Geology Study Guide
... a) When rock is ________________________________, energy builds up in it. b) _____________waves cannot travel through parts of the Earth that are completely liquid. c) When rock “snaps” back to its original shape, _______________________________occurs. d) ___________________ lava cools in wavy rope- ...
... a) When rock is ________________________________, energy builds up in it. b) _____________waves cannot travel through parts of the Earth that are completely liquid. c) When rock “snaps” back to its original shape, _______________________________occurs. d) ___________________ lava cools in wavy rope- ...
final_examgq - Chemistry at Winthrop University
... 10. [True or False] Seismic P-waves can’t travel through the liquid outer core of the Earth but Swaves can. This results in a P-wave shadow on the side of the Earth opposite an earthquake. 11. To reach its dew point temperature, a packet of unsaturated air must usually be [heated / cooled ]. 12. Whi ...
... 10. [True or False] Seismic P-waves can’t travel through the liquid outer core of the Earth but Swaves can. This results in a P-wave shadow on the side of the Earth opposite an earthquake. 11. To reach its dew point temperature, a packet of unsaturated air must usually be [heated / cooled ]. 12. Whi ...
See Q. “Sampler” on packet, pages 12
... ! Matter became clustered in stars with the outer eddies condensed in chunks ! A hypothesis concerning the origin of the solar system according to which a rotating nebula cooled and contracted, throwing off rings of matter that contracted into the planets and their moons, while the great mass of the ...
... ! Matter became clustered in stars with the outer eddies condensed in chunks ! A hypothesis concerning the origin of the solar system according to which a rotating nebula cooled and contracted, throwing off rings of matter that contracted into the planets and their moons, while the great mass of the ...
Vocabulary Review
... 9. the ongoing processes that form and change rock from one kind to another 10. natural, solid materials found on Earth that are the building blocks of rock; different minerals have different physical and chemical properties that determine their use and value 11. minerals that are mined because they ...
... 9. the ongoing processes that form and change rock from one kind to another 10. natural, solid materials found on Earth that are the building blocks of rock; different minerals have different physical and chemical properties that determine their use and value 11. minerals that are mined because they ...
Practice Questions - Earth`s History 1
... EARTH’S HISTORY SET 1 1. Which best explains how geologic time scales can help scientists study the evolution of life on Earth? A. They describe the existence of rocks before there was life on Earth B. They show that geological features have evolved at the same rate as organisms C. They compare the ...
... EARTH’S HISTORY SET 1 1. Which best explains how geologic time scales can help scientists study the evolution of life on Earth? A. They describe the existence of rocks before there was life on Earth B. They show that geological features have evolved at the same rate as organisms C. They compare the ...
Plate Tectonics.common.assessment.studyguide
... 6. When you touch a hot pot or pan, the heat moves from the pot to your hand (example) 7. Mantle or asthenosphere 8. the name of the supercontinent that existed millions of years ago 9. the continents were once joined together in a single landmass 10. evidence from landforms, fossils, and climate 11 ...
... 6. When you touch a hot pot or pan, the heat moves from the pot to your hand (example) 7. Mantle or asthenosphere 8. the name of the supercontinent that existed millions of years ago 9. the continents were once joined together in a single landmass 10. evidence from landforms, fossils, and climate 11 ...
Plate-Study-Guide-11-12
... which are an example of indirect evidence. F. Geologists observe earth’s interior by studying rocks, which are an example of indirect _____________________________. II. ...
... which are an example of indirect evidence. F. Geologists observe earth’s interior by studying rocks, which are an example of indirect _____________________________. II. ...
Rock Webquest
... Explore the Rock Creations area to complete each section. For thousands, even millions of years, little pieces of our earth have been eroded-- broken down and worn away by __________ and __________. These little bits of our earth are washed downstream where they settle to the bottom of the _________ ...
... Explore the Rock Creations area to complete each section. For thousands, even millions of years, little pieces of our earth have been eroded-- broken down and worn away by __________ and __________. These little bits of our earth are washed downstream where they settle to the bottom of the _________ ...
PowerPoint slides
... Apply concepts of statistics and probability to scientific and engineering questions and problems, using digital tools when feasible. Middle School – Earth’s Systems MS-ESS3-1. Students who demonstrate understanding can construct a scientific explanation based on evidence for how the uneven distribu ...
... Apply concepts of statistics and probability to scientific and engineering questions and problems, using digital tools when feasible. Middle School – Earth’s Systems MS-ESS3-1. Students who demonstrate understanding can construct a scientific explanation based on evidence for how the uneven distribu ...
The Solid Earth
... by amount of silica present rich = felsic (eg granite, rhyolite) intermediate (eg diorite, andesite) poor = mafic (eg. basalt, gabbro) low in silica = low viscosity = flows easily high in silica = high viscosity kinds of feldspars present, other minerals Sedimentary Rocks weathering moves particles ...
... by amount of silica present rich = felsic (eg granite, rhyolite) intermediate (eg diorite, andesite) poor = mafic (eg. basalt, gabbro) low in silica = low viscosity = flows easily high in silica = high viscosity kinds of feldspars present, other minerals Sedimentary Rocks weathering moves particles ...
PHYSICAL GEOLOGY GEOLOGY 1 - UCLA
... works. The goals of the class are (1) to gain a general understanding of important earth processes (e.g., plate tectonics, Earthquake, volcanism, weathering and erosion, and glaciation) and (2) to learn the knowledge of rocks, minerals, and geologic resources. The course provides a fundamental scien ...
