natural selection
... point of extinction the remaining individuals do not carry a true representation of the original gene pool. – FOUNDER EFFECT – when a small number of individuals colonize a new area they only carry with them a small representation of the total number of the alleles from the gene pool. ...
... point of extinction the remaining individuals do not carry a true representation of the original gene pool. – FOUNDER EFFECT – when a small number of individuals colonize a new area they only carry with them a small representation of the total number of the alleles from the gene pool. ...
Fossil Record-Homologies-Mechanisms of Evolution Notes
... Mature Forms But Develop From The Same Embryonic Tissues ...
... Mature Forms But Develop From The Same Embryonic Tissues ...
No Slide Title
... Natural Selection In the evolutionary struggle for existence, entire organisms, not individual genes, either survive and reproduce or do not. Natural selection can operate only on the phenotypic variation among individuals. An organism's phenotype includes all the physical and behavioral characteris ...
... Natural Selection In the evolutionary struggle for existence, entire organisms, not individual genes, either survive and reproduce or do not. Natural selection can operate only on the phenotypic variation among individuals. An organism's phenotype includes all the physical and behavioral characteris ...
Evolutionary Psychology - HomePage Server for UT Psychology
... Imagine you are a bouncer at a bar. If a person is drinking beer, he must be at least 21 years of age. One side of each card shows a person’s age, and the other side tells what he or she is drinking. Indicate the cards you need to turn over to find out whether anyone is breaking the law and needs to ...
... Imagine you are a bouncer at a bar. If a person is drinking beer, he must be at least 21 years of age. One side of each card shows a person’s age, and the other side tells what he or she is drinking. Indicate the cards you need to turn over to find out whether anyone is breaking the law and needs to ...
41040-2-12118
... other genes. Although very advantageous, gene silencing has a number of limitations pertaining, in particular, to the technical aspect and cost of the experiment. We propose a method for investigation of potential effects of silencing, before physically performing an experiment. This should allow a ...
... other genes. Although very advantageous, gene silencing has a number of limitations pertaining, in particular, to the technical aspect and cost of the experiment. We propose a method for investigation of potential effects of silencing, before physically performing an experiment. This should allow a ...
Genetics Challenge Name 1. The abbreviation for deoxyribonucleic
... 8. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ are rod-shaped structures found in the nucleus of every cell in an organism. ...
... 8. __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ __ are rod-shaped structures found in the nucleus of every cell in an organism. ...
Selection and Adaptation - WFSC 406 | Wildlife Habitat Management
... 10. Today when we think of the term fitness we often think about physical fitness, such as being muscular or in superb physical shape from some type of exercise. Darwin’s definition of fitness was different and was measured by the proportion of its genes left in the gene pool. So the term “survival ...
... 10. Today when we think of the term fitness we often think about physical fitness, such as being muscular or in superb physical shape from some type of exercise. Darwin’s definition of fitness was different and was measured by the proportion of its genes left in the gene pool. So the term “survival ...
Quiz 2 – (5%) – Using Matlab With a vast number of genes
... 1st Q: Because the gene types are String, Cell Array is used to store strings. Normal array only can store numeric variables. 3rd Q: The selected patients are with the Status = 1, which are patient 1,2 & 4 (From question 2). Compare the genes among 1, 2, & 4, and display the same gene, for example: ...
... 1st Q: Because the gene types are String, Cell Array is used to store strings. Normal array only can store numeric variables. 3rd Q: The selected patients are with the Status = 1, which are patient 1,2 & 4 (From question 2). Compare the genes among 1, 2, & 4, and display the same gene, for example: ...
Chapter 16
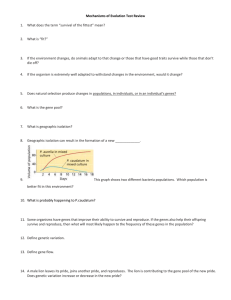
... Variation and Gene Pools • Gene Pool :All genes (and diff’t alleles) present in a population • Relative frequency: how often an allele shows up in a gene pool • Evolution: is a group process “ any change in the relative frequency of alleles in a population” ...
... Variation and Gene Pools • Gene Pool :All genes (and diff’t alleles) present in a population • Relative frequency: how often an allele shows up in a gene pool • Evolution: is a group process “ any change in the relative frequency of alleles in a population” ...
Microevolution is a change in a population*s gene pool
... A change in the gene pool of a population due to chance GENETIC DRIFT ALL populations are subject to genetic drift ...
... A change in the gene pool of a population due to chance GENETIC DRIFT ALL populations are subject to genetic drift ...
