App 3 Module 1_Non-Excel - Scholar Commons
... In 1772, Nevil Maskelyne was pondering Sir Isaac Newton’s theory of gravitation, in which it was proposed that ANY object should exert a gravitational attraction towards any other object. Maskelyne surmised that this should mean that one could measure the gravitational attraction of, for instance, a ...
... In 1772, Nevil Maskelyne was pondering Sir Isaac Newton’s theory of gravitation, in which it was proposed that ANY object should exert a gravitational attraction towards any other object. Maskelyne surmised that this should mean that one could measure the gravitational attraction of, for instance, a ...
Thermal Convection
... and brings heat to the boundary between the core and the mantle where some of it is transferred into the mantle. Temperatures are hot enough in the upper mantle ( 1200 C) to cause thermal convection of the highly viscous upper mantle rocks, although it flows very slowly – approximately one cm/yr. Th ...
... and brings heat to the boundary between the core and the mantle where some of it is transferred into the mantle. Temperatures are hot enough in the upper mantle ( 1200 C) to cause thermal convection of the highly viscous upper mantle rocks, although it flows very slowly – approximately one cm/yr. Th ...
Plate tectonics of the Mediterranean area and its mountain belts
... The Mediterranean area is characterized by a collage of small tectonic plates that are surrounded by arcuate mountain belts (Fig. 1). These are the sites of both active and ancient plate boundaries, including several volcanic arcs and oceanic basins. What makes these microplates unusual is their mob ...
... The Mediterranean area is characterized by a collage of small tectonic plates that are surrounded by arcuate mountain belts (Fig. 1). These are the sites of both active and ancient plate boundaries, including several volcanic arcs and oceanic basins. What makes these microplates unusual is their mob ...
File
... The lithosphere is broken into pieces called plates. Those plates carry the continents with them as they move over the asthenosphere, driven by convection currents in the mantle. Describe paleomagnetism. Be specific and very detailed! Iron-rich rocks will show the magnetic poles at the time they for ...
... The lithosphere is broken into pieces called plates. Those plates carry the continents with them as they move over the asthenosphere, driven by convection currents in the mantle. Describe paleomagnetism. Be specific and very detailed! Iron-rich rocks will show the magnetic poles at the time they for ...
PLATE TECTONICS
... • The evidence Wegener had to support his theory was not enough to convince many people during his lifetime. • Not until the 1960’s were his beliefs accepted by the ...
... • The evidence Wegener had to support his theory was not enough to convince many people during his lifetime. • Not until the 1960’s were his beliefs accepted by the ...
past exam questions - University of Idaho
... 2. Which of the following shows Earth’s internal layers in their correct order from the surface towards the center? A. crust, core, mantle B. core, crust, mantle C. lithosphere, asthenosphere, lower mantle, outer core, inner core D. inner core, mantle, lithosphere, asthenosphere E. inner core, outer ...
... 2. Which of the following shows Earth’s internal layers in their correct order from the surface towards the center? A. crust, core, mantle B. core, crust, mantle C. lithosphere, asthenosphere, lower mantle, outer core, inner core D. inner core, mantle, lithosphere, asthenosphere E. inner core, outer ...
Word - University of Idaho
... Which of the following shows Earth’s internal layers in their correct order from the surface towards the center? A. crust, core, mantle B. core, crust, mantle C. lithosphere, asthenosphere, lower mantle, outer core, inner core D. inner core, mantle, lithosphere, asthenosphere E. inner core, outer co ...
... Which of the following shows Earth’s internal layers in their correct order from the surface towards the center? A. crust, core, mantle B. core, crust, mantle C. lithosphere, asthenosphere, lower mantle, outer core, inner core D. inner core, mantle, lithosphere, asthenosphere E. inner core, outer co ...
Earth Structure, Materials, Systems, and Cycles
... Precipitation from living organisms - the process that results in biochemical sedimentary rocks Change to more stable state - the process that results in the formation of soil, through weathering, and the formation of metamorphic rocks. Precipitation from vapor. (not common, but sometimes does occur ...
... Precipitation from living organisms - the process that results in biochemical sedimentary rocks Change to more stable state - the process that results in the formation of soil, through weathering, and the formation of metamorphic rocks. Precipitation from vapor. (not common, but sometimes does occur ...
Chapter 17 Plate Tectonics
... c. magnetic and sonar data proved that Wegener’s hypothesis was incorrect. d. mantle convection currents weren’t in motion at that time. 3. Compared to ocean crust near deep-sea trenches, crust near ocean ridges is a. younger. b. older. c. the same age. d. magnetically reversed. 4. The magnetic patt ...
