1. What are the two most abundant permanent gasses, and roughly
... images are just as good at night? 24.Explain how an infrared satellite image can distinguish between regions covered by high cloud, low-lying cloud, and no cloud. 25.What does the "greenhouse effect" refer to? 26.Can you think of another planet beside Earth whose surface temperature is much more str ...
... images are just as good at night? 24.Explain how an infrared satellite image can distinguish between regions covered by high cloud, low-lying cloud, and no cloud. 25.What does the "greenhouse effect" refer to? 26.Can you think of another planet beside Earth whose surface temperature is much more str ...
Volcano Research Project
... Use at least 2 book(s) OR website(s) and include the SOURCES on your project. Include one PHOTO of the volcano and a MAP showing its location. Answers to all research questions below should be represented in the format of your choice. (bullets, paragraph, thought bubbles, etc.) ...
... Use at least 2 book(s) OR website(s) and include the SOURCES on your project. Include one PHOTO of the volcano and a MAP showing its location. Answers to all research questions below should be represented in the format of your choice. (bullets, paragraph, thought bubbles, etc.) ...
Chapter 14
... sustainable manufacturing processes are helping to decrease our use and waste of such resources. Recent, dramatic increases in the cost of minerals are driving aggressive recycling of many resources and particularly metals (e.g., copper). ...
... sustainable manufacturing processes are helping to decrease our use and waste of such resources. Recent, dramatic increases in the cost of minerals are driving aggressive recycling of many resources and particularly metals (e.g., copper). ...
Earth Systems,Structures and Processes-Science Exam
... slowly moved and changed positions on the globe throughout geologic time. ...
... slowly moved and changed positions on the globe throughout geologic time. ...
Melting and Crystallisation
... melting of rock deep beneath Earth's surface; and it rises towards the surface because it is less dense than the surrounding rock. When this molten material runs onto Earth's surface, it is called lava. When magma or lava cool, they crystallise to form igneous rocks. ...
... melting of rock deep beneath Earth's surface; and it rises towards the surface because it is less dense than the surrounding rock. When this molten material runs onto Earth's surface, it is called lava. When magma or lava cool, they crystallise to form igneous rocks. ...
Journey to the Center of Earth
... Layer that we live on (Lithosphere) 5-25 miles thick Consists of cooled rock Thinnest layer of the earth There are 2 kinds of Crust: Continental (thicker) and Oceanic (thinner) ...
... Layer that we live on (Lithosphere) 5-25 miles thick Consists of cooled rock Thinnest layer of the earth There are 2 kinds of Crust: Continental (thicker) and Oceanic (thinner) ...
ch. 6 part II - OCPS TeacherPress
... Focus- the site where the earthquake originates below the surface Epicenter- located on the earth’s surface, directly above the focus Richter scale and the moment magnitude scales are used to measure the magnitude; size 8 is 10x greater than ...
... Focus- the site where the earthquake originates below the surface Epicenter- located on the earth’s surface, directly above the focus Richter scale and the moment magnitude scales are used to measure the magnitude; size 8 is 10x greater than ...
Chapter 1 Introduction
... Figure 1-3. Variation in P and S wave velocities with depth. Compositional subdivisions of the Earth are on the left, rheological subdivisions on the right. After Kearey and Vine (1990), Global Tectonics. © Blackwell Scientific. Oxford. ...
... Figure 1-3. Variation in P and S wave velocities with depth. Compositional subdivisions of the Earth are on the left, rheological subdivisions on the right. After Kearey and Vine (1990), Global Tectonics. © Blackwell Scientific. Oxford. ...
Igneous, metamorphic and sedimentary rocks.
... of molten material within the crust or at the Earth’s surface. Sedimentary Rocks: all rocks formed by deposition and consolidation of mineral grains and those formed from precipitation of minerals from solution in water. The grains and solutions derived from the breakdown of pre-existing rocks at th ...
... of molten material within the crust or at the Earth’s surface. Sedimentary Rocks: all rocks formed by deposition and consolidation of mineral grains and those formed from precipitation of minerals from solution in water. The grains and solutions derived from the breakdown of pre-existing rocks at th ...
Volcano Variations 1 – Teacher Notes File
... 1. Plate convergence - Strato (or composite) volcanoes Where two tectonic plates are pushed together at a zone of convergence, continental crust may be pushed down (subducted) and partially melted. The convergence of the northward moving Pacific Plate and the Asian Plate produce the famous belt of v ...
... 1. Plate convergence - Strato (or composite) volcanoes Where two tectonic plates are pushed together at a zone of convergence, continental crust may be pushed down (subducted) and partially melted. The convergence of the northward moving Pacific Plate and the Asian Plate produce the famous belt of v ...
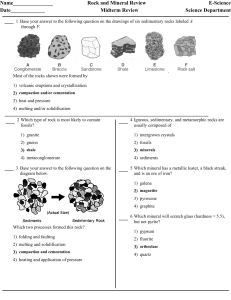
Rocks and Minerals Midterm Rev
... Most of the rocks shown were formed by 1) volcanic eruptions and crystallization 2) compaction and/or cementation 3) heat and pressure 4) melting and/or solidification 2 Which type of rock is most likely to contain ...