... works. The goals of the class are (1) to gain a general understanding of important earth processes (e.g., plate tectonics, Earthquake, volcanism, weathering and erosion, and glaciation) and (2) to learn the knowledge of rocks, minerals, and geologic resources. The course provides a fundamental scien ...
Geology and Earth Resources
... most important metals. What are they, and where do they come from? 7. Give some examples of nonmetal mineral resources and describe how they are used. 8. Describe some ways metals and other mineral resources can be recycled. 9. What are some environmental hazards associated with mineral extraction? ...
... most important metals. What are they, and where do they come from? 7. Give some examples of nonmetal mineral resources and describe how they are used. 8. Describe some ways metals and other mineral resources can be recycled. 9. What are some environmental hazards associated with mineral extraction? ...
Earth Science Final Exam Study Guide
... 4. What mineral creates stalactites & stalagmites? 5. What are some threats to groundwater systems? Plate Tectonics (~10) 1. What does the theory of plate tectonics state about the earth? 2. What do magnetic stripes on the ocean floor represent? 3. What are the three types of plate boundaries & what ...
... 4. What mineral creates stalactites & stalagmites? 5. What are some threats to groundwater systems? Plate Tectonics (~10) 1. What does the theory of plate tectonics state about the earth? 2. What do magnetic stripes on the ocean floor represent? 3. What are the three types of plate boundaries & what ...
Name: Date:____ Period:______ Geology Vocabulary Chart
... 11. Lithosphere- a rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust. 12. Asthenosphere-the soft layer of the mantle on which the lithosphere floats. 13. Continental drift- the hypothesis that the continents slowly move across Earth’s surface. 14. Hot spot- an area where magma fr ...
... 11. Lithosphere- a rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust. 12. Asthenosphere-the soft layer of the mantle on which the lithosphere floats. 13. Continental drift- the hypothesis that the continents slowly move across Earth’s surface. 14. Hot spot- an area where magma fr ...
study guide - Hull Lessons
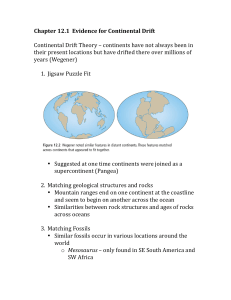
... together like pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. The theory that says the earth’s surface is made up of about 20 moving pieces is called plate tectonics. Plate tectonics is the scientific theory that explains how continents move. The earth’s plates move very slowly. Mountains, earthquakes, and volcanoes are ...
... together like pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. The theory that says the earth’s surface is made up of about 20 moving pieces is called plate tectonics. Plate tectonics is the scientific theory that explains how continents move. The earth’s plates move very slowly. Mountains, earthquakes, and volcanoes are ...
Building Earth`s Surface - Academic Resources at Missouri Western
... Epicenter A point of the surface of the Earth directly above the focus ...
... Epicenter A point of the surface of the Earth directly above the focus ...
Layers of the Earth - study notes
... Most of the earthquakes and volcanoes in the world occur where two plates meet. The most active area of volcanoes and earthquakes is called the Ring of Fire. It circles around the Pacific Ocean. The Atlantic Ocean is growing because the Mid Atlantic Ridge continues to separate. Magma seeps up ...
... Most of the earthquakes and volcanoes in the world occur where two plates meet. The most active area of volcanoes and earthquakes is called the Ring of Fire. It circles around the Pacific Ocean. The Atlantic Ocean is growing because the Mid Atlantic Ridge continues to separate. Magma seeps up ...
Earth Science Study Guide - Effingham County Schools
... Mechanical and Chemical. Mechanical is the breaking of larger rocks into smaller pieces of rock, called sediment. It does not change the type of rock. Chemical weathering changes rock into other materials. Acidic water dissolves certain minerals in the rock, changing it to a new type. ...
... Mechanical and Chemical. Mechanical is the breaking of larger rocks into smaller pieces of rock, called sediment. It does not change the type of rock. Chemical weathering changes rock into other materials. Acidic water dissolves certain minerals in the rock, changing it to a new type. ...
Earth Science
... Epicenter-point where the earthquake originates Fault-crack in Earth’s crust where movement takes place Magma-melted rock, becomes lava at surface Seismic waves-waves sent through Earth’s surface during earthquakes Ring of Fire-area along the edge of the Pacific ...
... Epicenter-point where the earthquake originates Fault-crack in Earth’s crust where movement takes place Magma-melted rock, becomes lava at surface Seismic waves-waves sent through Earth’s surface during earthquakes Ring of Fire-area along the edge of the Pacific ...
Rock cycle, snap! - Teachit Geography
... Rock cycle, snap! Rock cycle, snap! – First game cementation ...
... Rock cycle, snap! Rock cycle, snap! – First game cementation ...
ESCI 107 Earth Science STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY
... a. Sketch and describe the major layers of the Earth. b. List and explain the lines of evidence that indicate that the continents have moved through time. c. Summarize the major types of plate boundaries and the processes that occur at each. d. Use Bowen’s Reaction Series as a conceptual framework f ...
... a. Sketch and describe the major layers of the Earth. b. List and explain the lines of evidence that indicate that the continents have moved through time. c. Summarize the major types of plate boundaries and the processes that occur at each. d. Use Bowen’s Reaction Series as a conceptual framework f ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.