A Class D AM Transmitter for 75 Meters
... There are a couple of characteristics of this topology I did not anticipate in the design. The first is a very large power spike appearing at the modulation input that occurs when carrier drive is cut. The drop in the current in the primary of the modulation transformer is effectively stepped down a ...
... There are a couple of characteristics of this topology I did not anticipate in the design. The first is a very large power spike appearing at the modulation input that occurs when carrier drive is cut. The drop in the current in the primary of the modulation transformer is effectively stepped down a ...
Measuring Loudspeaker Driver Parameters
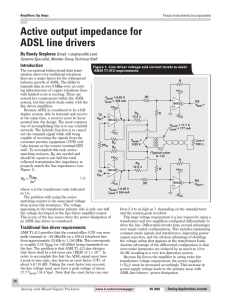
... Figure 1 shows a typical impedance curve for a loudspeaker (see Figure 5 for the equivalent circuit of this speaker, which was simulated for this article). Resonance causes a large increase in impedance, and at some higher frequency, the inductance (or semi-inductance) of the voice coil causes the i ...
... Figure 1 shows a typical impedance curve for a loudspeaker (see Figure 5 for the equivalent circuit of this speaker, which was simulated for this article). Resonance causes a large increase in impedance, and at some higher frequency, the inductance (or semi-inductance) of the voice coil causes the i ...
- Yokogawa
... 701917 DC to 50 MHz 701918 DC to 120 MHz Low noise compact current probe for measuring low level currents from 1 mA to 5 A. Best suited for design and verification applications requiring high-sensitivity at low currents. High-sensitivity (10x more sensitive than previous models) In comparison with e ...
... 701917 DC to 50 MHz 701918 DC to 120 MHz Low noise compact current probe for measuring low level currents from 1 mA to 5 A. Best suited for design and verification applications requiring high-sensitivity at low currents. High-sensitivity (10x more sensitive than previous models) In comparison with e ...
2008. Lecture 11 (361-1
... output resistance, about 26 at IE=1 mA. However, compared to a lower than 1 series resistance of the inductor, it is still too high. Of course, it will be low enough at IE=100 mA, but it is too much of power consumption.) In a general case, the small-signal voltage gains of these amplifiers are ...
... output resistance, about 26 at IE=1 mA. However, compared to a lower than 1 series resistance of the inductor, it is still too high. Of course, it will be low enough at IE=100 mA, but it is too much of power consumption.) In a general case, the small-signal voltage gains of these amplifiers are ...
Faculty of Engineering - Pharos University in Alexandria
... Pharos University Faculty of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering SEMESTER: 3rd level - 5th semester Course Title: Electrical Power Engineering 1 Instructor: Dr. Sahar Abd El Moneim ...
... Pharos University Faculty of Engineering Department of Electrical Engineering SEMESTER: 3rd level - 5th semester Course Title: Electrical Power Engineering 1 Instructor: Dr. Sahar Abd El Moneim ...
AD8074/AD8075 500 MHz, G = +1 and +2 Triple
... within 2.6 V of either rail. The system designer may opt to use this characteristic to his or her advantage by using the soft-saturation regime, (2.2 V–2.6 V from the supply rails), to tame excessive overshoot. The designer is cautioned that a charge storage associated time delay of several nanoseco ...
... within 2.6 V of either rail. The system designer may opt to use this characteristic to his or her advantage by using the soft-saturation regime, (2.2 V–2.6 V from the supply rails), to tame excessive overshoot. The designer is cautioned that a charge storage associated time delay of several nanoseco ...
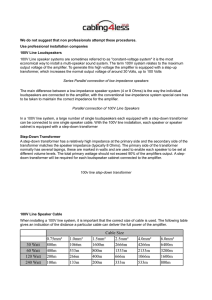
Nominal impedance
Nominal impedance in electrical engineering and audio engineering refers to the approximate designed impedance of an electrical circuit or device. The term is applied in a number of different fields, most often being encountered in respect of:The nominal value of the characteristic impedance of a cable or other form of transmission line.The nominal value of the input, output or image impedance of a port of a network, especially a network intended for use with a transmission line, such as filters, equalisers and amplifiers.The nominal value of the input impedance of a radio frequency antennaThe actual impedance may vary quite considerably from the nominal figure with changes in frequency. In the case of cables and other transmission lines, there is also variation along the length of the cable, if it is not properly terminated. It is usual practice to speak of nominal impedance as if it were a constant resistance, that is, it is invariant with frequency and has a zero reactive component, despite this often being far from the case. Depending on the field of application, nominal impedance is implicitly referring to a specific point on the frequency response of the circuit under consideration. This may be at low-frequency, mid-band or some other point and specific applications are discussed in the sections below.In most applications, there are a number of values of nominal impedance that are recognised as being standard. The nominal impedance of a component or circuit is often assigned one of these standard values, regardless of whether the measured impedance exactly corresponds to it. The item is assigned the nearest standard value.