Geology Unit Study Guide - Mr. Ruggiero`s Science 8-2
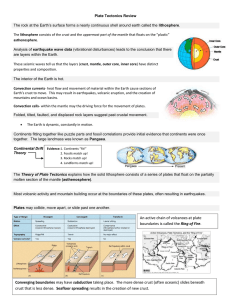
... Chapter 1 – Plate Tectonics (E.S. 2) Layers of the earth – Inner Core, Outer Core, Mantle, Asthenosphere, Lithosphere o Heat Transfer ( E.S. 3) Convection – responsible for plate movements o Theory of Continental Drift (E.S. 5, 6, 7) Pangaea Evidences to support theory – Fossils, Geology, Cl ...
... Chapter 1 – Plate Tectonics (E.S. 2) Layers of the earth – Inner Core, Outer Core, Mantle, Asthenosphere, Lithosphere o Heat Transfer ( E.S. 3) Convection – responsible for plate movements o Theory of Continental Drift (E.S. 5, 6, 7) Pangaea Evidences to support theory – Fossils, Geology, Cl ...
Due Date_________________ Test Date
... - Transportation- to the movement of eroded debris, whether by rivers, glaciers, wind or ocean currents, and tides - Deposition- is the geological process by which material is added to a landform or land mass - Lithification-process of changing sediment into rock 9. What are unconformities? How do t ...
... - Transportation- to the movement of eroded debris, whether by rivers, glaciers, wind or ocean currents, and tides - Deposition- is the geological process by which material is added to a landform or land mass - Lithification-process of changing sediment into rock 9. What are unconformities? How do t ...
STEM-Exam-3-Earth-Sci-Study-Guide
... 13. How does scientist know that the continents were at one time joined together and then moved apart? Continental drift and tectonic plates theory An example can be Fossils of the fern Glossopteris have been found in Africa, Australia, Antarctica, and South America. Scientists explain this observat ...
... 13. How does scientist know that the continents were at one time joined together and then moved apart? Continental drift and tectonic plates theory An example can be Fossils of the fern Glossopteris have been found in Africa, Australia, Antarctica, and South America. Scientists explain this observat ...
Earthquakes
... on top. Rocks will get older the deeper you get into the crust. ◦ Sediments are continuously deposited on top of each other. ◦ If rock layers are undisturbed, the deeper you get the older the rocks, fossils, etc. are. ...
... on top. Rocks will get older the deeper you get into the crust. ◦ Sediments are continuously deposited on top of each other. ◦ If rock layers are undisturbed, the deeper you get the older the rocks, fossils, etc. are. ...
Plate Tectonics Review The rock at the Earth`s surface forms a
... These seismic waves tell us that the layers (crust, mantle, outer core, inner core) have distinct properties and composition. The interior of the Earth is hot. Convection currents- heat flow and movement of material within the Earth cause sections of Earth’s crust to move. This may result in earthqu ...
... These seismic waves tell us that the layers (crust, mantle, outer core, inner core) have distinct properties and composition. The interior of the Earth is hot. Convection currents- heat flow and movement of material within the Earth cause sections of Earth’s crust to move. This may result in earthqu ...
Figure 15-4
... • The extremely slow movements of these plates cause them to grind into one another at convergent plate boundaries, move apart at divergent plate boundaries and slide past at LATERAL plate boundaries. Figure 15-4 ...
... • The extremely slow movements of these plates cause them to grind into one another at convergent plate boundaries, move apart at divergent plate boundaries and slide past at LATERAL plate boundaries. Figure 15-4 ...
What Kind of Rock am I Looking At?
... being buried very deep in the earth's crust, or from the huge plates of the earth's crust pushing against each other. The deeper below the surface of the earth, the higher the temperature, so deep burial also means high temperatures. Another way that high temperatures occur is when magma rises throu ...
... being buried very deep in the earth's crust, or from the huge plates of the earth's crust pushing against each other. The deeper below the surface of the earth, the higher the temperature, so deep burial also means high temperatures. Another way that high temperatures occur is when magma rises throu ...
Midterm Study Guide2013
... 32. What features are common at convergent continental-continental boundaries? Give an example. 33. Describe what happens at transform fault boundaries, and include the geologic hazard that is associated with this type of boundary on continental crust. 34. List the lines of evidence that support the ...
