Plate Tectonics and Earth`s Interior
... Title each graph and label all axes, including relevant units. On each graph draw a dashed vertical line at the appropriate depth to identify where each layer begins. ...
... Title each graph and label all axes, including relevant units. On each graph draw a dashed vertical line at the appropriate depth to identify where each layer begins. ...
Word Sort Template
... Why is most of in glaciers. the Earth’s fresh water not available to drink? Surface water, Groundwater Name the 2 types of freshwater: Give examples of Lakes, streams, ponds, rain runoff Surface water: Water in an aquifer Give examples of Groundwater: All parts of Earth that support Biosphere ...
... Why is most of in glaciers. the Earth’s fresh water not available to drink? Surface water, Groundwater Name the 2 types of freshwater: Give examples of Lakes, streams, ponds, rain runoff Surface water: Water in an aquifer Give examples of Groundwater: All parts of Earth that support Biosphere ...
6th Regular Study Guide-Canu
... 2. What tool is used to measure wind speed? 3. What tool is used to measure wind direction? 4. What tool is used to measure air pressure? 5. What tool measures the amount of rainfall? 6. All forms of energy can be in either of two states _____________ & _____________ 7. Give an example of kinetic en ...
... 2. What tool is used to measure wind speed? 3. What tool is used to measure wind direction? 4. What tool is used to measure air pressure? 5. What tool measures the amount of rainfall? 6. All forms of energy can be in either of two states _____________ & _____________ 7. Give an example of kinetic en ...
The Dynamic Earth Chapter 3
... Water has a higher specific heat than land. • Water takes a long time to heat up and a long time to cool down. • This helps regulate the temps in the atm as well. • Without the oceans, the temps on Earth would be too extreme for life to survive. ...
... Water has a higher specific heat than land. • Water takes a long time to heat up and a long time to cool down. • This helps regulate the temps in the atm as well. • Without the oceans, the temps on Earth would be too extreme for life to survive. ...
The Living Planet PPT
... Waves: swells or ridges produced by wind Tides: created by gravitational pull of moon or sun ...
... Waves: swells or ridges produced by wind Tides: created by gravitational pull of moon or sun ...
Study Guide Chapter 3 – Plate Tectonics GPS: S6E5. Students will
... 3. The three main layers of the Earth are the _______________, the ________________, and the _______________ , which is separated into the outer core and the inner core. 4. The oceanic crust consists mostly of rocks such as ___________________ which is a rock with a fine, dark texture. 5. The Earth’ ...
... 3. The three main layers of the Earth are the _______________, the ________________, and the _______________ , which is separated into the outer core and the inner core. 4. The oceanic crust consists mostly of rocks such as ___________________ which is a rock with a fine, dark texture. 5. The Earth’ ...
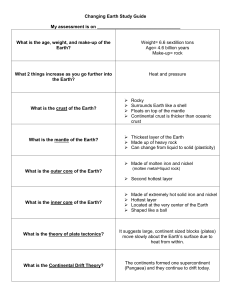
Study Guide 2-1 1. List the Compositional Layers and identify what
... b. Oblate Spheroid c. Differentiation d. Seismic Waves e. Plasticity ...
... b. Oblate Spheroid c. Differentiation d. Seismic Waves e. Plasticity ...
Environmental Science
... livestock for food or for other products that are useful to humans. The agricultural revolution allowed human populations to grow at an unprecedented rate. As populations grew, they began to concentrate in smaller areas placing increased pressure on the local environments. ...
... livestock for food or for other products that are useful to humans. The agricultural revolution allowed human populations to grow at an unprecedented rate. As populations grew, they began to concentrate in smaller areas placing increased pressure on the local environments. ...
200 300 400 500 100 200 300 400 500 100 200 300 400 500 100
... This is the soil texture which is a combination of equal parts sand, silt, and clay. ...
... This is the soil texture which is a combination of equal parts sand, silt, and clay. ...
Chapter 20 The Origin and Evolution of Life
... Chapter 20 The Origin and Evolution of Life In the beginning… Explain the big bang theory ...
... Chapter 20 The Origin and Evolution of Life In the beginning… Explain the big bang theory ...
Earth`s Moving Plates
... explains how the earth has evolved over time. Explains the formation, movement, collisions and destruction of the Earth’s crust. ...
... explains how the earth has evolved over time. Explains the formation, movement, collisions and destruction of the Earth’s crust. ...
Oceanography Notes - Intro (Day 1-3)
... 1. Intense ____________________ /____________________ Bombardment brought __________, __________, __________, __________ gases into the atmosphere 2. Tectonic Plate Movement created ____________________ that released lava and __________, __________, __________, __________ into the atmosphere E. ...
... 1. Intense ____________________ /____________________ Bombardment brought __________, __________, __________, __________ gases into the atmosphere 2. Tectonic Plate Movement created ____________________ that released lava and __________, __________, __________, __________ into the atmosphere E. ...
Changes to Earth`s Surface Vocabulary Builder
... 9. glacier – immense sheets of ice that cover earth’s surface 10. meteorite – rocks from space that hit earth’s surface 11. plate tectonics – the theory that the lithosphere is divided into plates that are always moving 12. mid-ocean ridge - chain of mountain that runs through the world’s oceans alo ...
... 9. glacier – immense sheets of ice that cover earth’s surface 10. meteorite – rocks from space that hit earth’s surface 11. plate tectonics – the theory that the lithosphere is divided into plates that are always moving 12. mid-ocean ridge - chain of mountain that runs through the world’s oceans alo ...