... c. magnetic and sonar data proved that Wegener’s hypothesis was incorrect. d. mantle convection currents weren’t in motion at that time. 3. Compared to ocean crust near deep-sea trenches, crust near ocean ridges is a. younger. b. older. c. the same age. d. magnetically reversed. 4. The magnetic patt ...
Candy Bar Tectonics
... What do you observe as you apply this force? The pieces of chocolate spread apart; some may "drop" into the caramel layer At what type of plate boundary would this force occur? Divergent At what type of fault would this force occur? Normal SHEARING What do you observe as you apply this force? The pi ...
... What do you observe as you apply this force? The pieces of chocolate spread apart; some may "drop" into the caramel layer At what type of plate boundary would this force occur? Divergent At what type of fault would this force occur? Normal SHEARING What do you observe as you apply this force? The pi ...
File - C. Shirley Science EJCHS
... The solid part of Earth that consist of all rocks and soil that extends form the center of the core to the surface of the crust. The deepest well that has been drilled into Earth’s interior is only about 12 km deep so alternative methods such as seismic waves are used to learn about the interior. Se ...
... The solid part of Earth that consist of all rocks and soil that extends form the center of the core to the surface of the crust. The deepest well that has been drilled into Earth’s interior is only about 12 km deep so alternative methods such as seismic waves are used to learn about the interior. Se ...
earthquakes - Archway Chandler
... 2. Compression – squeezes rock until it folds or breaks 3. Shearing – pushes a mass of rock in opposite directions till it breaks or slips c. Fault – a crack resulting within the Earth’s crust as a result of the stress, usually along a plate boundary, i. Three types of faults 1. normal – caused by t ...
... 2. Compression – squeezes rock until it folds or breaks 3. Shearing – pushes a mass of rock in opposite directions till it breaks or slips c. Fault – a crack resulting within the Earth’s crust as a result of the stress, usually along a plate boundary, i. Three types of faults 1. normal – caused by t ...
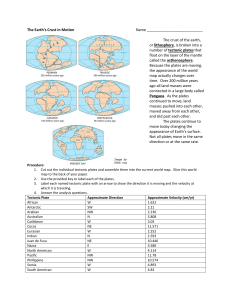
The Earth`s Crust in Motion Name The crust of the earth, or
... The crust of the earth, or lithosphere, is broken into a number of tectonic plates that float on the layer of the mantle called the asthenosphere. Because the plates are moving, the appearance of the world map actually changes over time. Over 200 million years ago all land masses were connected in a ...
... The crust of the earth, or lithosphere, is broken into a number of tectonic plates that float on the layer of the mantle called the asthenosphere. Because the plates are moving, the appearance of the world map actually changes over time. Over 200 million years ago all land masses were connected in a ...
Plate Tectonics - Earth Science Teachers` Association
... Hot spots are rising plumes of hot rock which originate at the core/mantle boundary and are unrelated to mantle convection cells. There are many around the world at present. Iceland and Hawaii are the best known examples. Learn Hawaii as an example to show that hot spots remain stationery for millio ...
... Hot spots are rising plumes of hot rock which originate at the core/mantle boundary and are unrelated to mantle convection cells. There are many around the world at present. Iceland and Hawaii are the best known examples. Learn Hawaii as an example to show that hot spots remain stationery for millio ...
SECOND GRADE EARTHQUAKES
... surface. But how has this been determined? Many people might answer that question by saying scientists can drill into the Earth with machines. However, the drilling rigs that scientists use can only drill about 20 km in the Earth which is not very deep! In other words, we can only drill into upper p ...
... surface. But how has this been determined? Many people might answer that question by saying scientists can drill into the Earth with machines. However, the drilling rigs that scientists use can only drill about 20 km in the Earth which is not very deep! In other words, we can only drill into upper p ...
mountain belt
... • When sufficiently cool and dense, these rocks may sink back into the mantle at subduction zones – Downward plunge of cold rocks gives rise to oceanic trenches ...
... • When sufficiently cool and dense, these rocks may sink back into the mantle at subduction zones – Downward plunge of cold rocks gives rise to oceanic trenches ...
Appalachian Mountain Building
... Orogeny is the process that for all mountain ranges. Orogeny results in broad, linear regions of deformation known as orogenic belts. Most orogenic belts are associated with plate boundaries. The greatest variety and the tallest of these belts Are found at convergent Boundaries. ...
