* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download “Real” Transformer
Induction motor wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Flexible electronics wikipedia , lookup
Power engineering wikipedia , lookup
Fault tolerance wikipedia , lookup
Ground (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Nominal impedance wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Mains electricity wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Circuit breaker wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Two-port network wikipedia , lookup
Resonant inductive coupling wikipedia , lookup
Earthing system wikipedia , lookup
Electrical wiring in the United Kingdom wikipedia , lookup
Transformer wikipedia , lookup
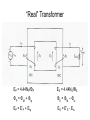
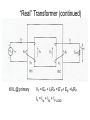
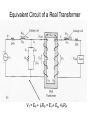
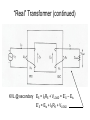
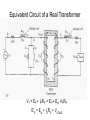
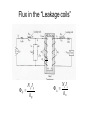
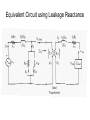
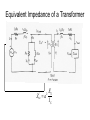
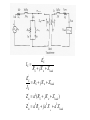
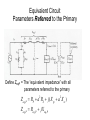
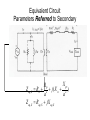
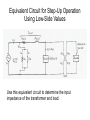
“Real” Transformer EP = 4.44NPfΦP ES = 4.44NSfΦS ΦP = ΦM + Φlp ΦS = ΦM – Φls EP = E’P + Elp ES = E’S - Els “Real” Transformer (continued) KVL @ primary VT = EP + IPRP = E’P+ Elp +IPRP IP = Ife + IM + IP LOAD Equivalent Circuit of a Real Transformer VT = EP + IPRP = E’P+ Elp +IPRP “Real” Transformer (continued) KVL @ secondary ES = ISRS + VLOAD = E’S – Els E’S = Els + ISRS + VLOAD Equivalent Circuit of a Real Transformer VT = EP + IPRP = E’P+ Elp +IPRP E’S = Els + ISRS + VLOAD Flux in the “Leakage coils” ls lp NpIp R lp Ns Is R ls Ns Is ls R ls Voltage generated by flux through the window of a coil e 2 fN max cos(2 ft ) Emax 2 fN max N p I p max Elp ,max 2 fN p R lp N p2 Elp ,max 2 f I R p max lp N p2 Elp ,rms 2 f I p ,rms R lp 2 N L R Elp (2 fLlp )( I p ) Elp I p X lp Similar expression for the secondary Equivalent Circuit using Leakage Reactance Equivalent Impedance of a Transformer ' E Zin' a 2 S IS ES' IS RS jX ls Z load ES' RS jX ls Z load IS Z in' a 2 ( RS jX ls Z load ) Z in' a 2 RS ja 2 X ls a 2 Z load Equivalent Circuit Parameters Referred to the Primary Z eq , P RP a 2 RS j ( X lp a 2 X ls ) Z eq , P Req , P jX eq , P Define ZeqP = The “equivalent impedance” with all parameters referred to the primary Z eq , P RP a 2 RS j ( X lp a 2 X ls ) Z eq , P Req , P jX eq , P Equivalent Circuit Parameters Referred to Secondary Z eq , S Z eq , S X lp RP RS 2 j ( X ls 2 ) a a Req , S jX eq ,S Note that the excitation branch has been moved to the left! It’s OK as long as the transformer is operated near rated conditions! Equivalent Circuit for Step-Down Operation Using High-Side Values Use this equivalent circuit to determine the input impedance of the transformer and load. Equivalent Circuit for Step-Down Operation Using Low-Side Values Use this equivalent circuit to determine the no-load voltage and the voltage regulation. Equivalent Circuit for Step-Up Operation Using Low-Side Values Use this equivalent circuit to determine the input impedance of the transformer and load. Equivalent Circuit for Step-Up High-Side Values Use this equivalent circuit to determine the no-load voltage and the voltage regulation.