to form a valley is a syncline. Anticlines and synclines are found on many parts of the ...
the junior version pdf file
... Do we want to discover the characteristics of the Earth’s surface and its internal structure? The planet we live on is the Earth and it is shaped like a large ball floating in Space. The Earth has a particular structure consisting of three parts: an external part known as the crust, a central part k ...
... Do we want to discover the characteristics of the Earth’s surface and its internal structure? The planet we live on is the Earth and it is shaped like a large ball floating in Space. The Earth has a particular structure consisting of three parts: an external part known as the crust, a central part k ...
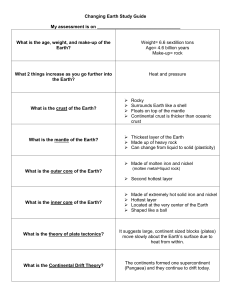
Changing Earth Study Guide My assessment is on What is the age
... move slowly about the Earth’s surface due to heat from within. ...
... move slowly about the Earth’s surface due to heat from within. ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.