File
... This concept can be used to calculate the frequency of different genotypes and to measure how fast allele frequencies are changing within a population (how fast the population is evolving). ...
... This concept can be used to calculate the frequency of different genotypes and to measure how fast allele frequencies are changing within a population (how fast the population is evolving). ...
File
... 1. Allele frequency – the percentage of an allele within a gene pool 2. Allopatric speciation – occurs when a populations becomes geographically or physically isolated from each other, preventing the two sub-populations from interbreeding and exchanging genetic material. 3. Assortative mating – the ...
... 1. Allele frequency – the percentage of an allele within a gene pool 2. Allopatric speciation – occurs when a populations becomes geographically or physically isolated from each other, preventing the two sub-populations from interbreeding and exchanging genetic material. 3. Assortative mating – the ...
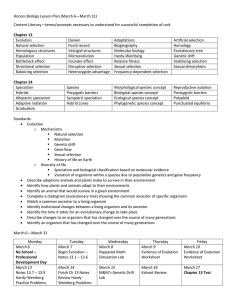
Honors Biology Lesson Plan (March 6—March 31) Content Literacy
... Gene flow Sexual selection History of life on Earth o Diversity of life Speciation and biological classification based on molecular evidence Variation of organisms within a species due to population genetics and gene frequency Describe adaptions animals and plants make to survive in thei ...
... Gene flow Sexual selection History of life on Earth o Diversity of life Speciation and biological classification based on molecular evidence Variation of organisms within a species due to population genetics and gene frequency Describe adaptions animals and plants make to survive in thei ...
Nucleo de Sequence Manipula on IMBB Workshop 20, May 2015
... ü DNA is a double stranded having a forward and reverse strand. ü Typically a sequence is read from direc1on 5’ – 3’ for the forward strand that means leK to right as the reverse right to ...
... ü DNA is a double stranded having a forward and reverse strand. ü Typically a sequence is read from direc1on 5’ – 3’ for the forward strand that means leK to right as the reverse right to ...
Gene selection: choice of parameters of the GA/KNN method
... Evolvability by introducing new genes Which chromosome? By a probability proportional to its fitness rank How many genes? Among 1 ~ 5, the number of mutations is assigned randomly with prob. 0.53125, 0.25 0.125, 0.0625, and 0.03125 ...
... Evolvability by introducing new genes Which chromosome? By a probability proportional to its fitness rank How many genes? Among 1 ~ 5, the number of mutations is assigned randomly with prob. 0.53125, 0.25 0.125, 0.0625, and 0.03125 ...
AIMS Vocabulary Review
... - two types of cell division chromosome - made of DNA; contains genes ...
... - two types of cell division chromosome - made of DNA; contains genes ...
Artificial Selection
... means that life changed ‘by chance.’ ” Chance is certainly a factor in evolution, but there are also non-random evolutionary mechanisms. Random mutation is the ultimate source of genetic variation, however natural selection, the process by which some variants survive and others do not, is not random ...
... means that life changed ‘by chance.’ ” Chance is certainly a factor in evolution, but there are also non-random evolutionary mechanisms. Random mutation is the ultimate source of genetic variation, however natural selection, the process by which some variants survive and others do not, is not random ...
Microevolution notes
... Microevolution: evolution on the smallest scale – generation to generation change in the frequencies of alleles in a population Gene Pool: consists of all the genes that are present in a population Relative Frequency: The number of times an allele occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of ti ...
... Microevolution: evolution on the smallest scale – generation to generation change in the frequencies of alleles in a population Gene Pool: consists of all the genes that are present in a population Relative Frequency: The number of times an allele occurs in a gene pool compared with the number of ti ...
Evolution Review Sheet
... 30. What was Lamarck’s theory of how things changed over time? ____________________________________________________________________ 31. What gas was not present before life began? ____________________ 32. What protects us from harmful UV light (other than sunscreen)? _________________ 33. Mutations, ...
... 30. What was Lamarck’s theory of how things changed over time? ____________________________________________________________________ 31. What gas was not present before life began? ____________________ 32. What protects us from harmful UV light (other than sunscreen)? _________________ 33. Mutations, ...
Reading: Charles Darwin and the Process of Natural Selection
... Methods of Evolution Evolution can create new species (speciation), and it can ...
... Methods of Evolution Evolution can create new species (speciation), and it can ...
Document
... • An operator is a part of DNA that turns a gene “on” or ”off.” • An operon includes a promoter, an operator, and one or more structural genes that code for all the proteins needed to do a job. – Operons are most common in prokaryotes. – The lac operon was one of the first examples of gene regulatio ...
... • An operator is a part of DNA that turns a gene “on” or ”off.” • An operon includes a promoter, an operator, and one or more structural genes that code for all the proteins needed to do a job. – Operons are most common in prokaryotes. – The lac operon was one of the first examples of gene regulatio ...