Slide 1
... Figure 1 Genes used to study RNA-mediated genetic interference in C.elegans. Intron–exon structure for genes used to test RNA-mediated inhibition are shown (grey and filled boxes, exons; open boxes, introns; patterned and striped boxes, 5' and 3' untranslated regions. unc-22. ref. 9, unc-54, ref. 1 ...
... Figure 1 Genes used to study RNA-mediated genetic interference in C.elegans. Intron–exon structure for genes used to test RNA-mediated inhibition are shown (grey and filled boxes, exons; open boxes, introns; patterned and striped boxes, 5' and 3' untranslated regions. unc-22. ref. 9, unc-54, ref. 1 ...
Evolution of Populations
... Genetic Drift: in small populations an individual that carries a particular allele may leave more offspring than others and over time that trait may become more prevalent in the population ...
... Genetic Drift: in small populations an individual that carries a particular allele may leave more offspring than others and over time that trait may become more prevalent in the population ...
Vocabulary Terms Natural Selection and Modern Genetics
... 3. gene pool: The total number of genes of every individual in an interbreeding population. 4. variation: Any difference among organisms of the same species. 5. mutations: Random changes in the genetic code; may be helpful or harmful. 6. adaptation: A genetic variation that provides an organism with ...
... 3. gene pool: The total number of genes of every individual in an interbreeding population. 4. variation: Any difference among organisms of the same species. 5. mutations: Random changes in the genetic code; may be helpful or harmful. 6. adaptation: A genetic variation that provides an organism with ...
Evolution Study Guide Part 2
... evolution only if they are mutations in the germ cells because these genes pass onto future generations. 2. Genetic Recombination and Sexual Reproduction is the most common way of genetic variation. Remember each chromosome pair moves independently during meiosis. In humans, who have 23 pairs of chr ...
... evolution only if they are mutations in the germ cells because these genes pass onto future generations. 2. Genetic Recombination and Sexual Reproduction is the most common way of genetic variation. Remember each chromosome pair moves independently during meiosis. In humans, who have 23 pairs of chr ...
Sources of heritable variation
... • Crossing over: as well as mixing in meiosis the homologous pairs can swap pieces. • Mutations: new gene variations for evolution to work on. Only source of new allelles, often harmful and carried as reccessive allelles. ...
... • Crossing over: as well as mixing in meiosis the homologous pairs can swap pieces. • Mutations: new gene variations for evolution to work on. Only source of new allelles, often harmful and carried as reccessive allelles. ...
4.2 Test Review File - Northwest ISD Moodle
... 20. You treat you home with a pesticide that kills 92% of the roaches the first time, but four months later you have to treat your home again and it only kills 65% of the roaches. Why does the pesticide seem to have decreased in effectiveness? ...
... 20. You treat you home with a pesticide that kills 92% of the roaches the first time, but four months later you have to treat your home again and it only kills 65% of the roaches. Why does the pesticide seem to have decreased in effectiveness? ...
How Evolution Works
... Norm Most traits are polygenic The normal trait is the average or mean in the population Selection changes the mean, usually lowers variation Selection will adjust mean ...
... Norm Most traits are polygenic The normal trait is the average or mean in the population Selection changes the mean, usually lowers variation Selection will adjust mean ...
11 - Group Selection
... We think that the only way that adaptations can arise is through natural selection. The effects of such adaptation can be seen at many levels: gene frequencies, frequencies of types of organisms, even populations. ...
... We think that the only way that adaptations can arise is through natural selection. The effects of such adaptation can be seen at many levels: gene frequencies, frequencies of types of organisms, even populations. ...
1 Sequence evolution of the disease resistance genes Rcr3 and
... Lycopersicon peruvianum. Both genes are involved in different disease resistance pathways. Knowledge of evolutionary mechanisms shaping these two genes will contribute to the understanding of the evolution of disease resistance pathways in plants. To reveal the evolutionary history of Rcr3 and Rin4 ...
... Lycopersicon peruvianum. Both genes are involved in different disease resistance pathways. Knowledge of evolutionary mechanisms shaping these two genes will contribute to the understanding of the evolution of disease resistance pathways in plants. To reveal the evolutionary history of Rcr3 and Rin4 ...
Speciation - Deans Community High School
... Use p131-132 Torrance ‘New Higher Biology’ to give examples of each of the above isolating mechanisms. (barriers to reproduction). Ensure you understand and remember the steps which lead to speciation (Fig 18.1) and realise that separate species result when natural selection affects each subgroup in ...
... Use p131-132 Torrance ‘New Higher Biology’ to give examples of each of the above isolating mechanisms. (barriers to reproduction). Ensure you understand and remember the steps which lead to speciation (Fig 18.1) and realise that separate species result when natural selection affects each subgroup in ...