Effect of Current Injection Cable on Lightning Surge
... Transient characteristic of a current injection cable, which is used for a surge measurement, is investigated in this paper. Measurements are carried out in order to confirm the accuracy of a numerical simulation by means of a circuit analysis program, Electromagnetic Transients Program (EMTP). The ...
... Transient characteristic of a current injection cable, which is used for a surge measurement, is investigated in this paper. Measurements are carried out in order to confirm the accuracy of a numerical simulation by means of a circuit analysis program, Electromagnetic Transients Program (EMTP). The ...
Understanding the Fundamental Principles of Vector
... resistance of RL. This condition occurs when RL = RS, and is true whether the stimulus is a DC voltage source or a source of RF sine waves (Figure 7). When the source impedance is not purely resistive, maximum power transfer occurs when the load impedance is equal to the complex conjugate of the sou ...
... resistance of RL. This condition occurs when RL = RS, and is true whether the stimulus is a DC voltage source or a source of RF sine waves (Figure 7). When the source impedance is not purely resistive, maximum power transfer occurs when the load impedance is equal to the complex conjugate of the sou ...
Experiment
... was accurate but the Triplett value was not. This result is due to the much larger input resistance of the Agilent meter. The first measurement made by the Triplett meter was (fairly) accurate because its input resistance is much larger than the 50Ω internal resistance of the function generator; but ...
... was accurate but the Triplett value was not. This result is due to the much larger input resistance of the Agilent meter. The first measurement made by the Triplett meter was (fairly) accurate because its input resistance is much larger than the 50Ω internal resistance of the function generator; but ...
D. Other Pulse Shaping Methods
... When components are physically separated, however, the shield will tend to establish a common ground potential for all components Computers are a potential source of high frequency noise pickup and may need to be kept at a distance from detectors and preamplifiers where signal levels are low A techn ...
... When components are physically separated, however, the shield will tend to establish a common ground potential for all components Computers are a potential source of high frequency noise pickup and may need to be kept at a distance from detectors and preamplifiers where signal levels are low A techn ...
80K-40 High Voltage Probe
... ac, 28 kV rms ac, Overvoltage Category I (voltages derived from limited energy transformer). * The input impedance of Autoranging Fluke handheld digital multimeters varies as a function of range. The only range that deviates significantly from 10 MΩ is the 3V (Models 21, 23, 25, 27, 70, 73, 75, 77) ...
... ac, 28 kV rms ac, Overvoltage Category I (voltages derived from limited energy transformer). * The input impedance of Autoranging Fluke handheld digital multimeters varies as a function of range. The only range that deviates significantly from 10 MΩ is the 3V (Models 21, 23, 25, 27, 70, 73, 75, 77) ...
Word
... loads respond to voltage and frequency deviation in a variety of ways that impedances do not capture. In general, stability performance is improved with constant impedance loads because the power decreases as voltage declines with the square of the voltage. Therefore, representing loads as constant ...
... loads respond to voltage and frequency deviation in a variety of ways that impedances do not capture. In general, stability performance is improved with constant impedance loads because the power decreases as voltage declines with the square of the voltage. Therefore, representing loads as constant ...
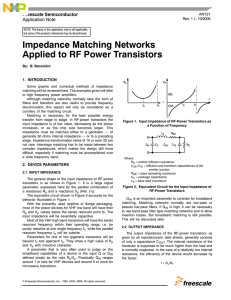
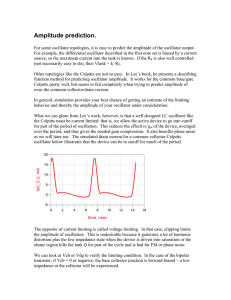
Impedance Matching Networks Applied to RF Power Transistors
... with VCE(sat) equal to 2 or 3 volts, increasing with frequency. The above equation just expresses a well-known relation, but also shows that the load, in first approximation, is not related to the device, except for V CE(sat). The load value is primarily dictated by the required output power and the ...
... with VCE(sat) equal to 2 or 3 volts, increasing with frequency. The above equation just expresses a well-known relation, but also shows that the load, in first approximation, is not related to the device, except for V CE(sat). The load value is primarily dictated by the required output power and the ...
Oscillator Notes 2
... The bias current of the amplifier is directly related to the output voltage swing and RL. If the supply voltage is fixed, then you can reduce current to save power. 1. Increase RL. This may be practical in situations where the frequency is relatively low and interconnection lengths short. This is qu ...
... The bias current of the amplifier is directly related to the output voltage swing and RL. If the supply voltage is fixed, then you can reduce current to save power. 1. Increase RL. This may be practical in situations where the frequency is relatively low and interconnection lengths short. This is qu ...
