* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Deep sea community wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Paleostress inversion wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Oceanic trench wikipedia , lookup
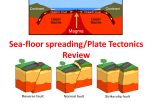
Name _____________________________________ Date______________ Period______ Chapter 9 & 11 – Plate Tectonics & Mountain Building STUDY GUIDE Describe Alfred Wegener’s theory of continental drift. Be specific and very detailed! About 225 million years ago, all the continents were one huge supercontinent, called Pangaea. Pangaea split and the continents drifted into their current positions. Describe all the types of evidence that supports Wegener’s theory of continental drift. Be specific and very detailed! ~ continents fit together like puzzle pieces ~ fossils of plants and animals from different continents all matched up ~ rocks/mountain ranges of same type and age from different continents all matched up ~ glacial deposits and grooves from ice sheets in currently warm areas ~ coal deposits that formed in warm, wet areas found in currently cold areas Why was Wegener’s theory of continental drift rejected? couldn’t explain HOW the continents moved to their current locations Describe the concept of seafloor spreading. Be specific and very detailed! New ocean crust is being made in the rift valley of a mid-ocean ridge. That new crust pushes the old crust away from the rift, going in opposite directions. Ocean crust is then pushed back down into the mantle where it melts at subduction zones in ocean trenches. Describe the theory of plate tectonics. Be specific and very detailed! The lithosphere is broken into pieces called plates. Those plates carry the continents with them as they move over the asthenosphere, driven by convection currents in the mantle. Describe paleomagnetism. Be specific and very detailed! Iron-rich rocks will show the magnetic poles at the time they form. The study of paleomagnetism shows that the Earth’s magnetic pole has reversed itself back and forth numerous times during geologic history. The pattern of magnetic reversals is seen as mirror images on either side of a mid-ocean ridge. For which idea do magnetic reversals provide evidence? seafloor spreading Describe how the ages of rocks and sediments change as you move away from the center (rift) of a mid-ocean ridge. youngest and thinnest sediments at the rift (center); get older and thicker as you move away from the rift How are mountains classified? by how they are formed List the three types of stress that can be seen in rocks. tension – pulls apart compression – pushes together shear – squeezing/deforming from multiple sides Describe each of the three types of faults. Be sure to include ALL types of features and stress that causes that fault. normal – hanging wall drops down from footwall; caused by tension stress; usually at divergent boundaries reverse – hanging wall moves up from footwall; caused by compression stress; usually at convergent boundaries strike-slip – rock moves sideways (horizontal) without up/down motion; caused by shear stress; usually at transform fault boundaries Draw and describe a divergent boundary. Be sure to include ALL types of features and stress that can be found at that boundary. plates move apart due to tensional stress; creates a mid-ocean ridge between the plates with a rift valley in the center; new ocean crust is being made at the rift which causes seafloor spreading Draw and describe a transform fault boundary. Be sure to include ALL types of features and stress that can be found at that boundary. plates grind past each other due to shearing stress; no new crust forms or old crust destroyed; creates earthquakes Draw and describe the general characteristics of any type of convergent boundary. plates collide (converge, come together) due to compressional stress; can have three different types of features seen based upon the types of crust in the colliding plates Describe fully all the characteristics of an oceanic-oceanic convergent boundary. one ocean plate pushed under the other, back into the mantle where it melts; this process (subduction) takes place at a subduction zone which creates a deep-sea trench; can also create a volcanic island arc Describe fully all the characteristics of an oceanic-continental convergent boundary. ocean plate (more dense) pushed under the continental plate (less dense), back into the mantle where it melts; this process (subduction) takes place at a subduction zone which creates a deep-sea trench; can also create a continental volcanic arc Describe fully all the characteristics of a continental-continental convergent boundary. both plates are less dense than the mantle so crumple upward; this process forms a mountain range Describe all that occurs at a subduction zone. oceanic plate gets pushed into the mantle (called subduction) creating a deep-sea trench Describe the concept of isostasy. condition of “gravitational balance” between Earth’s crust and mantle; gravity pulls down on crust while mantle pushes up until equilibrium (“balance”) is reached What kind of boundary is shown above? oceanic-continental convergent What is feature A? continental volcanic arc Feature B? trench What type of crustal plate is C? oceanic F? continental The process shown at letter G is called subduction What kind of boundary is shown above? oceanic-oceanic convergent What is feature A? volcanic island Feature B? trench What type of crustal plate is above C? oceanic E? oceanic The area where H is being pushed downward is called a: subduction zone What is the difference in the temperature between area X and area Y? X is hotter (Y is cooler) since X is deeper into the mantle