volcanoes-study-guide
... Blocky lava- is cool, stiff lava that does not travel far from the erupting vent. Blocky lava usually oozes from a volcano and forms jumbled heaps of sharp edged chunks. 7. Describe the four types of pyroclastic material. Volcanic bombs – are large blobs of magma that harden in the air. The shape of ...
... Blocky lava- is cool, stiff lava that does not travel far from the erupting vent. Blocky lava usually oozes from a volcano and forms jumbled heaps of sharp edged chunks. 7. Describe the four types of pyroclastic material. Volcanic bombs – are large blobs of magma that harden in the air. The shape of ...
Plate Tectonics
... mountain ranges. – Rocks types match up on different continents, supporting that continents were together. – Mountain ranges such as the Appalachian Mountains of the eastern U.S. are similar to those found in Greenland and western Europe. – S. American rocks on the eastern side match up with rocks o ...
... mountain ranges. – Rocks types match up on different continents, supporting that continents were together. – Mountain ranges such as the Appalachian Mountains of the eastern U.S. are similar to those found in Greenland and western Europe. – S. American rocks on the eastern side match up with rocks o ...
How accurately can we measure density within the Earth?
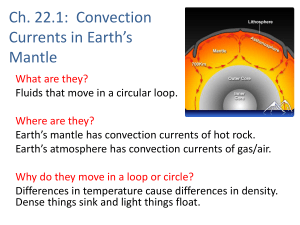
... convecting adiabatic mantle interior ...
... convecting adiabatic mantle interior ...
Slide 1
... In the late 1950’s a geologist named Henry Hess proposed a new hypothesis. He proposed that the valley at the center of the ridge was a crack, or rift, in the earth’s crust. Hess suggested that magma from deep inside the earth would rise through these cracks as the ocean floor moved away. The magma ...
... In the late 1950’s a geologist named Henry Hess proposed a new hypothesis. He proposed that the valley at the center of the ridge was a crack, or rift, in the earth’s crust. Hess suggested that magma from deep inside the earth would rise through these cracks as the ocean floor moved away. The magma ...
Plate Tectonics Review
... and polarity of the Earth’s magnetic field recorded in rocks containing the mineral ...
... and polarity of the Earth’s magnetic field recorded in rocks containing the mineral ...
plate boundaries
... • When sufficiently cool and dense, these rocks may sink back into the mantle at subduction zones – Downward plunge of cold rocks gives rise to oceanic trenches ...
... • When sufficiently cool and dense, these rocks may sink back into the mantle at subduction zones – Downward plunge of cold rocks gives rise to oceanic trenches ...
part 1 - Research at UVU
... *Make sure to symbolize the three types of plate boundaries differently and be as precise with your line work. Describe your symbols here: ...
... *Make sure to symbolize the three types of plate boundaries differently and be as precise with your line work. Describe your symbols here: ...
Plate Tectonics _2010
... They found that the lithosphere was moving due to Earth’s internal heat. This developed into the theory of Plate Tectonics ...
... They found that the lithosphere was moving due to Earth’s internal heat. This developed into the theory of Plate Tectonics ...
Chapter 10-3 - Theory of Plate Tectonics
... Wegener had suggested the idea of seafloor spreading. His idea showed more than just continents were moving. It was now clear to scientists that sections of the seafloor and continents move in relation to one another. Plate Movements In the 1960’s, scientists came up with a new theory. This theory c ...
... Wegener had suggested the idea of seafloor spreading. His idea showed more than just continents were moving. It was now clear to scientists that sections of the seafloor and continents move in relation to one another. Plate Movements In the 1960’s, scientists came up with a new theory. This theory c ...
earth science for foreign students
... In Iceland, some 400 km are exposed of the Mid-Atlantic ridge, allowing the student to observe and investigate the tectonic processes of crustal accretion, the central rift, fracture zones, submarine/subglacial volcanism and associated features and processes. The volcanics, too, are surprisingly var ...
... In Iceland, some 400 km are exposed of the Mid-Atlantic ridge, allowing the student to observe and investigate the tectonic processes of crustal accretion, the central rift, fracture zones, submarine/subglacial volcanism and associated features and processes. The volcanics, too, are surprisingly var ...
