Plate Tectonics, Tectonic Plates Information, Facts, News, Photos
... pushes apart two or more plates. Mountains and volcanoes rise along the seam. The process renews the ocean floor and widens the giant basins. A single mid-ocean ridge system connects the world's oceans, making the ridge the longest mountain range in the world. On land, giant troughs such as the Grea ...
... pushes apart two or more plates. Mountains and volcanoes rise along the seam. The process renews the ocean floor and widens the giant basins. A single mid-ocean ridge system connects the world's oceans, making the ridge the longest mountain range in the world. On land, giant troughs such as the Grea ...
Tectonic Plates
... that states that con8nents once formed a single landmass, broke up, and driCed to their present loca8ons. • Scien8st Alfred Wegener developed the hypothesis in the early 1900s. hKp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1‐HwPR_4mP4 ...
... that states that con8nents once formed a single landmass, broke up, and driCed to their present loca8ons. • Scien8st Alfred Wegener developed the hypothesis in the early 1900s. hKp://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1‐HwPR_4mP4 ...
Part B KEY
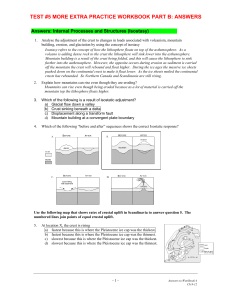
... Use the following map to answer questions 38 to 43 on the next page. The map area is generally flat except for the northeast section where the land surface rises steeply in a hill formed from nearly horizontal layers of schist, gabbro and quartzite units. 38. Name the type of fold which is shown on ...
... Use the following map to answer questions 38 to 43 on the next page. The map area is generally flat except for the northeast section where the land surface rises steeply in a hill formed from nearly horizontal layers of schist, gabbro and quartzite units. 38. Name the type of fold which is shown on ...
History of Continental Drift, part 1
... The only explanation is that continents used to be somewhere else ...
... The only explanation is that continents used to be somewhere else ...
The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics
... - buoyant (less dense than oceanic crust) - mostly old ...
... - buoyant (less dense than oceanic crust) - mostly old ...
Layers of the Earth
... plates which are moved in various directions. • This plate motion causes them to collide, pull apart, or scrape against each other. • Each type of interaction causes a characteristic set of Earth structures or ...
... plates which are moved in various directions. • This plate motion causes them to collide, pull apart, or scrape against each other. • Each type of interaction causes a characteristic set of Earth structures or ...
Continental Drift, Mountain Building, and Plate Tectonics
... below the CURIE POINT. These fossil magnets reflect changes in the magnetic field through time. INCLINATION is the angle the magnetic makes with the earth’s surface = latitiude DECLINATION is the angle between the magnetic and geographic north pole Sea floor spreading shows a pattern of increasing a ...
... below the CURIE POINT. These fossil magnets reflect changes in the magnetic field through time. INCLINATION is the angle the magnetic makes with the earth’s surface = latitiude DECLINATION is the angle between the magnetic and geographic north pole Sea floor spreading shows a pattern of increasing a ...
Geology Library Notes Wk8.cwk (WP)
... Oceanic crust is denser than continental crust, thus where oceanic crust meets continental crust the oceanic plate dives under the continent. Where two oceanic plates collide, one usually dives under the other. Associated with substantial volcanism and earthquakes. ...
... Oceanic crust is denser than continental crust, thus where oceanic crust meets continental crust the oceanic plate dives under the continent. Where two oceanic plates collide, one usually dives under the other. Associated with substantial volcanism and earthquakes. ...
The Solid Earth - Cloudfront.net
... called plates. The plates are made of the crust plus the upper mantle (lithosphere). These plates “float” on the asthenosphere and move. ...
... called plates. The plates are made of the crust plus the upper mantle (lithosphere). These plates “float” on the asthenosphere and move. ...
Birth of the Himalaya
... To understand the fascinating mechanics of the collision of India with Asia we must first look beneath the Earth's surface. The continents are carried by the Earth's tectonic plates like people on an escalator. There are currently 7 giant plates sliding across the Earth's surface, and a handful of s ...
... To understand the fascinating mechanics of the collision of India with Asia we must first look beneath the Earth's surface. The continents are carried by the Earth's tectonic plates like people on an escalator. There are currently 7 giant plates sliding across the Earth's surface, and a handful of s ...
Earth and Science Stems and Expectation
... earth are washed downstream where they settle to the bottom of the rivers, lakes, and oceans. Layer after layer of eroded earth is deposited on top of each. These layers are pressed down more and more through time, until the bottom layers slowly turn into rock. ...
... earth are washed downstream where they settle to the bottom of the rivers, lakes, and oceans. Layer after layer of eroded earth is deposited on top of each. These layers are pressed down more and more through time, until the bottom layers slowly turn into rock. ...
The importance of the Earth`s biosphere in stabilizing the large
... of the mantle using elements of plate tectonics and mantle convection. We show that even a late origin of photosynthetic life (2.0 – 2.5 Ga) could have stabilized the large continental surface area of Earth and its wet mantle we observe at present. ...
