Lecture 4
... Basic and most common circuit building device. Ideally, 1. No current can enter terminals V+ or V-. Called infinite input impedance. ...
... Basic and most common circuit building device. Ideally, 1. No current can enter terminals V+ or V-. Called infinite input impedance. ...
HW 2
... pf of 0.75 lagging. A new pf of 0.90 is desired. Find the required reactive power per phase that must be added to achieve this new pf. Find the required capacitance if the capacitor ...
... pf of 0.75 lagging. A new pf of 0.90 is desired. Find the required reactive power per phase that must be added to achieve this new pf. Find the required capacitance if the capacitor ...
Analog Telephony Overview
... In addition to the public switched services, where the user can dial different numbers, private point-to-point services are provided in both two-wire and four-wire formats. ...
... In addition to the public switched services, where the user can dial different numbers, private point-to-point services are provided in both two-wire and four-wire formats. ...
glossary
... prior to a function being carried out; it usually has a warning symbol or icon, the message, and control buttons (typically Yes, OK, No, Cancel). ...
... prior to a function being carried out; it usually has a warning symbol or icon, the message, and control buttons (typically Yes, OK, No, Cancel). ...
Circuits - Lake Area Radio Klub
... The impedance of a low-pass filter should be about the same as the impedance of the transmission line into which it is inserted. (G7C06) The effect of lead inductance in a capacitor used at VHF frequencies and above is that effective capacitance may be reduced because of the lead inductance. (G6 ...
... The impedance of a low-pass filter should be about the same as the impedance of the transmission line into which it is inserted. (G7C06) The effect of lead inductance in a capacitor used at VHF frequencies and above is that effective capacitance may be reduced because of the lead inductance. (G6 ...
EE6501_PSA_Unit_ - e
... 12. A 90 MVA, 11 kV, 3 phase generator has a reactance of 25%. The generator supplies two motors through transformer and transmission line as shown. The transformer T1 is a 3phase transformer, 100 MVA, 10/132 kV, 6% reactance. The transformer T2 is composed of 3 single phase units each rated 300 MVA ...
... 12. A 90 MVA, 11 kV, 3 phase generator has a reactance of 25%. The generator supplies two motors through transformer and transmission line as shown. The transformer T1 is a 3phase transformer, 100 MVA, 10/132 kV, 6% reactance. The transformer T2 is composed of 3 single phase units each rated 300 MVA ...
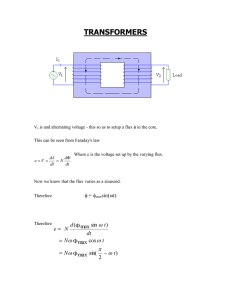
Transformer Notes
... The second option is the more feasible one as a smaller transformer needs to be need be purchased which is much cheaper than the purchase of a brand new big transformer. In paralleling transformers, however, some basic rules need to be followed. Obviously the voltage and turns ratio need to be the s ...
... The second option is the more feasible one as a smaller transformer needs to be need be purchased which is much cheaper than the purchase of a brand new big transformer. In paralleling transformers, however, some basic rules need to be followed. Obviously the voltage and turns ratio need to be the s ...
3 Abbreviations, Acronyms, AND definitions
... more CPE are expected to be attached, i.e. KSU-less systems, the on-hook performance limits need to be scaled. See Annex A for an example of scaled calculations. ...
... more CPE are expected to be attached, i.e. KSU-less systems, the on-hook performance limits need to be scaled. See Annex A for an example of scaled calculations. ...
May 2001 LT1880 SOT-23 Op Amp Saves Board Space in Precision Applications
... stage of the LT1880 makes it ideal for precision integrators and current sources. Figure 8 shows the LT1880 providing a simple precision current source for a remote 1kΩ RTD on a 4-wire connection. The LT1634 reference places 1.25V at the noninverting input of the LT1880, which then maintains its inv ...
... stage of the LT1880 makes it ideal for precision integrators and current sources. Figure 8 shows the LT1880 providing a simple precision current source for a remote 1kΩ RTD on a 4-wire connection. The LT1634 reference places 1.25V at the noninverting input of the LT1880, which then maintains its inv ...
Impedance Spectroscopy and Cell Constant of the
... solution for the surrounding medium, according to the physiological fluid in the brain. For the calculation of the resistivity in the Conductive Media DC application mode the surrounding medium and each of the stimulating electrodes were modeled as conductors with conductivities of 0.005 S/m and 1e6 ...
... solution for the surrounding medium, according to the physiological fluid in the brain. For the calculation of the resistivity in the Conductive Media DC application mode the surrounding medium and each of the stimulating electrodes were modeled as conductors with conductivities of 0.005 S/m and 1e6 ...
Nominal impedance
Nominal impedance in electrical engineering and audio engineering refers to the approximate designed impedance of an electrical circuit or device. The term is applied in a number of different fields, most often being encountered in respect of:The nominal value of the characteristic impedance of a cable or other form of transmission line.The nominal value of the input, output or image impedance of a port of a network, especially a network intended for use with a transmission line, such as filters, equalisers and amplifiers.The nominal value of the input impedance of a radio frequency antennaThe actual impedance may vary quite considerably from the nominal figure with changes in frequency. In the case of cables and other transmission lines, there is also variation along the length of the cable, if it is not properly terminated. It is usual practice to speak of nominal impedance as if it were a constant resistance, that is, it is invariant with frequency and has a zero reactive component, despite this often being far from the case. Depending on the field of application, nominal impedance is implicitly referring to a specific point on the frequency response of the circuit under consideration. This may be at low-frequency, mid-band or some other point and specific applications are discussed in the sections below.In most applications, there are a number of values of nominal impedance that are recognised as being standard. The nominal impedance of a component or circuit is often assigned one of these standard values, regardless of whether the measured impedance exactly corresponds to it. The item is assigned the nearest standard value.