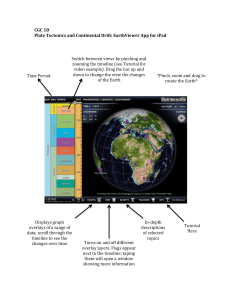
Earth`s Surface:
... Earth’s crust is composed of about a dozen large plates, with many smaller plates wedged between. Plate motion is responsible for a significant part of the Earth’s active surface geology. Volcanoes and earthquakes, expressions of Earth’s restless crust, are observed to be clustered along plate bound ...
... Earth’s crust is composed of about a dozen large plates, with many smaller plates wedged between. Plate motion is responsible for a significant part of the Earth’s active surface geology. Volcanoes and earthquakes, expressions of Earth’s restless crust, are observed to be clustered along plate bound ...
Power Point format
... • Earth system is also powered by internal processes driven by heat flow within earth. What are some sources of heat? ...
... • Earth system is also powered by internal processes driven by heat flow within earth. What are some sources of heat? ...
Chapter 1
... ecosystems and therefore change them as a result of population growth, technology, and consumption Problems: habitat destruction, pollution, atmospheric changes, over fishing the oceans, poaching, etc. ...
... ecosystems and therefore change them as a result of population growth, technology, and consumption Problems: habitat destruction, pollution, atmospheric changes, over fishing the oceans, poaching, etc. ...
Closer to Poles
... Influence of the earth’s rotation on movement of air and fluids Turns them Right in the Northern Hemisphere Turns them Left in the Southern Hemisphere ...
... Influence of the earth’s rotation on movement of air and fluids Turns them Right in the Northern Hemisphere Turns them Left in the Southern Hemisphere ...
Earth Movements Crossword
... 4. Ancient northern hemisphere supercontinent.[8] 6. Ancient original supercontinent.[7] 7. Type of volcano that has not erupted for some time but will erupt again.[7] 9. Rock formed from cooled lava.[6] 11. Point on earth's surface directly above the focus of a quake.[9] 12. Large earth break.[5] 1 ...
... 4. Ancient northern hemisphere supercontinent.[8] 6. Ancient original supercontinent.[7] 7. Type of volcano that has not erupted for some time but will erupt again.[7] 9. Rock formed from cooled lava.[6] 11. Point on earth's surface directly above the focus of a quake.[9] 12. Large earth break.[5] 1 ...
Earth Movements
... 4. Ancient northern hemisphere supercontinent.[8] 6. Ancient original supercontinent.[7] 7. Type of volcano that has not erupted for some time but will erupt again.[7] 9. Rock formed from cooled lava.[6] 11. Point on earth's surface directly above the focus of a quake.[9] 12. Large earth break.[5] 1 ...
... 4. Ancient northern hemisphere supercontinent.[8] 6. Ancient original supercontinent.[7] 7. Type of volcano that has not erupted for some time but will erupt again.[7] 9. Rock formed from cooled lava.[6] 11. Point on earth's surface directly above the focus of a quake.[9] 12. Large earth break.[5] 1 ...
Factors That Affect Climate Change File
... The presence of ice and snow on the earth’s surface can have an effect on how much solar radiation gets reflected from the earth’s surface back out into space. albedo- a measure of the fraction (or amount) of solar radiation or light that is reflected by a surface. Lighter-coloured materials have a ...
... The presence of ice and snow on the earth’s surface can have an effect on how much solar radiation gets reflected from the earth’s surface back out into space. albedo- a measure of the fraction (or amount) of solar radiation or light that is reflected by a surface. Lighter-coloured materials have a ...
Chapter three worksheet 2012-13
... e. People started noticing the first signs of the upcoming eruption _______ months before the event. f. What portion of Rakata Island sank back into the ocean? g. The volcano caused massive __________________________ to form in the ocean. h. The largest tsunami created on that day was ______________ ...
... e. People started noticing the first signs of the upcoming eruption _______ months before the event. f. What portion of Rakata Island sank back into the ocean? g. The volcano caused massive __________________________ to form in the ocean. h. The largest tsunami created on that day was ______________ ...
Earth Science S5E1a (EarthScienceS5E1a)
... 8. Which landforms are a result of deposition? A. beaches and river deltas B. mountains and valleys C. bays and peninsulas D. plateaus and mesas 9. Which landform results when one of Earth's plates slides past another? A. faults B. plateaus C. mountains D. deltas 10. Volcanoes are formed from A. hot ...
... 8. Which landforms are a result of deposition? A. beaches and river deltas B. mountains and valleys C. bays and peninsulas D. plateaus and mesas 9. Which landform results when one of Earth's plates slides past another? A. faults B. plateaus C. mountains D. deltas 10. Volcanoes are formed from A. hot ...
