landforms
... A supercontinent containing all of Earth’s land existing about 225 million years ago. ...
... A supercontinent containing all of Earth’s land existing about 225 million years ago. ...
Earth Science Name Web Inquiry—Plate Tectonics/Earth`s Interior
... d. Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the earth. e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. f. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposition, volcanic eruption, gravity) on geo ...
... d. Describe processes that change rocks and the surface of the earth. e. Recognize that lithospheric plates constantly move and cause major geological events on the earth’s surface. f. Explain the effects of physical processes (plate tectonics, erosion, deposition, volcanic eruption, gravity) on geo ...
Earth`s Composition Tectonic Plates Virginia Geology Rock Cycle
... - earthquake activity is associated with all plate boundaries; result when movement occurs along a fault; 3 seismograph stations needed to locate the epicenter of an earthquake ⋅ faults are breaks or cracks in the crust along which movement has occurred - most active faults are located at or near pl ...
... - earthquake activity is associated with all plate boundaries; result when movement occurs along a fault; 3 seismograph stations needed to locate the epicenter of an earthquake ⋅ faults are breaks or cracks in the crust along which movement has occurred - most active faults are located at or near pl ...
Chapter 04 Plate Tectonics
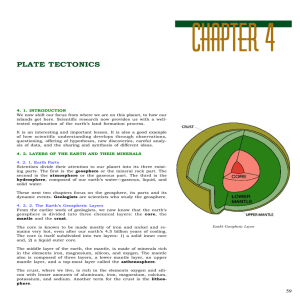
... The Earth’s outer layer is called the lithosphere. It is made of the rigid upper mantle and the crust. The lithosphere moves on the asthenosphere, part of the mantle that flows. ...
... The Earth’s outer layer is called the lithosphere. It is made of the rigid upper mantle and the crust. The lithosphere moves on the asthenosphere, part of the mantle that flows. ...
Blizzard Bag 1
... Magma rises from the subduction zone and builds submarine volcanoes that, over time, grow above sea level. This process can result in an arc-shaped island chain. The Aleutian chain and the Indonesian chain are examples of island arcs. ...
... Magma rises from the subduction zone and builds submarine volcanoes that, over time, grow above sea level. This process can result in an arc-shaped island chain. The Aleutian chain and the Indonesian chain are examples of island arcs. ...
how to collect meteorological data italy
... Rain is the most common type of atmospheric precipitation and it happens when separate drops of water fall from the clouds to the ground. The rain plays a very important role in the water cycle. Water evaporates from the oceans, condenses in the clouds and falls to the ground, then it returns to t ...
... Rain is the most common type of atmospheric precipitation and it happens when separate drops of water fall from the clouds to the ground. The rain plays a very important role in the water cycle. Water evaporates from the oceans, condenses in the clouds and falls to the ground, then it returns to t ...
Volcanoes - British Geological Survey
... The surface of the Earth is made up of rigid plates that move, at a rate of a few centimetres per year. When they collide, one plate can be pushed beneath another. As it sinks it heats up and begins to melt. This molten rock then rises and erupts on the surface as lava, building up a volcano. Volcan ...
... The surface of the Earth is made up of rigid plates that move, at a rate of a few centimetres per year. When they collide, one plate can be pushed beneath another. As it sinks it heats up and begins to melt. This molten rock then rises and erupts on the surface as lava, building up a volcano. Volcan ...
Earth`s Systems Study Guide 1. Name the four parts of Earth`s
... 28.____________________ is a measure of the amount of dissolved salts in a given amount of liquid. 29 Name the three temperature zones of the ocean. ...
... 28.____________________ is a measure of the amount of dissolved salts in a given amount of liquid. 29 Name the three temperature zones of the ocean. ...
KCSE ONLINE GEOGRAPHY PP1 MARKING SCHEME SECTION A
... (ii) Semi diurnal tide occur when both high tides rise to the same level and low tides drop to the same level. Mixed tides occurs in pairs with two high tides and two low tides but one pair may fluctuate in level while the other remain constant. ...