Sample Questions for Mrs. Igo`s Earth Science Final
... d. inner core 19. Some volcanoes form islands as ____ flows from rifts in the seafloor and builds up high enough to break the ocean's surface. a. lava c. water b. tephra d. gas 20. ____ is the transfer of energy in the form of rays or waves. a. Conduction c. Radiation b. Convection d. Condensation 2 ...
... d. inner core 19. Some volcanoes form islands as ____ flows from rifts in the seafloor and builds up high enough to break the ocean's surface. a. lava c. water b. tephra d. gas 20. ____ is the transfer of energy in the form of rays or waves. a. Conduction c. Radiation b. Convection d. Condensation 2 ...
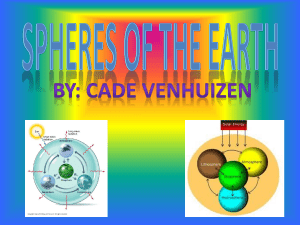
Spheres of the Earth
... • Functions: protects Earth from radiation from space and the sun’s rays • Protects Earth from rapid cooling at night and heating in the day • Reservoir for carbon dioxide and oxygen • Protects Earth from meteors • The closer you are to the Earth, the more pressure there is, because there is more gr ...
... • Functions: protects Earth from radiation from space and the sun’s rays • Protects Earth from rapid cooling at night and heating in the day • Reservoir for carbon dioxide and oxygen • Protects Earth from meteors • The closer you are to the Earth, the more pressure there is, because there is more gr ...
7th Grade Science Learning Goals
... 7th Grade Science Topics and Learning Goals Science Inquiry o Scientific method 1. Recognize that investigations involve specific skills in order to devise hypotheses and explanations. 2. Model an investigation and carry it out to answer a research question. o Measurement 1. Choose and apply appropr ...
... 7th Grade Science Topics and Learning Goals Science Inquiry o Scientific method 1. Recognize that investigations involve specific skills in order to devise hypotheses and explanations. 2. Model an investigation and carry it out to answer a research question. o Measurement 1. Choose and apply appropr ...
THE ATMOSPHERE
... atmosphere and comes from the decay of plants/animals and volcanic eruptions Oxygen makes up 18% of the atmosphere and comes from plants Other gases such as methane, argon, and carbon dioxide make up the rest As we get closer to the earth the air becomes denser (heavy) as we rise through the laye ...
... atmosphere and comes from the decay of plants/animals and volcanic eruptions Oxygen makes up 18% of the atmosphere and comes from plants Other gases such as methane, argon, and carbon dioxide make up the rest As we get closer to the earth the air becomes denser (heavy) as we rise through the laye ...
The Water Cycle - Mr. HIckey @CPHS
... being cycled through the atmosphere, ocean, and land. This process, known as the water cycle, is driven by energy from the sun. The water cycle is crucial to the existence of life on our planet. ...
... being cycled through the atmosphere, ocean, and land. This process, known as the water cycle, is driven by energy from the sun. The water cycle is crucial to the existence of life on our planet. ...
The Water Cycle
... being cycled through the atmosphere, ocean, and land. This process, known as the water cycle, is driven by energy from the sun. The water cycle is crucial to the existence of life on our planet. ...
... being cycled through the atmosphere, ocean, and land. This process, known as the water cycle, is driven by energy from the sun. The water cycle is crucial to the existence of life on our planet. ...
The Water Cycle - Science Education at Jefferson Lab
... being cycled through the atmosphere, ocean, and land. This process, known as the water cycle, is driven by energy from the sun. The water cycle is crucial to the existence of life on our planet. ...
... being cycled through the atmosphere, ocean, and land. This process, known as the water cycle, is driven by energy from the sun. The water cycle is crucial to the existence of life on our planet. ...
The Water Cycle
... being cycled through the atmosphere, ocean, and land. This process, known as the water cycle, is driven by energy from the sun. The water cycle is crucial to the existence of life on our planet. ...
... being cycled through the atmosphere, ocean, and land. This process, known as the water cycle, is driven by energy from the sun. The water cycle is crucial to the existence of life on our planet. ...
Nature

Nature, in the broadest sense, is the natural, physical, or material world or universe. ""Nature"" can refer to the phenomena of the physical world, and also to life in general. The study of nature is a large part of science. Although humans are part of nature, human activity is often understood as a separate category from other natural phenomena.The word nature is derived from the Latin word natura, or ""essential qualities, innate disposition"", and in ancient times, literally meant ""birth"". Natura is a Latin translation of the Greek word physis (φύσις), which originally related to the intrinsic characteristics that plants, animals, and other features of the world develop of their own accord. The concept of nature as a whole, the physical universe, is one of several expansions of the original notion; it began with certain core applications of the word φύσις by pre-Socratic philosophers, and has steadily gained currency ever since. This usage continued during the advent of modern scientific method in the last several centuries.Within the various uses of the word today, ""nature"" often refers to geology and wildlife. Nature can refer to the general realm of living plants and animals, and in some cases to the processes associated with inanimate objects – the way that particular types of things exist and change of their own accord, such as the weather and geology of the Earth. It is often taken to mean the ""natural environment"" or wilderness–wild animals, rocks, forest, and in general those things that have not been substantially altered by human intervention, or which persist despite human intervention. For example, manufactured objects and human interaction generally are not considered part of nature, unless qualified as, for example, ""human nature"" or ""the whole of nature"". This more traditional concept of natural things which can still be found today implies a distinction between the natural and the artificial, with the artificial being understood as that which has been brought into being by a human consciousness or a human mind. Depending on the particular context, the term ""natural"" might also be distinguished from the unnatural or the supernatural.