Chapter 2 – A Living Planet - smallworldbigthoughts-eub-geo
... The Earth Earth's inner core is solid iron, its outer core is liquid iron mixed with other components, and its mantle is dense rock. ...
... The Earth Earth's inner core is solid iron, its outer core is liquid iron mixed with other components, and its mantle is dense rock. ...
Grade 6: Earth Science
... over time, matter is transferred from one organism to others in the food web, and between organisms and the physical environment. c. populations of organisms can be categorized by the functions they serve in an ecosystem. d. different kinds of organisms may play similar ecological roles in similar b ...
... over time, matter is transferred from one organism to others in the food web, and between organisms and the physical environment. c. populations of organisms can be categorized by the functions they serve in an ecosystem. d. different kinds of organisms may play similar ecological roles in similar b ...
The Physical world
... another.—Think of an egg! • Core – solid metallic center made of nickel and iron • Mantle – soft layer of molten rock (magma) • Crust – thin layer of rock on earth’s surface ...
... another.—Think of an egg! • Core – solid metallic center made of nickel and iron • Mantle – soft layer of molten rock (magma) • Crust – thin layer of rock on earth’s surface ...
EarthViewer Questions
... a. In which period did these first land plants form? _____________________________ 11. How long ago were the first land vertebrates formed? _______________________________ 12. When did Homo Sapiens first appear? (in T ...
... a. In which period did these first land plants form? _____________________________ 11. How long ago were the first land vertebrates formed? _______________________________ 12. When did Homo Sapiens first appear? (in T ...
Chapter_2_Section_2_NOTES
... Forces that wear down and __break apart _____ the Earth’s crust. a. Weathering: _the process that breaks rocks down into tiny pieces Caused by: _water, ice, and living things (lichens) Helps create: ___soil ___ b. Erosion: __removal of small pieces of rock by water, ice, and wind. Creates ___new lan ...
... Forces that wear down and __break apart _____ the Earth’s crust. a. Weathering: _the process that breaks rocks down into tiny pieces Caused by: _water, ice, and living things (lichens) Helps create: ___soil ___ b. Erosion: __removal of small pieces of rock by water, ice, and wind. Creates ___new lan ...
Shaping Earths surface Ch 4 lesson 2
... Is the vibrations caused by the rupture and sudden movement of rocks along a break or a crack in Earth’s crust. ...
... Is the vibrations caused by the rupture and sudden movement of rocks along a break or a crack in Earth’s crust. ...
Dimensions of the Earth
... smaller spheres (zones) with distinct differences in air temperature and composition. The interface between these zones are called pauses. ...
... smaller spheres (zones) with distinct differences in air temperature and composition. The interface between these zones are called pauses. ...
File
... 3. What is the name of magma that has escaped onto Earth's surface 4. This is where the volanic materials that erupt are stored? 5. What two things burst through an opening in the top of the volcano 6. What is a thick liquid that flows out of the volcanoes called? 7. How can lava affect rocks 8. Wha ...
... 3. What is the name of magma that has escaped onto Earth's surface 4. This is where the volanic materials that erupt are stored? 5. What two things burst through an opening in the top of the volcano 6. What is a thick liquid that flows out of the volcanoes called? 7. How can lava affect rocks 8. Wha ...
Chapter 1 notes - Freedom Area School District
... Map projections - trying to represent the round earth on a flat surface cylindrical projection (Mercator)- this type of projection allows for strait line navigation (important in the 1500's), but it enlarges the areas in the high latitudes Robinson map is the projection the National Geographic Soci ...
... Map projections - trying to represent the round earth on a flat surface cylindrical projection (Mercator)- this type of projection allows for strait line navigation (important in the 1500's), but it enlarges the areas in the high latitudes Robinson map is the projection the National Geographic Soci ...
chp. 6
... The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species This organization bans the international trade of _____________ that are made from ...
... The Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species This organization bans the international trade of _____________ that are made from ...
Professor Bruce Watson
... The first 700 million years of Earth’s existence (the Hadean Eon) are widely regarded as the most geodynamically vigorous period in the history of our planet. It has been variously inferred that during this time the Earth: 1) collided with a Mars-sized-object; 2) formed a deep magma ocean; 3) grew t ...
... The first 700 million years of Earth’s existence (the Hadean Eon) are widely regarded as the most geodynamically vigorous period in the history of our planet. It has been variously inferred that during this time the Earth: 1) collided with a Mars-sized-object; 2) formed a deep magma ocean; 3) grew t ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.