Unit 2 Meteorology Test
... B Winds die down. C Cloud formation decreases. D Stormy weather patterns develop. 27. Snow on the ground prevents polar climates from gaining heat by what mechanism? A heating by greenhouse gases B heat spread from the equator C reflection of solar radiation D release of heat from Earth’s core 28. W ...
... B Winds die down. C Cloud formation decreases. D Stormy weather patterns develop. 27. Snow on the ground prevents polar climates from gaining heat by what mechanism? A heating by greenhouse gases B heat spread from the equator C reflection of solar radiation D release of heat from Earth’s core 28. W ...
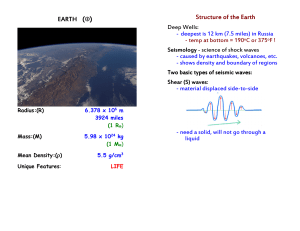
Earth's interior layers.
... Collision between two oceanic plates can result in the prosses when one plate bends and descends beneath the other to produce deep oceanic trench. (Marianas Trench) • Oceanic – Continental Convergence When an oceanic plate and a continental plate converge, the denser oceanic plate is subducted benea ...
... Collision between two oceanic plates can result in the prosses when one plate bends and descends beneath the other to produce deep oceanic trench. (Marianas Trench) • Oceanic – Continental Convergence When an oceanic plate and a continental plate converge, the denser oceanic plate is subducted benea ...
Weathering and Erosion
... • Lichens that grow on rocks produce weak acids that chemically weather rock ...
... • Lichens that grow on rocks produce weak acids that chemically weather rock ...
Aim: How do we put all four atmospheric variables on a weather map?
... B) Stratosphere. C) Thermosphere. D) Troposphere. 4. What frequencies of electromagnetic ...
... B) Stratosphere. C) Thermosphere. D) Troposphere. 4. What frequencies of electromagnetic ...
Chapter 4 Rocks: Mixtures of Minerals
... • Igneous – Formed when magma cools and solidifies. The type of texture is determined by the composition of the magma and the time it took to cool. Magma contains many different types of minerals in it that will solidify at different rates. Magma forms if either the pressure or temperature increases ...
... • Igneous – Formed when magma cools and solidifies. The type of texture is determined by the composition of the magma and the time it took to cool. Magma contains many different types of minerals in it that will solidify at different rates. Magma forms if either the pressure or temperature increases ...
2. The youngest rocks on the ocean floor are typically located near
... A mountain building at a continent-continent convergent boundary B magma rising up from the mantle at a divergent boundary C two tectonic plates sliding past one another at a transform boundary D subduction of one oceanic plate under another at a convergent boundary ...
... A mountain building at a continent-continent convergent boundary B magma rising up from the mantle at a divergent boundary C two tectonic plates sliding past one another at a transform boundary D subduction of one oceanic plate under another at a convergent boundary ...
Metamorphic Rocks - Classroom Unsquared
... CLASSROOM UNSQUARED EARTH MATERIALS EQ:What are metamorphic rocks? A rock that has changed its mineral assemblage and texture from a preexiting one due to increases in temperature and pressure . ...
... CLASSROOM UNSQUARED EARTH MATERIALS EQ:What are metamorphic rocks? A rock that has changed its mineral assemblage and texture from a preexiting one due to increases in temperature and pressure . ...
metIstudyguide_S16
... 9. Air that has reached its water vapor capacity is _____________________. 10. Which can hold more water vapor… Warm air or cold air? 11. What is dew point? 12. Walking across hot pavement, warming your feet, is what form of heat transfer? 13. Hand receiving energy from a fire is heat transfer throu ...
... 9. Air that has reached its water vapor capacity is _____________________. 10. Which can hold more water vapor… Warm air or cold air? 11. What is dew point? 12. Walking across hot pavement, warming your feet, is what form of heat transfer? 13. Hand receiving energy from a fire is heat transfer throu ...
types of rocks powerpoint
... Obsidian is a dark-colored volcanic glass that forms from the very rapid cooling of molten rock material. It cools so rapidly that crystals do not form. ...
... Obsidian is a dark-colored volcanic glass that forms from the very rapid cooling of molten rock material. It cools so rapidly that crystals do not form. ...
learning targets for
... Rock Cycle through any form that you wish. It can be a diorama, a project display board, a power point, or anything else that works for you. The display should be a teaching tool, easily to understand and a quality piece of work. ...
... Rock Cycle through any form that you wish. It can be a diorama, a project display board, a power point, or anything else that works for you. The display should be a teaching tool, easily to understand and a quality piece of work. ...
Rock cycle and Rocks made simple
... when it is beneath the surface of the earth and lava when it’s above the surface of the earth. Igneous rocks are classified into two groups. Igneous rocks that form above the surface are called extrusive igneous rocks. Igneous rocks that form below the earth’s surface are called intrusive igneous ro ...
... when it is beneath the surface of the earth and lava when it’s above the surface of the earth. Igneous rocks are classified into two groups. Igneous rocks that form above the surface are called extrusive igneous rocks. Igneous rocks that form below the earth’s surface are called intrusive igneous ro ...
Magmas and Igneous Rocks
... But, processes that operate during transportation toward the surface or during storage in the crust can alter the chemical composition of the magma. These processes are referred to as magmatic differentiation and include assimilation, mixing, and fractional crystallization. Assimilation - As magma p ...
... But, processes that operate during transportation toward the surface or during storage in the crust can alter the chemical composition of the magma. These processes are referred to as magmatic differentiation and include assimilation, mixing, and fractional crystallization. Assimilation - As magma p ...
GeomorphReview1 - University of Colorado Denver
... Igneous body touching & “cooking” surrounding area ...
... Igneous body touching & “cooking” surrounding area ...
Ch02Pres - UK Ag Weather Center
... – Gases and suspended particles – ½ of the mass is found in the lower 5500 m (18,000 ft) – 99% of the mass is below 32 km (20 miles) ...
... – Gases and suspended particles – ½ of the mass is found in the lower 5500 m (18,000 ft) – 99% of the mass is below 32 km (20 miles) ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.