PP5-AbbeyNaji - Stout Middle School
... The difference between the Lithosphere and the Asthenosphere is the Lithosphere is made up of the crust of the upper part of the mantle . While the asthenosphere is on upper mantle material. ...
... The difference between the Lithosphere and the Asthenosphere is the Lithosphere is made up of the crust of the upper part of the mantle . While the asthenosphere is on upper mantle material. ...
What are Earthquakes
... Where do they occur most often? Within areas of the crust are fractures, known as faults, One block may move up while the other moves down, or one may move horizontally in one direction and the other in the opposite direction. Geologists and seismologists (scientists who study earthquakes and ...
... Where do they occur most often? Within areas of the crust are fractures, known as faults, One block may move up while the other moves down, or one may move horizontally in one direction and the other in the opposite direction. Geologists and seismologists (scientists who study earthquakes and ...
plate driving force
... PLATE MOTIONS CAUSE EARTHQUAKES, VOLCANOS, MOUNTAIN BUILDING AT PLATE BOUNDARIES PLATE TECTONICS MAKES EARTH WHAT IT IS - DIFFERENT FROM ...
... PLATE MOTIONS CAUSE EARTHQUAKES, VOLCANOS, MOUNTAIN BUILDING AT PLATE BOUNDARIES PLATE TECTONICS MAKES EARTH WHAT IT IS - DIFFERENT FROM ...
The Structure of the Earth and Plate Tectonics
... h i l surveys: seismic, i i gravity, i magnetics, i electrical, geodesy – Acquisition: land, air, sea and satellite – Geological surveys: fieldwork, boreholes, mines ...
... h i l surveys: seismic, i i gravity, i magnetics, i electrical, geodesy – Acquisition: land, air, sea and satellite – Geological surveys: fieldwork, boreholes, mines ...
Forces of Change
... breaks down rocks Erosion- Ground surface moved from one place to another (wind /water /glaciers) Human Factors – Entertainment, Urbanization, Mining, Deforestation Volcanism - ...
... breaks down rocks Erosion- Ground surface moved from one place to another (wind /water /glaciers) Human Factors – Entertainment, Urbanization, Mining, Deforestation Volcanism - ...
Earth Communication
... move slowly and change in size. Intense geologic activity, like earthquakes and volcanoes occur at plate boundaries where plates move away from each other, past each other or toward one another. There are eight large plates and four smaller plates that make up the outer shell of the Earth like a puz ...
... move slowly and change in size. Intense geologic activity, like earthquakes and volcanoes occur at plate boundaries where plates move away from each other, past each other or toward one another. There are eight large plates and four smaller plates that make up the outer shell of the Earth like a puz ...
Earth Communication
... move slowly and change in size. Intense geologic activity, like earthquakes and volcanoes occur at plate boundaries where plates move away from each other, past each other or toward one another. There are eight large plates and four smaller plates that make up the outer shell of the Earth like a puz ...
... move slowly and change in size. Intense geologic activity, like earthquakes and volcanoes occur at plate boundaries where plates move away from each other, past each other or toward one another. There are eight large plates and four smaller plates that make up the outer shell of the Earth like a puz ...
Slide 1
... • Energy transferred directly from one object to another (i.e. burning feet at the beach). ...
... • Energy transferred directly from one object to another (i.e. burning feet at the beach). ...
File
... In a process called sea floor spreading, molten rock forces its way upward through cracks, or rifts. The molten rock hardens into new oceanic crust. ...
... In a process called sea floor spreading, molten rock forces its way upward through cracks, or rifts. The molten rock hardens into new oceanic crust. ...
platetectonics-1232003374497953-1 - RCPL
... The size of the Earth -- about 12,750 kilometers (km) in diameter-was known by the ancient Greeks, but it was not until the turn of the 20th century that scientists determined that our planet is made up of three main layers: crust, mantle, and core. ...
... The size of the Earth -- about 12,750 kilometers (km) in diameter-was known by the ancient Greeks, but it was not until the turn of the 20th century that scientists determined that our planet is made up of three main layers: crust, mantle, and core. ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.