... 32. What features are common at convergent continental-continental boundaries? Give an example. 33. Describe what happens at transform fault boundaries, and include the geologic hazard that is associated with this type of boundary on continental crust. 34. List the lines of evidence that support the ...
Name:
... 12) What are the five layers of the Earth? What is the material each layer is made out of? (Liquid, solid...) ...
... 12) What are the five layers of the Earth? What is the material each layer is made out of? (Liquid, solid...) ...
Earth`s History in Fossils - PAMS
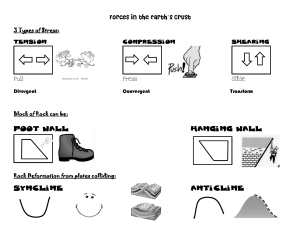
... •A fault is a crack in the rock where one side can move, rock layers are always older than the fault •Intrusion of magma has to have formed after the rock layers were present, therefore the intrusion is younger •Extrusion is when magma is forced to the top of the rock layers, layers were there first ...
... •A fault is a crack in the rock where one side can move, rock layers are always older than the fault •Intrusion of magma has to have formed after the rock layers were present, therefore the intrusion is younger •Extrusion is when magma is forced to the top of the rock layers, layers were there first ...
Course Outline and General Information
... Lecture Outline: (order of topics may change) Introduction to the course An overview of physical geology: Important concepts and its place among Earth sciences. Earth’s structure. Geologic time. Why is geology important? From atoms to minerals Atoms, elements and isotopes. Crystal structures. Minera ...
... Lecture Outline: (order of topics may change) Introduction to the course An overview of physical geology: Important concepts and its place among Earth sciences. Earth’s structure. Geologic time. Why is geology important? From atoms to minerals Atoms, elements and isotopes. Crystal structures. Minera ...
Unit C: Earth Science Chapter 1: The Changing Earth Lesson 1
... climates 6. Glacial deposits in warm climates Plate Tectonics 1. This is the theory of how continents move 2. The earth's surface is broken into about twenty sections or plates 3. Plates are large sections of the earth's surface made of the crust and the top rigid portion of the mantle 4. They fit t ...
... climates 6. Glacial deposits in warm climates Plate Tectonics 1. This is the theory of how continents move 2. The earth's surface is broken into about twenty sections or plates 3. Plates are large sections of the earth's surface made of the crust and the top rigid portion of the mantle 4. They fit t ...
Earth Resources
... Oceanic plate runs into continental—continental over oceanic Subduction—distinct subduction zones ...
... Oceanic plate runs into continental—continental over oceanic Subduction—distinct subduction zones ...
Chapter 1 - HCC Learning Web
... experimental or observational support over time, it is accepted as the best explanation. ...
... experimental or observational support over time, it is accepted as the best explanation. ...
Science: Constructive and Destructive Forces Vocabulary
... An area of new land at the mouth of a river, formed from sediments carried by the river ...
... An area of new land at the mouth of a river, formed from sediments carried by the river ...
Lab 3 - Geologic Structures, Maps, and Block Diagrams
... Definitions • Structural Geology – study of how geologic units (bodies of rock or sediment) are arranged when first formed and how they are deformed afterward. ...
... Definitions • Structural Geology – study of how geologic units (bodies of rock or sediment) are arranged when first formed and how they are deformed afterward. ...
300_S2005_solid_earth
... Rifts (oceanic or continental ) Hot spots Subduction zones Geologic Time relative dating – use geological record to order events sequentially principle of superposition – oldest layers under newer layers sediment settles in horizontal layers principle of cross-cutting: fracture must be young ...
... Rifts (oceanic or continental ) Hot spots Subduction zones Geologic Time relative dating – use geological record to order events sequentially principle of superposition – oldest layers under newer layers sediment settles in horizontal layers principle of cross-cutting: fracture must be young ...
Physical Geology 1330
... What is Geology – The scientific study of the processes, events, and consequences of the Earth's past, present, and future. ...
... What is Geology – The scientific study of the processes, events, and consequences of the Earth's past, present, and future. ...
Yr 7 Rocks and Fossils Unit Overview
... identify a range of common rock types using a key based on observable physical and chemical properties Give a basic explanation of fossils are formed and how they can be used to learn about earth’s past ...
... identify a range of common rock types using a key based on observable physical and chemical properties Give a basic explanation of fossils are formed and how they can be used to learn about earth’s past ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.