... of the mantle using elements of plate tectonics and mantle convection. We show that even a late origin of photosynthetic life (2.0 – 2.5 Ga) could have stabilized the large continental surface area of Earth and its wet mantle we observe at present. ...
1 Historical perspective perspective
... region of Canada, and Asia), and consisted of North America, Greenland, Europe, and Asia. The southerly supercontinent is termed Gondwana (literally “land of the Gonds” after an ancient tribe of northern India), and consisted of South America, Antarctica, Africa, Madagascar, India, and Australasia. ...
... region of Canada, and Asia), and consisted of North America, Greenland, Europe, and Asia. The southerly supercontinent is termed Gondwana (literally “land of the Gonds” after an ancient tribe of northern India), and consisted of South America, Antarctica, Africa, Madagascar, India, and Australasia. ...
How Magma Forms
... T is different from the fluid (mass flux). Important near Earth’s surface due to fractured nature of crust. • Conduction: transfer of kinetic energy by atomic vibration. Cannot occur in a vacuum. For a given volume, heat is conducted away faster if the enclosing surface area is larger. • Convect ...
... T is different from the fluid (mass flux). Important near Earth’s surface due to fractured nature of crust. • Conduction: transfer of kinetic energy by atomic vibration. Cannot occur in a vacuum. For a given volume, heat is conducted away faster if the enclosing surface area is larger. • Convect ...
PLATE TECTONICS REVIEW SHEET Write rock or metal to indicate
... 7. What method of heat transfer likely causes the plates to move? ____Convection_______________________ 8. Continental mountain ranges are often found along what kind of plate boundary? ___Convergent________________ 9. The type of boundary where plates collide is called a _____Convergent____________ ...
... 7. What method of heat transfer likely causes the plates to move? ____Convection_______________________ 8. Continental mountain ranges are often found along what kind of plate boundary? ___Convergent________________ 9. The type of boundary where plates collide is called a _____Convergent____________ ...
idea proposed by Alfred Wegener that the continents started as one
... Plate boundaries Divergent: when plates of lithosphere move apart. o Builds oceans Convergent: when plates of lithosphere move together. o Ophioltes: sections of the oceantic crust that are uplifted and exposed within the continental crust. o Subduction: one plate moves below another plate. Resul ...
... Plate boundaries Divergent: when plates of lithosphere move apart. o Builds oceans Convergent: when plates of lithosphere move together. o Ophioltes: sections of the oceantic crust that are uplifted and exposed within the continental crust. o Subduction: one plate moves below another plate. Resul ...
Mineral resource
... There Are Three Major Types of Rocks (2) 1. Sedimentary • Sediments from eroded rocks or plant/animal remains • Transported by water, wind, gravity • Deposited in layers and compacted ...
... There Are Three Major Types of Rocks (2) 1. Sedimentary • Sediments from eroded rocks or plant/animal remains • Transported by water, wind, gravity • Deposited in layers and compacted ...
The Earth
... • 75% of the Earth’s surface is covered by oceans • For the last ~3.8 billion years, the Earth has had a relatively stable water cycle (see video), with possibly a few freeze-ups or “Snowball Earth” episodes… • The planets are misnamed in Chinese: Earth is the “Water Planet,” not Mercury (水星)! ...
... • 75% of the Earth’s surface is covered by oceans • For the last ~3.8 billion years, the Earth has had a relatively stable water cycle (see video), with possibly a few freeze-ups or “Snowball Earth” episodes… • The planets are misnamed in Chinese: Earth is the “Water Planet,” not Mercury (水星)! ...
: 3.8 MB - Okala Practitioner
... We began massive extracEon of carbon from fossil fuels into the atmosphere 200 years ago. We now extract and concentrate toxic metals in amounts rarely found in nature. ...
... We began massive extracEon of carbon from fossil fuels into the atmosphere 200 years ago. We now extract and concentrate toxic metals in amounts rarely found in nature. ...
Opposition to Continental Drift
... This is a major departure from Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis, which proposed that the continents move through the ocean floor, not with it. ...
... This is a major departure from Wegener’s continental drift hypothesis, which proposed that the continents move through the ocean floor, not with it. ...
Kaminski Kate Kaminski (203) 586-9570
... Proficient in Microsoft Word, Excel, and PowerPoint; Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator Trained on Raman Spectrometer, SEM, LA-ICPMS, and in fission track counting Experienced in C++ and MATLAB ...
... Proficient in Microsoft Word, Excel, and PowerPoint; Adobe Photoshop and Illustrator Trained on Raman Spectrometer, SEM, LA-ICPMS, and in fission track counting Experienced in C++ and MATLAB ...
Geography - Oxford University Press
... happens, one plate slides ‘under’ the other one. The plate melts and forms a hot liquid called magma. The heat inside the earth causes a lot of pressure. Because the plates are always moving, holes or cracks sometimes form in the crust. If there is a lot of pressure, the hot liquid magma will explod ...
... happens, one plate slides ‘under’ the other one. The plate melts and forms a hot liquid called magma. The heat inside the earth causes a lot of pressure. Because the plates are always moving, holes or cracks sometimes form in the crust. If there is a lot of pressure, the hot liquid magma will explod ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.