Sycamore Canyon Geology
... About another mile down the canyon there is a drastic narrowing and the floor of the canyon and the walls are swept clean of all debris by the fast flowing water. You will see areas of well-bedded steeply dipping formations containing pebbles in some places. There are tuffaceous sediments and the fi ...
... About another mile down the canyon there is a drastic narrowing and the floor of the canyon and the walls are swept clean of all debris by the fast flowing water. You will see areas of well-bedded steeply dipping formations containing pebbles in some places. There are tuffaceous sediments and the fi ...
power point - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
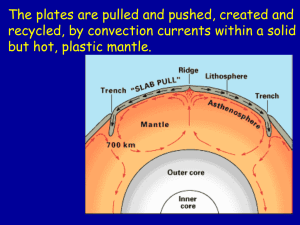
... Core - solid and very hot, great pressure ► Outer Core – liquid and hot ► Mantle – melted rock called magma – hot, dense, slow moving ► Crust – solid rock of the surface ...
... Core - solid and very hot, great pressure ► Outer Core – liquid and hot ► Mantle – melted rock called magma – hot, dense, slow moving ► Crust – solid rock of the surface ...
Document
... • An ocean plate and a continental plate hit head-on. The ocean plate subducts under the continent forming a trench. The subducting plate melts. Magma rises to the surface creating a string of volcanic mountains parallel to the shoreline. ...
... • An ocean plate and a continental plate hit head-on. The ocean plate subducts under the continent forming a trench. The subducting plate melts. Magma rises to the surface creating a string of volcanic mountains parallel to the shoreline. ...
Chapter 2 - Minerals and Rocks Extra Credit
... 1. The way a mineral reflects light from its surface. 2. A scale ranking ten minerals from softest to hardest’ used in testing the hardness of minerals. 3. The way a mineral looks when it breaks apart in an irregular way. 4. A type of rock that forms from an existing rock that is changed by heat, pr ...
... 1. The way a mineral reflects light from its surface. 2. A scale ranking ten minerals from softest to hardest’ used in testing the hardness of minerals. 3. The way a mineral looks when it breaks apart in an irregular way. 4. A type of rock that forms from an existing rock that is changed by heat, pr ...
Rocks
... • Magma—molten material that forms inside the Earth – It crystallizes either beneath the surface or as a result of volcanic activity to make ...
... • Magma—molten material that forms inside the Earth – It crystallizes either beneath the surface or as a result of volcanic activity to make ...
Dynamic Planet Review
... • The ocean floor is subducting into the mantle. • We are losing Pacific ocean floor. ...
... • The ocean floor is subducting into the mantle. • We are losing Pacific ocean floor. ...
4 Lithosphere Research
... bar. There you will find several links on Earth’s layers, use these links to fill out the worksheet. 1. Please indicate the following information on the Earth’s layers. Layer Thickness Composition (what it’s made of) Crust Mantel Outer Core Inner Core ...
... bar. There you will find several links on Earth’s layers, use these links to fill out the worksheet. 1. Please indicate the following information on the Earth’s layers. Layer Thickness Composition (what it’s made of) Crust Mantel Outer Core Inner Core ...
Distribution of volcanoes
... Away from plate boundary, a plate moving over fixed ‘hot spots’ Which are localised heat sources in the mantle to produce groups of volcanoes e.g. the Hawaiian Islands ...
... Away from plate boundary, a plate moving over fixed ‘hot spots’ Which are localised heat sources in the mantle to produce groups of volcanoes e.g. the Hawaiian Islands ...
Coal: A Climate Crisis
... leaving is the same as what came in. Radiation occurs when the energy is changed before it leaves. In this case, the energy is changed from short wave UV rays to long wave infrared rays. ...
... leaving is the same as what came in. Radiation occurs when the energy is changed before it leaves. In this case, the energy is changed from short wave UV rays to long wave infrared rays. ...
Some volcanic eruptions are quiet. The lava oozes down the side of
... The Kilauea Iki eruption began on the morning of November 14, 1959, three months after a rapid increase in inflation of the ground surface and the number and size of earthquakes. The eruption started halfway up the 600-650 foo (180-200 m) south wall of the crater as a curtain of fire a half-a-mile ...
... The Kilauea Iki eruption began on the morning of November 14, 1959, three months after a rapid increase in inflation of the ground surface and the number and size of earthquakes. The eruption started halfway up the 600-650 foo (180-200 m) south wall of the crater as a curtain of fire a half-a-mile ...
Weathering, Soil, and Erosion Study Guide
... a. Rock is lifted up and the rocks above it are worn away. The rocks form sheets and break off (exfoliation). 2. Define erosion and give an example of how this occurs. a. The removal and transport of materials by natural agents such as wind and running water. b. Ex: A river carries silt to the ocean ...
... a. Rock is lifted up and the rocks above it are worn away. The rocks form sheets and break off (exfoliation). 2. Define erosion and give an example of how this occurs. a. The removal and transport of materials by natural agents such as wind and running water. b. Ex: A river carries silt to the ocean ...
Practice Test-1 - Florida International University
... 7. Which layer of our earth is rich in aluminum, silcon and oxygen? A) Asthenosphere B) Mantle C) Outer core D) continental crust 8. The East African Rift Valley represent what kind of plate boundary? A) Transform B) Divergent C) Convergent D) none of the above 9. Which of the following events is no ...
... 7. Which layer of our earth is rich in aluminum, silcon and oxygen? A) Asthenosphere B) Mantle C) Outer core D) continental crust 8. The East African Rift Valley represent what kind of plate boundary? A) Transform B) Divergent C) Convergent D) none of the above 9. Which of the following events is no ...
Constructive and Destructive Forces on Earth vocb
... Forces on Earth 1. Uniformitarianism- the theory that changes in the earth's crust during geological history have resulted from the action of continuous and uniform processes (Erosion and Deposition) 2. Earth Processes dynamic actions that occur on and below the Earth's surface 3. Geology the study ...
... Forces on Earth 1. Uniformitarianism- the theory that changes in the earth's crust during geological history have resulted from the action of continuous and uniform processes (Erosion and Deposition) 2. Earth Processes dynamic actions that occur on and below the Earth's surface 3. Geology the study ...
Famous Volcanoes Pw Pt
... estimated 2800 cubit kilometers of ash was thrown into the atmosphere. For comparison, Mt. St Helens in Washington State only spewed 1 cubit kilometer of ash. ...
... estimated 2800 cubit kilometers of ash was thrown into the atmosphere. For comparison, Mt. St Helens in Washington State only spewed 1 cubit kilometer of ash. ...
ErikaandCandiceVolPr..
... written observation made by Pliny the Younger. These accounts were being written to the roman historian Tactitus. He wrote this account to record the events concerning the events surrounding the death of his father, Pliny the Elder. ...
... written observation made by Pliny the Younger. These accounts were being written to the roman historian Tactitus. He wrote this account to record the events concerning the events surrounding the death of his father, Pliny the Elder. ...
GCPS_05_SC_ES_T5 (_GCPS_05_SC_ES_T5)
... C. bays and peninsulas D. plateaus and mesas 2. The time it takes for a mountain range to form is A. less than 10 years. B. between 10 and 50 years. C. between 50 and 100 years. D. more than 100 years. 3. Stone Mountain in Georgia is a granite dome that formed deep underground. Over time, uplift and ...
... C. bays and peninsulas D. plateaus and mesas 2. The time it takes for a mountain range to form is A. less than 10 years. B. between 10 and 50 years. C. between 50 and 100 years. D. more than 100 years. 3. Stone Mountain in Georgia is a granite dome that formed deep underground. Over time, uplift and ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.