* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Igneous Rock PPT notes
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Great Lakes tectonic zone wikipedia , lookup
Sedimentary rock wikipedia , lookup
Geology of Great Britain wikipedia , lookup
Mackenzie Large Igneous Province wikipedia , lookup
Algoman orogeny wikipedia , lookup
Clastic rock wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
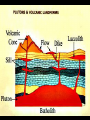
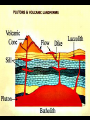
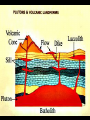
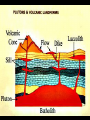
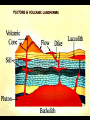
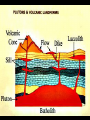
IGNEOUS ROCKS I. Igneous rocks are formed from molten material. - The term igneous is derived from Latin term meaning “from FIRE”!! ENVIRONMENT A. Extrusive igneous rocks are formed when molten rock cools above ground. Usually they are formed after the material has been erupted by a volcano. 1. This molten material cools quickly. 2. No crystals are visible to the eye. B. Intrusive igneous rocks are formed when molten rock cools below ground. 1. These rocks cool very slowly. 2. There is lots of time for visible crystals to grow EXTRUSIVE Cools quickly Cools above ground No visible crystals INTRUSIVE Cools slowly Cools below ground Visible crystals TEXTURE • Coarse: – INTRUSIVE igneous rock composed of large mineral grains. • GRANITE TEXTURE • Fine: – EXTRUSIVE igneous rock composed of fine-grained minerals. • BASALT TEXTURE • Glassy: – HIGHLY VISCOUS, silica-rich magma cools rapidly, no crystals. • OBSIDIAN TEXTURE • Vesicular: – HIGHLY VISCOUS, large amount of dissolved gases, rock full of holes. • PUMICE COMPOSITION • Mafic: – Low silica – Rich in Iron and Magnesium • DARK COLOR. • BASALT COMPOSITION • Felsic: – High silica • LIGHT COLOR. • RHYOLITE Igneous Rock Structures • Intrusions vs. Extrusions: - Form Underground - Form on the surface of the Earth INTRUSIONS • Batholiths: – At least 100 km2 of surface exposure. • Means “Deep Rock” • Sierra Nevada Mountains Exposed Batholiths INTRUSIONS • Laccoliths: – Flat-bottom intrusion that pushes overlying rock layers into an arc. • Means “Lake of Rock” • Black Hills –South Dakota • Stocks: INTRUSIONS – Like a Batholith, but covers less than 100 km2. • Devils Tower –Wyoming • Dikes: INTRUSIONS – Igneous intrusion that cuts across rock layers. • Black Canyon –Colorado • Sills: INTRUSIONS – Hardened magma formed between parallel layers of rock. • Salisbary Crags –Scotland EXTRUSIONS • Volcanic Necks: – Solidified central neck of a volcano. • Shiprock –New Mexico