... Most of the rocks shown were formed by 1) volcanic eruptions and crystallization 2) compaction and/or cementation 3) heat and pressure 4) melting and/or solidification 2 Which type of rock is most likely to contain ...
Mena Pfest - Mrs. Pfest`s Science Place
... e. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the argument presented. 7. Conduct short research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question), drawing on several sources and generating additional related, focused questions that allow for multiple a ...
... e. Provide a concluding statement or section that follows from and supports the argument presented. 7. Conduct short research projects to answer a question (including a self-generated question), drawing on several sources and generating additional related, focused questions that allow for multiple a ...
Earth/Space Review Sheet
... Igneous Rock – molten rock that has cooled on earth’s surface Metamorphic Rock – rock whose texture and mineral content has changed inside of the earth due to heat and pressure Sedimentary Rock – rock that forms from compressed or cemented layers of sediment on earth’s surface. Older Sedimentary Roc ...
... Igneous Rock – molten rock that has cooled on earth’s surface Metamorphic Rock – rock whose texture and mineral content has changed inside of the earth due to heat and pressure Sedimentary Rock – rock that forms from compressed or cemented layers of sediment on earth’s surface. Older Sedimentary Roc ...
Virginia Standards of Learning
... Soil is formed from the weathering of rocks and organic activity. Karst topography is developed in areas underlain by carbonate rocks, including limestone and dolomite. Soil is loose rock fragments and clay derived from weathered rock mixed with organic material. Karst topography includes fe ...
... Soil is formed from the weathering of rocks and organic activity. Karst topography is developed in areas underlain by carbonate rocks, including limestone and dolomite. Soil is loose rock fragments and clay derived from weathered rock mixed with organic material. Karst topography includes fe ...
Laramide Orogeny - Major Tectonic event that formed the Rocky
... ‐Over 16 Million years old (Hot Spot Migrated; toward the SW, North American Plate Movement) ‐Many Shield Volcanoes (various sizes, liquid lava; low viscosity) ...
... ‐Over 16 Million years old (Hot Spot Migrated; toward the SW, North American Plate Movement) ‐Many Shield Volcanoes (various sizes, liquid lava; low viscosity) ...
MSTPRES
... from sand, shells, and pebble particles. They accumulate layers which causes them to harden into rocks. These rocks are usually soft enough to break easily. 9.What is a metamorphic rock? Explain using details Metamorphic rocks are formed under the surface of the earth from intense heat and pressure. ...
... from sand, shells, and pebble particles. They accumulate layers which causes them to harden into rocks. These rocks are usually soft enough to break easily. 9.What is a metamorphic rock? Explain using details Metamorphic rocks are formed under the surface of the earth from intense heat and pressure. ...
Earth`s Layers Notes Printable
... Outermost, Solid Layer 2: continental and oceanic Composed of; oxygen, silicon and aluminum Oceanic must denser (due to 2x the iron, calcium and magnesium) 30 km MANTLE Hot, slow-flowing rock Convection takes place here Cooler rock sinks, warmer rock rises Denser than crust 2,900 ...
... Outermost, Solid Layer 2: continental and oceanic Composed of; oxygen, silicon and aluminum Oceanic must denser (due to 2x the iron, calcium and magnesium) 30 km MANTLE Hot, slow-flowing rock Convection takes place here Cooler rock sinks, warmer rock rises Denser than crust 2,900 ...
The Difference Between Weather and Climate
... Drought: a long period of very low rainfall; may last up to several years *** A drought can be very dangerous to people, animals, and plants, since we all need water to survive. ...
... Drought: a long period of very low rainfall; may last up to several years *** A drought can be very dangerous to people, animals, and plants, since we all need water to survive. ...
Physical Geology Lecture - FacultyWeb Support Center
... “Aristotelian Thought” centers on the metaphysical concept that reality (the earth) is surrounded by “spheres of the heavenly bodies” called “Celestial Spheres”. [This idea is thought to have arisen from the impression that the night sky gives an observer even today. It is the feeling of being insid ...
... “Aristotelian Thought” centers on the metaphysical concept that reality (the earth) is surrounded by “spheres of the heavenly bodies” called “Celestial Spheres”. [This idea is thought to have arisen from the impression that the night sky gives an observer even today. It is the feeling of being insid ...
Tectonic–climatic interaction

Tectonic–climatic interaction is the interrelationship between tectonic processes and the climate system. The tectonic processes in question include orogenesis, volcanism, and erosion, while relevant climatic processes include atmospheric circulation, orographic lift, monsoon circulation and the rain shadow effect. As the geological record of past climate changes over millions of years is sparse and poorly resolved, many questions remain unresolved regarding the nature of tectonic-climate interaction, although it is an area of active research by geologists and palaeoclimatologists.