Subthreshold amplitude and phase resonance in single cells
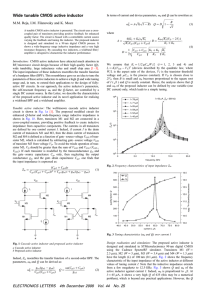
... at the same time. For input frequencies f < fphas , the voltage response is advanced, while for input frequencies f > fphas the voltage response is delayed. The voltage response for 3D linear systems is more complex than for 2D linear systems. The impedance profile may exhibit a local minimum at an ...
... at the same time. For input frequencies f < fphas , the voltage response is advanced, while for input frequencies f > fphas the voltage response is delayed. The voltage response for 3D linear systems is more complex than for 2D linear systems. The impedance profile may exhibit a local minimum at an ...
Electromagnetic compatibility of power converters
... A “hot” conductor is a piece of circuit submitted to high dV/dt, to high dI/dt, or both. First, we need do identify all of them (essentially the H bridges in the upper figure). The stray capacitance between high dV/dt and chassis ground must be reduced to reduce common mode current generation: ...
... A “hot” conductor is a piece of circuit submitted to high dV/dt, to high dI/dt, or both. First, we need do identify all of them (essentially the H bridges in the upper figure). The stray capacitance between high dV/dt and chassis ground must be reduced to reduce common mode current generation: ...
Electronics Standards and Definitions
... impedance allows connection of almost any load without loss of signal amplitude. For example, a 100-Ω load may be driven to the full ...
... impedance allows connection of almost any load without loss of signal amplitude. For example, a 100-Ω load may be driven to the full ...
Wide tunable CMOS active inductor
... is designed and simulated in a 90 nm digital CMOS process. It shows a wide-frequency range inductive impedance and a very high resonance frequency. By cascading two inductors, a wideband filter/ amplifier is designed to characterise the inductor performance. ...
... is designed and simulated in a 90 nm digital CMOS process. It shows a wide-frequency range inductive impedance and a very high resonance frequency. By cascading two inductors, a wideband filter/ amplifier is designed to characterise the inductor performance. ...
GUIDE TO CONSTANT-VOLTAGE SYSTEMS
... Other high-voltage systems might run at other voltages. Although rare, the 200V system has been used for cable length exceeding one mile. ADVANTAGES OF 70V OPERATION As stated before, a 70V line reduces power loss due to cable heating. That's because the speaker cable carries the audio signal as a ...
... Other high-voltage systems might run at other voltages. Although rare, the 200V system has been used for cable length exceeding one mile. ADVANTAGES OF 70V OPERATION As stated before, a 70V line reduces power loss due to cable heating. That's because the speaker cable carries the audio signal as a ...
Introduction to oscilloscopes • Triggering • 10x probes • DC coupling
... Z1 and Z2 are frequency dependent and changes for each circuit ...
... Z1 and Z2 are frequency dependent and changes for each circuit ...
Experiment FT2: Measurement of Inductance and Mutual Inductance
... production of mutually induced e.m.f in the secondary coil. A mutual inductance M may be defined to quantify the ability of one coil to produce an e.m.f in a nearby coil by induction when the current in the first coil changes. This action is reciprocal, i.e., the second coil can also induce an e.m.f ...
... production of mutually induced e.m.f in the secondary coil. A mutual inductance M may be defined to quantify the ability of one coil to produce an e.m.f in a nearby coil by induction when the current in the first coil changes. This action is reciprocal, i.e., the second coil can also induce an e.m.f ...
AN-806 Data Transmission Lines and Their Characteristics (Rev. A)
... sections—rather, it is a distributed network. For the lumped model to accurately represent the transmission line (see Figure 5 ), the section length must be quite small in comparison with the shortest wavelengths (highest frequencies) to be used in analysis of the model. Within these limits, as diff ...
... sections—rather, it is a distributed network. For the lumped model to accurately represent the transmission line (see Figure 5 ), the section length must be quite small in comparison with the shortest wavelengths (highest frequencies) to be used in analysis of the model. Within these limits, as diff ...
uhf/vhf/fm active color antenna installation and operating
... Install the antenna on the mast; when the received wave is horizontally, follow (Fig. 1); when vertically polarized, install as in.(Fig. 2) Now, adjust the antenna direction for the best possible picture and fix in position. For UHF (Bands IV, V),especially, not only antenna direction but also the h ...
... Install the antenna on the mast; when the received wave is horizontally, follow (Fig. 1); when vertically polarized, install as in.(Fig. 2) Now, adjust the antenna direction for the best possible picture and fix in position. For UHF (Bands IV, V),especially, not only antenna direction but also the h ...
ACTIVE NEGATIVE INDUCTOR BASED ON MAGNETIC FLUX D. D.
... All of these NICs use circuit techniques to invert the voltage or current across an impedance element, thus realizing the negative of the element impedance. These techniques are independent of the element, and can be used with resistors, capacitors, and inductors. In contrast, the negative inductor ...
... All of these NICs use circuit techniques to invert the voltage or current across an impedance element, thus realizing the negative of the element impedance. These techniques are independent of the element, and can be used with resistors, capacitors, and inductors. In contrast, the negative inductor ...
Nominal impedance
Nominal impedance in electrical engineering and audio engineering refers to the approximate designed impedance of an electrical circuit or device. The term is applied in a number of different fields, most often being encountered in respect of:The nominal value of the characteristic impedance of a cable or other form of transmission line.The nominal value of the input, output or image impedance of a port of a network, especially a network intended for use with a transmission line, such as filters, equalisers and amplifiers.The nominal value of the input impedance of a radio frequency antennaThe actual impedance may vary quite considerably from the nominal figure with changes in frequency. In the case of cables and other transmission lines, there is also variation along the length of the cable, if it is not properly terminated. It is usual practice to speak of nominal impedance as if it were a constant resistance, that is, it is invariant with frequency and has a zero reactive component, despite this often being far from the case. Depending on the field of application, nominal impedance is implicitly referring to a specific point on the frequency response of the circuit under consideration. This may be at low-frequency, mid-band or some other point and specific applications are discussed in the sections below.In most applications, there are a number of values of nominal impedance that are recognised as being standard. The nominal impedance of a component or circuit is often assigned one of these standard values, regardless of whether the measured impedance exactly corresponds to it. The item is assigned the nearest standard value.