Mgr. Petr Schnabl - Dissertation Paleomagnetism and
... between the Crassicolaria and Calpionella zones is present within geopolarity zone M19n. The boundary between the ammonite zones Jacobi and Durangites also lies close to this point. Paleomagnetic directions of Silurian and Devonian rocks in the Bohemian Massif are very difficult to interpret and hav ...
... between the Crassicolaria and Calpionella zones is present within geopolarity zone M19n. The boundary between the ammonite zones Jacobi and Durangites also lies close to this point. Paleomagnetic directions of Silurian and Devonian rocks in the Bohemian Massif are very difficult to interpret and hav ...
additional Powerpoint for these notes.
... deflected west • Things moving poleward are deflected east • Counterclockwise in Northern Hemisphere • Clockwise in Southern Hemisphere ...
... deflected west • Things moving poleward are deflected east • Counterclockwise in Northern Hemisphere • Clockwise in Southern Hemisphere ...
Ancient rocks yield clues about Earth`s earliest crust
... A sample of ancient rock from the Acasta Gneiss studying ancient rock samples from the Acasta Gneiss Complex in the Northwest Territories, part Complex in the Northwest Territories of his PhD research to understand the environment in which they formed. "The timing and mode of continental crust forma ...
... A sample of ancient rock from the Acasta Gneiss studying ancient rock samples from the Acasta Gneiss Complex in the Northwest Territories, part Complex in the Northwest Territories of his PhD research to understand the environment in which they formed. "The timing and mode of continental crust forma ...
Earth`s Atmosphere
... below the ground to thirty meters above it and in the top 200 meters of the oceans and seas. ...
... below the ground to thirty meters above it and in the top 200 meters of the oceans and seas. ...
Earth`s Atmosphere
... below the ground to thirty meters above it and in the top 200 meters of the oceans and seas. ...
... below the ground to thirty meters above it and in the top 200 meters of the oceans and seas. ...
Closer to Poles
... Influence of the earth’s rotation on movement of air and fluids Turns them Right in the Northern Hemisphere Turns them Left in the Southern Hemisphere ...
... Influence of the earth’s rotation on movement of air and fluids Turns them Right in the Northern Hemisphere Turns them Left in the Southern Hemisphere ...
CH 5 Earth`s Phys Enviro
... Def: periodic large scale warming of surface waters of tropical eastern Pacific Ocean ...
... Def: periodic large scale warming of surface waters of tropical eastern Pacific Ocean ...
AtmStructure
... But no significant heat because density low. Heated by ionization by UV from the sun, and the solar wind. ...
... But no significant heat because density low. Heated by ionization by UV from the sun, and the solar wind. ...
answerkeyPLATE TECTONICS STUDY GUIDE
... 16. WHAT ARE 3 THINGS THAT ARE FORMED AT A DIVERGENT BOUNDARY? Mid-ocean ridge, rift valley, new seafloor 17. WHAT CAN MINERALS IN ROCKS SHOW THAT PROVIDE EVIDENCE FOR PLATE TECTONICS? Change in magnetic field of Earth 18. DESCRIBE THE 3 DIFFERENT TYPES OF CONVERGENT BOUNDARIES a. ...
... 16. WHAT ARE 3 THINGS THAT ARE FORMED AT A DIVERGENT BOUNDARY? Mid-ocean ridge, rift valley, new seafloor 17. WHAT CAN MINERALS IN ROCKS SHOW THAT PROVIDE EVIDENCE FOR PLATE TECTONICS? Change in magnetic field of Earth 18. DESCRIBE THE 3 DIFFERENT TYPES OF CONVERGENT BOUNDARIES a. ...
Petrology Instructor Fundamentals Magmatic Rock Bodies Study of
... From Mineral Composition to Rock Composition • Determine the minerals present • Estimate their abundance • Calculate the rock composition using proper weightings ...
... From Mineral Composition to Rock Composition • Determine the minerals present • Estimate their abundance • Calculate the rock composition using proper weightings ...
Intro to the Atmosphere
... surface up to the bottom of the stratosphere. It has decreasing temperature with height (at an average rate of 3.5° F per thousand feet (6.5 ° C per kilometer); whereas the stratosphere has either constant or slowly increasing temperature with height. The troposphere is where all of Earth's weather ...
... surface up to the bottom of the stratosphere. It has decreasing temperature with height (at an average rate of 3.5° F per thousand feet (6.5 ° C per kilometer); whereas the stratosphere has either constant or slowly increasing temperature with height. The troposphere is where all of Earth's weather ...
Meteorology Part 1
... the temperature lower. How do clouds affect Earth’s temperature during the night? Why? Clouds insulate the air, keeping heat from escaping, keeping the temperature higher. ...
... the temperature lower. How do clouds affect Earth’s temperature during the night? Why? Clouds insulate the air, keeping heat from escaping, keeping the temperature higher. ...
UNIT 5_THE ATMOSPHERE
... How are the clouds formed?: In the areas heated by the Sun, the water evaporates and goes up to the troposphere. In the high part of the troposphere, the water vapour cools down. The cold vapor is condensed in small drops. Those drops form the clouds. There are three basic types of clouds: cirrus, c ...
... How are the clouds formed?: In the areas heated by the Sun, the water evaporates and goes up to the troposphere. In the high part of the troposphere, the water vapour cools down. The cold vapor is condensed in small drops. Those drops form the clouds. There are three basic types of clouds: cirrus, c ...
Powerpoint Presentation Physical Geology, 10/e
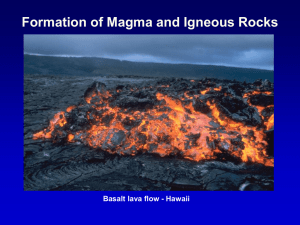
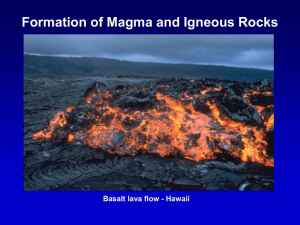
... Large variety of igneous rocks is produced by large variety of magma compositions Mafic magmas will crystallize into basalt or gabbro if early-formed minerals are not removed from the magma Intermediate magmas will similarly crystallize into diorite or andesite if minerals are not removed Separation ...
... Large variety of igneous rocks is produced by large variety of magma compositions Mafic magmas will crystallize into basalt or gabbro if early-formed minerals are not removed from the magma Intermediate magmas will similarly crystallize into diorite or andesite if minerals are not removed Separation ...
Weathering and Erosion
... • Lichens that grow on rocks produce weak acids that chemically weather rock ...
... • Lichens that grow on rocks produce weak acids that chemically weather rock ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.