Geologic Change Over Time Study Guide 1. Describe what
... the time it existed. Then explain how you could find the age of these fossils and other materials. Fossils can show what the environment was like at the time they existed. For example a fish fossil would indicate an aquatic environment. A tropical plant fossil would indicate a tropical past climate. ...
... the time it existed. Then explain how you could find the age of these fossils and other materials. Fossils can show what the environment was like at the time they existed. For example a fish fossil would indicate an aquatic environment. A tropical plant fossil would indicate a tropical past climate. ...
7.4 Forces that move plates.
... Because of this, rocks near mid-ocean ridges tend to be higher up than those that are father away. As you move farther away from the mid-ocean ridge rocks tend to subside. ...
... Because of this, rocks near mid-ocean ridges tend to be higher up than those that are father away. As you move farther away from the mid-ocean ridge rocks tend to subside. ...
Dangerous Earth
... the mantle. Underneath the lithosphere is a thin zone within the mantle called the asthenosphere. Because of radioactive decay deep in the Earth the asthenosphere is so hot that there are films of molten material between the crystals. This means the asthenosphere is solid but it can also flow. Slow ...
... the mantle. Underneath the lithosphere is a thin zone within the mantle called the asthenosphere. Because of radioactive decay deep in the Earth the asthenosphere is so hot that there are films of molten material between the crystals. This means the asthenosphere is solid but it can also flow. Slow ...
Ideas and Evidence in Science
... the mantle. Underneath the lithosphere is a thin zone within the mantle called the asthenosphere. Because of radioactive decay deep in the Earth the asthenosphere is so hot that there are films of molten material between the crystals. This means the asthenosphere is solid but it can also flow. Slow ...
... the mantle. Underneath the lithosphere is a thin zone within the mantle called the asthenosphere. Because of radioactive decay deep in the Earth the asthenosphere is so hot that there are films of molten material between the crystals. This means the asthenosphere is solid but it can also flow. Slow ...
Earth`s Interior Notes/KEY
... of what Earth’s __________ is like. They base their model on __________ from ______ samples and __________ waves released by ____________________. Earth’s interior is __________ into __________. The • A ___________layer of ___________ rock • Includes ______ _________and __________ floor • Thickest p ...
... of what Earth’s __________ is like. They base their model on __________ from ______ samples and __________ waves released by ____________________. Earth’s interior is __________ into __________. The • A ___________layer of ___________ rock • Includes ______ _________and __________ floor • Thickest p ...
Chapter 17 Study Guide 16
... Explain how mid-ocean ridges and deep-sea trenches are different. Describe their many differences: how they form, what they look like, their elevations, etc. ...
... Explain how mid-ocean ridges and deep-sea trenches are different. Describe their many differences: how they form, what they look like, their elevations, etc. ...
ROCKS
... Pumice rocks are extrusive igneous rocks which were formed when lava cooled quickly above ground. You can see where little pockets of air had been. This rock is so light, that many pumice rocks will actually float in water. Pumice is actually a kind of glass and not a mixture of minerals. Because th ...
... Pumice rocks are extrusive igneous rocks which were formed when lava cooled quickly above ground. You can see where little pockets of air had been. This rock is so light, that many pumice rocks will actually float in water. Pumice is actually a kind of glass and not a mixture of minerals. Because th ...
Chapter 1
... inside to surface - plates ride the currents • RIDGE-PUSH - upwelling pressure so great at MOR that forces plates to split • SLAB-PULL - cooled slabs are so heavy that drag plate down a subduction zone-gravity assisted • RIDGE MASS - mass is so great @ MOR that forces plates to move away ...
... inside to surface - plates ride the currents • RIDGE-PUSH - upwelling pressure so great at MOR that forces plates to split • SLAB-PULL - cooled slabs are so heavy that drag plate down a subduction zone-gravity assisted • RIDGE MASS - mass is so great @ MOR that forces plates to move away ...
Unconformity
... Unconformity • It is one of the most common geological feature found in rocks or in succession. • It is different then all other geological structures viz. the fold, joints and faults • Unconformities are resulted due to tectonic activity in form of uplift or subsidence of land • It is referred to ...
... Unconformity • It is one of the most common geological feature found in rocks or in succession. • It is different then all other geological structures viz. the fold, joints and faults • Unconformities are resulted due to tectonic activity in form of uplift or subsidence of land • It is referred to ...
Changes Within the Earth
... • Scientist Alfred Wegener created the theory of “Pangaea” started 180 million years ago. 1 land mass breaks off into the 7 current continents. • Scientists developed the theory of plate tectonics. These are plates of the earth’s crust that are constantly moving at a slow pace and creating pressure ...
... • Scientist Alfred Wegener created the theory of “Pangaea” started 180 million years ago. 1 land mass breaks off into the 7 current continents. • Scientists developed the theory of plate tectonics. These are plates of the earth’s crust that are constantly moving at a slow pace and creating pressure ...