8.6 Gene Expression and Regulation
... • An operator is a part of DNA that turns a gene “on” or ”off.” • An operon includes a promoter, an operator, and one or more structural genes that code for all the proteins needed to do a job. – Operons are most common in prokaryotes. – The lac operon was one of the first examples of gene regulatio ...
... • An operator is a part of DNA that turns a gene “on” or ”off.” • An operon includes a promoter, an operator, and one or more structural genes that code for all the proteins needed to do a job. – Operons are most common in prokaryotes. – The lac operon was one of the first examples of gene regulatio ...
8.6 Gene Expression and Regulation KEY CONCEPT prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
... • An operator is a part of DNA that turns a gene “on” or ”off.” • An operon includes a promoter, an operator, and one or more structural genes that code for all the proteins needed to do a job. – Operons are most common in prokaryotes. – The lac operon was one of the first examples of gene regulatio ...
... • An operator is a part of DNA that turns a gene “on” or ”off.” • An operon includes a promoter, an operator, and one or more structural genes that code for all the proteins needed to do a job. – Operons are most common in prokaryotes. – The lac operon was one of the first examples of gene regulatio ...
Ch01
... the observational evidence from field research. • Evolution is gradual: small genetic changes regulated by natural selection accumulate over long periods and many genes can “drift” through a population at a given time. Discontinuities amongst species (or other taxa) are explained as originating grad ...
... the observational evidence from field research. • Evolution is gradual: small genetic changes regulated by natural selection accumulate over long periods and many genes can “drift” through a population at a given time. Discontinuities amongst species (or other taxa) are explained as originating grad ...
15.3 Evolution by Natural Selection
... increases an organism’s chance for survival. The possibilities are limitless! Just look at an organism and see how it works well in its habitat. Ex of adaptations: o _______________- blending in with one’s surroundings to increase chances of survival o ________________ looking like another organis ...
... increases an organism’s chance for survival. The possibilities are limitless! Just look at an organism and see how it works well in its habitat. Ex of adaptations: o _______________- blending in with one’s surroundings to increase chances of survival o ________________ looking like another organis ...
Evolution by Natural Selection
... - Process by which organisms with variations best suited for environment will survive and leave more offspring - environment influences fitness - Process does not make organisms “better” and does not act in a fixed direction ...
... - Process by which organisms with variations best suited for environment will survive and leave more offspring - environment influences fitness - Process does not make organisms “better” and does not act in a fixed direction ...
Mechanisms of Evolution
... chances of survival. These variations can be inherited. So, frequency of alleles changes over generations due to natural selection. Adaptation: over time, those traits that improve survival and reproduction become more common. ...
... chances of survival. These variations can be inherited. So, frequency of alleles changes over generations due to natural selection. Adaptation: over time, those traits that improve survival and reproduction become more common. ...
Exam 1 Key
... by the environmental event then the resulting group could become two separate populations or a diversifying effect. Most environmental events tend towards pushing the whole population in one direction or another in the expression of a trait and leading to a directional affect. 21. (2) Cite and descr ...
... by the environmental event then the resulting group could become two separate populations or a diversifying effect. Most environmental events tend towards pushing the whole population in one direction or another in the expression of a trait and leading to a directional affect. 21. (2) Cite and descr ...
eandb-essay-1 15 kb eandb-essay
... Natural selection is now combined with modern synthesis which allows an even greater understanding of the process. Genes from the parent are replicated and pass on intact to offspring, allowing a stable process of heredity. Each individual gene will occur in several different forms called alleles an ...
... Natural selection is now combined with modern synthesis which allows an even greater understanding of the process. Genes from the parent are replicated and pass on intact to offspring, allowing a stable process of heredity. Each individual gene will occur in several different forms called alleles an ...
STIM1 monoclonal antibody (M01), clone 5A2
... several genes located in the imprinted gene domain of 11p15.5, an important tumor-suppressor gene region. Alterations in this region have been associated with the Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, Wilms tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, adrenocrotical carcinoma, and lung, ovarian, and breast cancer. This gene may ...
... several genes located in the imprinted gene domain of 11p15.5, an important tumor-suppressor gene region. Alterations in this region have been associated with the Beckwith-Wiedemann syndrome, Wilms tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, adrenocrotical carcinoma, and lung, ovarian, and breast cancer. This gene may ...
Natural Selection
... Natural Selection (Darwin’s Mechanism) Natural Selection – the process by which organisms that are better suited to an environment survive and reproduce in greater number than those less suited. ...
... Natural Selection (Darwin’s Mechanism) Natural Selection – the process by which organisms that are better suited to an environment survive and reproduce in greater number than those less suited. ...