Shure M63 User Guide
... The resultant curve shown might be typical of a sound system where low-frequency noise was a problem (stage noise, etc.) and the room was relatively dead (heavily draped and carpeted). The low-frequency rolloff would keep objectionable thumping noises to a minimum, while the slight increase in respo ...
... The resultant curve shown might be typical of a sound system where low-frequency noise was a problem (stage noise, etc.) and the room was relatively dead (heavily draped and carpeted). The low-frequency rolloff would keep objectionable thumping noises to a minimum, while the slight increase in respo ...
Chapter 13
... Current and Voltage in a Series RLC Circuit • At the series resonant frequency, the current is maximum (Imax = Vs/R) • Above and below resonance, the current decreases because the impedance increases • At resonance, impedance is equal to R • The voltages across L and C are maximum at resonance, but ...
... Current and Voltage in a Series RLC Circuit • At the series resonant frequency, the current is maximum (Imax = Vs/R) • Above and below resonance, the current decreases because the impedance increases • At resonance, impedance is equal to R • The voltages across L and C are maximum at resonance, but ...
Section 3
... Transformers. Transformer phase shift. Wye-delta connections and impact on zero sequence. Inductance and capacitance calculations for transmission lines. GMR, GMD, L, and C matrices, effect of ground conductivity. Underground cables. Equivalent Circuits The standard transformer equivalent circuit us ...
... Transformers. Transformer phase shift. Wye-delta connections and impact on zero sequence. Inductance and capacitance calculations for transmission lines. GMR, GMD, L, and C matrices, effect of ground conductivity. Underground cables. Equivalent Circuits The standard transformer equivalent circuit us ...
Appendix D - Oxford University Press
... by a current source In and a parallel impedance Zn , as shown in Fig. D.2. Figure D.2(a) shows a network divided into two parts, A and B. In Fig. D.2(b), part A has been replaced by its Norton’s equivalent: a current source In and a parallel impedance Zn . The Norton’s current source In can be measu ...
... by a current source In and a parallel impedance Zn , as shown in Fig. D.2. Figure D.2(a) shows a network divided into two parts, A and B. In Fig. D.2(b), part A has been replaced by its Norton’s equivalent: a current source In and a parallel impedance Zn . The Norton’s current source In can be measu ...
TT2D User Manual - Electronic Devices, Inc.
... where the most power is transferred from the face of the transducer. Check the energy transfer at each resonant point by pressing on the center of the transducer face with a fingertip while observing the impedance displayed on the top line of the LCD. The readings will change noticeably with moderat ...
... where the most power is transferred from the face of the transducer. Check the energy transfer at each resonant point by pressing on the center of the transducer face with a fingertip while observing the impedance displayed on the top line of the LCD. The readings will change noticeably with moderat ...
Tips and tricks for high-speed, high-voltage
... amplifier with high input impedance that can drive 50-W lines. It has an input common-mode range of ±1.5 V and a >700-MHz small-signal bandwidth, as well as an input impedance of 1 pF in parallel with 1 MW. Using this amplifier for drain voltages as high as 600 V will require a 1000:1 voltage attenu ...
... amplifier with high input impedance that can drive 50-W lines. It has an input common-mode range of ±1.5 V and a >700-MHz small-signal bandwidth, as well as an input impedance of 1 pF in parallel with 1 MW. Using this amplifier for drain voltages as high as 600 V will require a 1000:1 voltage attenu ...
Nominal impedance
Nominal impedance in electrical engineering and audio engineering refers to the approximate designed impedance of an electrical circuit or device. The term is applied in a number of different fields, most often being encountered in respect of:The nominal value of the characteristic impedance of a cable or other form of transmission line.The nominal value of the input, output or image impedance of a port of a network, especially a network intended for use with a transmission line, such as filters, equalisers and amplifiers.The nominal value of the input impedance of a radio frequency antennaThe actual impedance may vary quite considerably from the nominal figure with changes in frequency. In the case of cables and other transmission lines, there is also variation along the length of the cable, if it is not properly terminated. It is usual practice to speak of nominal impedance as if it were a constant resistance, that is, it is invariant with frequency and has a zero reactive component, despite this often being far from the case. Depending on the field of application, nominal impedance is implicitly referring to a specific point on the frequency response of the circuit under consideration. This may be at low-frequency, mid-band or some other point and specific applications are discussed in the sections below.In most applications, there are a number of values of nominal impedance that are recognised as being standard. The nominal impedance of a component or circuit is often assigned one of these standard values, regardless of whether the measured impedance exactly corresponds to it. The item is assigned the nearest standard value.