... (ii) Semi diurnal tide occur when both high tides rise to the same level and low tides drop to the same level. Mixed tides occurs in pairs with two high tides and two low tides but one pair may fluctuate in level while the other remain constant. ...
Earthquakes and volcanoes theory - racce
... or move apart (Β) each other. Also, occur in plates interior at the areas called hot spots. ...
... or move apart (Β) each other. Also, occur in plates interior at the areas called hot spots. ...
Topic 6 Notes- Volcanoes - École St. Joseph School
... A volcano is an opening in the Earth’s crust that releases lava, steam and ash when it erupts. These openings are called vents. When volcanoes are not active (they do not erupt) they are called dormant. Like earthquakes, volcanoes can be formed when rock surfaces beneath the earth’s crust push again ...
... A volcano is an opening in the Earth’s crust that releases lava, steam and ash when it erupts. These openings are called vents. When volcanoes are not active (they do not erupt) they are called dormant. Like earthquakes, volcanoes can be formed when rock surfaces beneath the earth’s crust push again ...
10 Things to Know About Plate Tectonics
... 2. Movement occurs because of convection currents in the asthenosphere, which move the lithosphere on top. Mantle heats up as it approaches the core, so it rises to the top, where it cools and cycles back down toward the core, and so on and so forth. 3. Divergent plate boundaries – two plates moving ...
... 2. Movement occurs because of convection currents in the asthenosphere, which move the lithosphere on top. Mantle heats up as it approaches the core, so it rises to the top, where it cools and cycles back down toward the core, and so on and so forth. 3. Divergent plate boundaries – two plates moving ...
The Atmosphere: Climate and Weather
... • Basic understanding of main processes: energy flow, air movement, water cycle, air pressure • Present some of the terminology ...
... • Basic understanding of main processes: energy flow, air movement, water cycle, air pressure • Present some of the terminology ...
Igneous Rocks Guide - Sedgwick Museum of Earth Sciences
... Basalt is the name of the rock which forms when a basic magma cools and solidifies. It is rich in iron. It is the equivalent composition to oceanic crust found around mid-ocean ridges. Olivine is a green iron-rich mineral commonly found in basalt. It weathers to a rusty red colour. Olivine has the e ...
... Basalt is the name of the rock which forms when a basic magma cools and solidifies. It is rich in iron. It is the equivalent composition to oceanic crust found around mid-ocean ridges. Olivine is a green iron-rich mineral commonly found in basalt. It weathers to a rusty red colour. Olivine has the e ...
Part A The Rock Cycle
... 27. In partial melting of rocks in the upper mantle, the first minerals to melt will be the constituents of granite; that is, they will be richer in SILICA / QUARTZ. 28. ASSIMILATION of continental crust is an alternative source for the granitic magmas of batholiths. 29. Increasing the amount of pre ...
... 27. In partial melting of rocks in the upper mantle, the first minerals to melt will be the constituents of granite; that is, they will be richer in SILICA / QUARTZ. 28. ASSIMILATION of continental crust is an alternative source for the granitic magmas of batholiths. 29. Increasing the amount of pre ...
Earth`s Life-Support Systems pp
... the layer of Earth called the mantle which is made of liquid rock called magma. As the crust moves, rocks are melted and changed in to metamorphic rocks by heat and pressure. Those metamorphic rocks melt into magma which might eventually ooze on to a volcano and cool into an igneous rock! Later on, ...
... the layer of Earth called the mantle which is made of liquid rock called magma. As the crust moves, rocks are melted and changed in to metamorphic rocks by heat and pressure. Those metamorphic rocks melt into magma which might eventually ooze on to a volcano and cool into an igneous rock! Later on, ...
Chapter 3 - Igneous Rocks
... Silica rich (felsic) magma/lavas are thick, viscous and resist flow Silica poor (mafic) magma/lavas are thinner, have a lower viscosity and don’t ...
... Silica rich (felsic) magma/lavas are thick, viscous and resist flow Silica poor (mafic) magma/lavas are thinner, have a lower viscosity and don’t ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.