* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Layers of the Earth (Notes 1/5)
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Anoxic event wikipedia , lookup
Physical oceanography wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
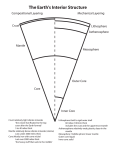
Unit 3: Plate Tectonics Vocabulary (use both the red textbook and your phone if necessary) Inner core Mantle Outer core Crust Protoplanet Protoplanet hypothesis Asthenosphere Epicenter Composite volcano Mid Ocean Ridge Basalt Granite Pangaea Converging boundary Diverging boundary Transform boundary Subduction Fault Lithosphere Plate tectonics Spreading centers/Sea Floor Spreading Earthquake Seismic Wave Sill & Dike Rift Valley I. EARTH’S ORIGIN & STRUCTURE A. Origin Facts 1. All the planets revolve in the same direction around the sun. 2. The path of the planets are elliptical. 3. The planet paths are nearly in the same plane (flat surface.) 4. Most of the planets have moons B. Protoplanet Hypothesis 1. Great ball of dust and gas slowly rotates in space. 2. Gravity compressed the ball. 3. The compression made the ball rotate faster, & the compressed material reacted into a hot core (Sun.) 4. Material around the ball compacted into masses called protoplanets. C. Origin of the Oceans & Atmosphere 1. Oceans: volcanoes produced gas vapor that condensed into the oceans 2. Atmosphere: Sunlight broke up water molecules into oxygen, & volcanoes released gases. a.) green plants also add Oxygen through photosynthesis. D. Structure of the Solid Earth Structure of the Solid Earth ? Crust: (10Km Thick at ocean basin, 65Km at mountain top) Outer Core: (2250 Km thick) Mantle: (2900KM thick) Inner Core: (1200Km thick) 1. Crust: solid rock, includes dry and wet land. a. Continental crust- made of granite b. Oceanic crust- made of basalt (more dense than granite). 2. Mantle: hot & solid rock a. Lithosphere: Upper, rigid part of the mantle b. Asthenosphere: Middle, soft layer of the mantle 3. Core: made up of mostly metals, very hot! a. outer core: liquid metal b. inner core: solid, dense metal Seismic waves Waves travel at different speeds through liquids & solids. (Also different types of minerals) Meteorite Show similar metals to what we believe the core is made of! CBA: Journey to the Center of the Earth Textbook Time Use the red textbook to answer the following questions: Pg. 130: “Analyzing Data” 1-4 Pg. 131 #’s 1 & 2 all Pg. 135 #’s 1-3 all GET A STAMP WHEN COMPLETE!