Earth`s Layers Vocabulary
... Crust: A thin outer layer of rock above a planet’s mantle, including all dry land and ocean basins made of silicates. Mantle: The layer of rock between Earth’s core and crust, in which most rock is hot enough to flow in convection currents; Earth’s thickest layer. Mainly made of iron, magnesium and ...
... Crust: A thin outer layer of rock above a planet’s mantle, including all dry land and ocean basins made of silicates. Mantle: The layer of rock between Earth’s core and crust, in which most rock is hot enough to flow in convection currents; Earth’s thickest layer. Mainly made of iron, magnesium and ...
science
... Middle School Earth and Space Science (Specified and Related Middle School TEKS) (6.10) Earth and space. The student understands the structure of Earth, the rock cycle, and plate tectonics. The student is expected to: (A) build a model to illustrate the structural layers of Earth, including the inne ...
... Middle School Earth and Space Science (Specified and Related Middle School TEKS) (6.10) Earth and space. The student understands the structure of Earth, the rock cycle, and plate tectonics. The student is expected to: (A) build a model to illustrate the structural layers of Earth, including the inne ...
instructor`s syllabus
... Student Learning Outcomes: Upon successful completion of this course, students should be able to do the following: 1. Differentiate between rocks and minerals and describe the formation of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, and classify rocks as igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic. 2. Out ...
... Student Learning Outcomes: Upon successful completion of this course, students should be able to do the following: 1. Differentiate between rocks and minerals and describe the formation of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, and classify rocks as igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic. 2. Out ...
Earth Science Name Web Inquiry—Plate Tectonics/Earth`s Interior
... e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. f. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposition, volcanic eruption, gravity) on geological features including oceans (composition, currents, and tides). ...
... e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. f. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposition, volcanic eruption, gravity) on geological features including oceans (composition, currents, and tides). ...
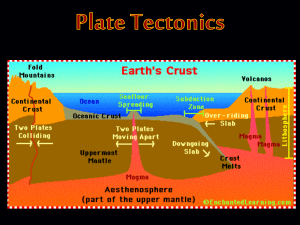
Plate Tectonics
... •Movement of the continent is caused by convection currents in the asthenosphere •The asthenosphere is the upper part of the mantle in which convection cells occur. •The rock that makes up the asthenosphere acts like a fluid. As a result convection can take place there because of the movement. ...
... •Movement of the continent is caused by convection currents in the asthenosphere •The asthenosphere is the upper part of the mantle in which convection cells occur. •The rock that makes up the asthenosphere acts like a fluid. As a result convection can take place there because of the movement. ...
instructor`s syllabus
... Student Learning Outcomes: Upon successful completion of this course, students should be able to do the following: 1. Differentiate between rocks and minerals and describe the formation of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, and classify rocks as igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic. 2. Out ...
... Student Learning Outcomes: Upon successful completion of this course, students should be able to do the following: 1. Differentiate between rocks and minerals and describe the formation of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, and classify rocks as igneous, sedimentary, or metamorphic. 2. Out ...
File
... -________________ fault: produced at divergent boundaries; plates move apart; rock from the fault moves downward. -_________________ fault: produced at convergent boundaries; plates push together; rock about the fault moves up and over rock below the fault. -_____________________ fault: produced at ...
... -________________ fault: produced at divergent boundaries; plates move apart; rock from the fault moves downward. -_________________ fault: produced at convergent boundaries; plates push together; rock about the fault moves up and over rock below the fault. -_____________________ fault: produced at ...
Erosion Notes and Fill in the Blank HW
... ___________________ crust is covered by soil. The ingredients in soils can vary from _____________ to place and around the Earth. Different soils have many properties such as texture, _______________size, pH, fertility and ability to hold moisture. Depending upon the combination of _________________ ...
... ___________________ crust is covered by soil. The ingredients in soils can vary from _____________ to place and around the Earth. Different soils have many properties such as texture, _______________size, pH, fertility and ability to hold moisture. Depending upon the combination of _________________ ...
Earth`s Systems and Resources Quiz 2
... A) The outlines of the different continents look like they could fit together like puzzle pieces. B) Similar fossil evidence has been found on continents separated by great distances. C) Nearly identical rock formations were found on the east coast of the U.S. and the west coast of Europe. D) No mou ...
... A) The outlines of the different continents look like they could fit together like puzzle pieces. B) Similar fossil evidence has been found on continents separated by great distances. C) Nearly identical rock formations were found on the east coast of the U.S. and the west coast of Europe. D) No mou ...
Earth`s Internal Properties
... • The heat that drives the motion of the mantle comes from two sources: ---Radioactive decay of materials in the mantle ---Heat left over from the formation of the earth ...
... • The heat that drives the motion of the mantle comes from two sources: ---Radioactive decay of materials in the mantle ---Heat left over from the formation of the earth ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.