... Orogeny is the process that for all mountain ranges. Orogeny results in broad, linear regions of deformation known as orogenic belts. Most orogenic belts are associated with plate boundaries. The greatest variety and the tallest of these belts Are found at convergent Boundaries. ...
Magnetic Reversals
... The science of the shaping of the Earth's crust goes by the name "tectonics," and the process described here is the essence of "plate tectonics" by the Earth's crust consists of distinct plates which are continually rearranged, sometimes carrying along continents or parts of continents. The entire m ...
... The science of the shaping of the Earth's crust goes by the name "tectonics," and the process described here is the essence of "plate tectonics" by the Earth's crust consists of distinct plates which are continually rearranged, sometimes carrying along continents or parts of continents. The entire m ...
Volcanic Landforms
... crust that allow lave through ● Basic lava -very runny ● Hot spot remains in the same place ● Plate above the hot spot moves ● This causes a chain of volcanic islands to form ...
... crust that allow lave through ● Basic lava -very runny ● Hot spot remains in the same place ● Plate above the hot spot moves ● This causes a chain of volcanic islands to form ...
EXAM 3
... C. tsunami waves D. lahars E. landslides 39. The bending of waves through different rock layers is called (1) ___________ whereas the bouncing of waves off of layer boundaries is called (2) ______________. A. (1) wave refraction; (2) wave interference B. (1) wave refraction; (2) wave reflection C. ( ...
... C. tsunami waves D. lahars E. landslides 39. The bending of waves through different rock layers is called (1) ___________ whereas the bouncing of waves off of layer boundaries is called (2) ______________. A. (1) wave refraction; (2) wave interference B. (1) wave refraction; (2) wave reflection C. ( ...
Plate Tectonics
... He was a German geophysicist remembered most for his theory of continental drift. His theory stated continents are slowly drifting around the Earth and was not accepted at the time. ...
... He was a German geophysicist remembered most for his theory of continental drift. His theory stated continents are slowly drifting around the Earth and was not accepted at the time. ...
Word format
... 30. Seismic waves are recorded by an instrument called a (1) _________ and the record that the instrument generates is called a (2) ____________. A. (1) seismograph; (2) seismometer B. (1) seismograph; (2) seismogram C. (1) seismometer; (2) seismograph D. (1) seismogram; (2) seismograph E. (1) seism ...
... 30. Seismic waves are recorded by an instrument called a (1) _________ and the record that the instrument generates is called a (2) ____________. A. (1) seismograph; (2) seismometer B. (1) seismograph; (2) seismogram C. (1) seismometer; (2) seismograph D. (1) seismogram; (2) seismograph E. (1) seism ...
1. What evidence did Alfred Wagner use to support his theory of
... 12. What are two bad things that can happen as a result of plate tectonics, how did plate tectonics cause these events? Two bad things that can happen as a result of plate tectonics are: volcanoes and earthquakes. 13. What are three good things that plate tectonics provide for humans, how do plate t ...
... 12. What are two bad things that can happen as a result of plate tectonics, how did plate tectonics cause these events? Two bad things that can happen as a result of plate tectonics are: volcanoes and earthquakes. 13. What are three good things that plate tectonics provide for humans, how do plate t ...
Chapter 3: Mountains, Coast and Shelf
... by penetrating water, air, roots and biological activity. As the rocks are gradually exhumed, they also crack from the release of pressure from the removal of the material above. Water becomes channelled along these fractures, and removes the softened rock on the sides of the joints, grain by grain, ...
... by penetrating water, air, roots and biological activity. As the rocks are gradually exhumed, they also crack from the release of pressure from the removal of the material above. Water becomes channelled along these fractures, and removes the softened rock on the sides of the joints, grain by grain, ...
Geology

Geology (from the Greek γῆ, gē, i.e. ""earth"" and -λoγία, -logia, i.e. ""study of, discourse"") is an earth science comprising the study of solid Earth, the rocks of which it is composed, and the processes by which they change. Geology can also refer generally to the study of the solid features of any celestial body (such as the geology of the Moon or Mars).Geology gives insight into the history of the Earth by providing the primary evidence for plate tectonics, the evolutionary history of life, and past climates. Geology is important for mineral and hydrocarbon exploration and exploitation, evaluating water resources, understanding of natural hazards, the remediation of environmental problems, and for providing insights into past climate change. Geology also plays a role in geotechnical engineering and is a major academic discipline.