Document
... What is Chemical Weathering? Minerals and rocks at earth’s surface weakens and breaks down from exposure to water and gases in the atmosphere & changes the mineral Composition What is the strongest acid type of acid rain? ...
... What is Chemical Weathering? Minerals and rocks at earth’s surface weakens and breaks down from exposure to water and gases in the atmosphere & changes the mineral Composition What is the strongest acid type of acid rain? ...
Restless Earth - IES Breckland
... and broken down before they form rich soils. When they do become soils though, they form some of the richest ones on the planet. Poverty – Some people in LEDC’s are not able to move away from a potentially dangerous volcano as they are too poor. Religious beliefs – e.g. the Aetas who live around ...
... and broken down before they form rich soils. When they do become soils though, they form some of the richest ones on the planet. Poverty – Some people in LEDC’s are not able to move away from a potentially dangerous volcano as they are too poor. Religious beliefs – e.g. the Aetas who live around ...
Geog 101: Chapter 3 Quiz
... 3. Where are earthquakes most likely to occur? 4. What is the place where the earth’s crust actually moves in an earthquake called? 5. What factors influence the amount of ground shaking caused by earthquakes? 6. What is the nature and behavior of magma? 7. In what kind of plate boundary is material ...
... 3. Where are earthquakes most likely to occur? 4. What is the place where the earth’s crust actually moves in an earthquake called? 5. What factors influence the amount of ground shaking caused by earthquakes? 6. What is the nature and behavior of magma? 7. In what kind of plate boundary is material ...
Molten rock that comes to the surface of the earth is called:
... d. determine the mineral’s chemical reactivity 30. What property of a rock determines if it will float or sink? a. Its mass b. Its volume c. Its color d. Its density 31. Which of these is most likely formed when a continental and oceanic plate collide? a. An alpine glacier b. A rain shadow desert c. ...
... d. determine the mineral’s chemical reactivity 30. What property of a rock determines if it will float or sink? a. Its mass b. Its volume c. Its color d. Its density 31. Which of these is most likely formed when a continental and oceanic plate collide? a. An alpine glacier b. A rain shadow desert c. ...
Plate Tectonics
... basins. Gas and dust from large volcanoes can change the atmosphere. The solid crust of the earth—including both the continents and the ocean basins— consists of separate plates that ride on a denser, hot, gradually deformable layer of the earth. The crust sections move very slowly, pressing against ...
... basins. Gas and dust from large volcanoes can change the atmosphere. The solid crust of the earth—including both the continents and the ocean basins— consists of separate plates that ride on a denser, hot, gradually deformable layer of the earth. The crust sections move very slowly, pressing against ...
A View of Earth - Cloudfront.net
... spheres: the hydrosphere, atmosphere, geosphere, and biosphere Hydrosphere – the water portion of Earth Atmosphere – the gaseous portion of a planet; the planet’s envelope of air Geosphere – layer of Earth under both the atmosphere and the oceans Because the geosphere is not uniform, it is divided i ...
... spheres: the hydrosphere, atmosphere, geosphere, and biosphere Hydrosphere – the water portion of Earth Atmosphere – the gaseous portion of a planet; the planet’s envelope of air Geosphere – layer of Earth under both the atmosphere and the oceans Because the geosphere is not uniform, it is divided i ...
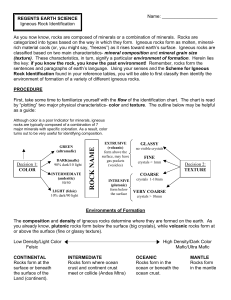
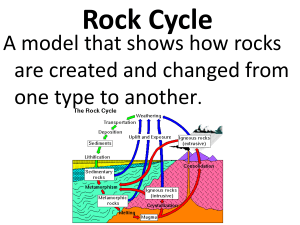
Rock Cycle
... Rocks that form when existing rocks are heated and squeezed deep inside the Earth. ...
... Rocks that form when existing rocks are heated and squeezed deep inside the Earth. ...
Earth Science Chapter 6: Volcanoes Lecture Notes
... subduction takes place. Along the rift valley, lava pours out of cracks in the ocean floor, gradually building new mountains. Many volcanoes form near colliding plate boundaries where oceanic plates return to the mantle. Volcanoes may form where two oceanic plates collide or where an oceanic plate c ...
... subduction takes place. Along the rift valley, lava pours out of cracks in the ocean floor, gradually building new mountains. Many volcanoes form near colliding plate boundaries where oceanic plates return to the mantle. Volcanoes may form where two oceanic plates collide or where an oceanic plate c ...
Pixelgost`s Dynamic Planet test
... 1. What are the layer of the earth labeled physically? 2. What are the layers of the earth layered chemically? 3. What is the name of the Most recent supercontinent? 4. What are the names of the two Supercontinents that broke apart to form today’s Earth? 5. What was the name of the ocean that surrou ...
... 1. What are the layer of the earth labeled physically? 2. What are the layers of the earth layered chemically? 3. What is the name of the Most recent supercontinent? 4. What are the names of the two Supercontinents that broke apart to form today’s Earth? 5. What was the name of the ocean that surrou ...
Chapters 4 and 5
... magmas which originate in the upper mantle, so the blocks of country rock tend to increase the silica content of the magma in a manner similar to crystal fractionation. ►One of the important ideas from Ch. 4 is that intrusive rocks (plutonic rocks) do not erupt! “Igneous” is not the same as “volcan ...
... magmas which originate in the upper mantle, so the blocks of country rock tend to increase the silica content of the magma in a manner similar to crystal fractionation. ►One of the important ideas from Ch. 4 is that intrusive rocks (plutonic rocks) do not erupt! “Igneous” is not the same as “volcan ...
Name: Introduction to Meteorology Homework #1 (Chapters 1 and 2
... 22. What are the three important rules regarding radiation? ...
... 22. What are the three important rules regarding radiation? ...
Rocky The Rock Cycle
... through a crack or fault in the rock at the Earth's surface. It pours out over the Earth's surface in a volcanic eruption. This process is called extrusion. ...
... through a crack or fault in the rock at the Earth's surface. It pours out over the Earth's surface in a volcanic eruption. This process is called extrusion. ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.