Physio study guide unit 2
... Discuss conduction velocity: which types of neurons conduct action potentials faster? Do you know what is meant by “gating” of a channel and when a channel is in a conducting state vs nonconducting state? What are the three ways a channel’s conductance can change? Discuss sodium’s three gating posit ...
... Discuss conduction velocity: which types of neurons conduct action potentials faster? Do you know what is meant by “gating” of a channel and when a channel is in a conducting state vs nonconducting state? What are the three ways a channel’s conductance can change? Discuss sodium’s three gating posit ...
Autonomní nervový systém
... cardiovascular: decrease of BP and CO negative chronotropic, inotropic, dromotropic effect. Decrease of rennin production, but due to inhibition of beta-vasodilatation peripheral vascular resistance can increase - increase of PVR (peripheral -receptors are not opposed) ...
... cardiovascular: decrease of BP and CO negative chronotropic, inotropic, dromotropic effect. Decrease of rennin production, but due to inhibition of beta-vasodilatation peripheral vascular resistance can increase - increase of PVR (peripheral -receptors are not opposed) ...
Mouse anti-receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase sigma, RPTPσ
... Background information: Type IIa receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases (RPTPs) are a group of well-characterized proteins that are involved in axon growth and guidance during neural development. Members of this subfamily, RPTPσ, RPTPδ and LAR contain two cytoplasmic phosphatase domains and extracel ...
... Background information: Type IIa receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases (RPTPs) are a group of well-characterized proteins that are involved in axon growth and guidance during neural development. Members of this subfamily, RPTPσ, RPTPδ and LAR contain two cytoplasmic phosphatase domains and extracel ...
Pharmacology Ch 9 110-126 Cholinergic Pharmacology
... Nicotinic Receptors – causes direct ligand-gated conductance. Two ACh molecules bind to one receptor to elicit a conformational change to create monovalent cation-selective pore that is equally permeable to Na and K ions (Na is predominant due to Nernst potential) -these can depolarize the cell imme ...
... Nicotinic Receptors – causes direct ligand-gated conductance. Two ACh molecules bind to one receptor to elicit a conformational change to create monovalent cation-selective pore that is equally permeable to Na and K ions (Na is predominant due to Nernst potential) -these can depolarize the cell imme ...
Communication between Mating Yeast Cells
... The gene for the syndrome is on the X chromosome in band Xq11-q12. The gene codes for the androgen receptor. ...
... The gene for the syndrome is on the X chromosome in band Xq11-q12. The gene codes for the androgen receptor. ...
Psychopharmacology and Other Biologic Treatments
... • Present in the presynaptic terminal • Released into the synaptic cleft, causing a particular effect on the postsynaptic receptors • An exogenous form of the chemical is administered as a drug causes identical action. • Chemical is removed from the synaptic cleft by a specific mechanism. ...
... • Present in the presynaptic terminal • Released into the synaptic cleft, causing a particular effect on the postsynaptic receptors • An exogenous form of the chemical is administered as a drug causes identical action. • Chemical is removed from the synaptic cleft by a specific mechanism. ...
Chemistry of Opioids
... o Partial agonist activity @ μ receptor due to metabolite nor-buprenorphine o Partial antagonist activity@ κ receptor o Antihyperalgesic effect: κ receptor antagonistic activity o ↓Adverse effects: ↓respiratory depression, not altered by age or renal dysfunction Meperidine o Binds to P-site: phenoli ...
... o Partial agonist activity @ μ receptor due to metabolite nor-buprenorphine o Partial antagonist activity@ κ receptor o Antihyperalgesic effect: κ receptor antagonistic activity o ↓Adverse effects: ↓respiratory depression, not altered by age or renal dysfunction Meperidine o Binds to P-site: phenoli ...
Supplementary Information (doc 1532K)
... NMDAR NR2A/B receptor subunits are required for the potentiation of NMDA synaptic transmission by AMPH The effects of additional NMDAR subunit-specific inhibitors were used to determine the subunit composition of NMDARs that are stimulated under baseline conditions. TCN 201 is a selective inhibitor ...
... NMDAR NR2A/B receptor subunits are required for the potentiation of NMDA synaptic transmission by AMPH The effects of additional NMDAR subunit-specific inhibitors were used to determine the subunit composition of NMDARs that are stimulated under baseline conditions. TCN 201 is a selective inhibitor ...
GABA-A receptor subtypes in the brain: a paradigm for CNS drug
... Role of α1, α2 and α3-containing GABA-A receptors The use of molecular biological techniques revealed that a single amino acid was responsible for this profound difference in affinity. The presence of a histidine residue at position 101 of the primary amino acid sequence of the α subunit (numbering ...
... Role of α1, α2 and α3-containing GABA-A receptors The use of molecular biological techniques revealed that a single amino acid was responsible for this profound difference in affinity. The presence of a histidine residue at position 101 of the primary amino acid sequence of the α subunit (numbering ...
11/19/2014 Sedative‐Hypnotic and Anxiolytic Medications
... Elderly patients metabolize more slowly – half‐lives may reach 7‐10 days for diazepam (Valium®) ...
... Elderly patients metabolize more slowly – half‐lives may reach 7‐10 days for diazepam (Valium®) ...
How Neurons Communicate (the Neuron Game)
... a) Dendrites: collects input signals from many neurons using receptors (more a on receptors later). They have many branches and sometimes even spines along each branch so that there is a lot a of area for other neurons to contact its surface. a b) Cell Body: decides whether or not to continue passin ...
... a) Dendrites: collects input signals from many neurons using receptors (more a on receptors later). They have many branches and sometimes even spines along each branch so that there is a lot a of area for other neurons to contact its surface. a b) Cell Body: decides whether or not to continue passin ...
03/14 PPT
... Is there a map of different smells in the brain? Plan: monitor neural activation in the brain Technologies: calcium-sensitive dyes, voltage-sensitive dyes and intrinsic signals (changes in blood flow, oxygen levels) Results: •Odors activate a few glomeruli •Same glomeruli activated on repeated expo ...
... Is there a map of different smells in the brain? Plan: monitor neural activation in the brain Technologies: calcium-sensitive dyes, voltage-sensitive dyes and intrinsic signals (changes in blood flow, oxygen levels) Results: •Odors activate a few glomeruli •Same glomeruli activated on repeated expo ...
GABA - the Houpt Lab
... Small peptides, from 4 amino acids to ~100 amino acids. Coded for by genes, synthesized by ribosomes (like other proteins). Signal peptide sequence directs neuropeptide into endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and into secretory vesicles. In neurons, neuropeptides are co-localized and released w ...
... Small peptides, from 4 amino acids to ~100 amino acids. Coded for by genes, synthesized by ribosomes (like other proteins). Signal peptide sequence directs neuropeptide into endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, and into secretory vesicles. In neurons, neuropeptides are co-localized and released w ...
GROWTH
... Functional consequences of IGF-I receptor b subunit activation. Binding sites for intracellular signaling molecules are indicated. Assignment of functions to specific phosphotyrosines is described in the text. Dotted areas in the extracellular a subunit indicate the cysteine-rich domains; dashed ar ...
... Functional consequences of IGF-I receptor b subunit activation. Binding sites for intracellular signaling molecules are indicated. Assignment of functions to specific phosphotyrosines is described in the text. Dotted areas in the extracellular a subunit indicate the cysteine-rich domains; dashed ar ...
Lamb Mechanisms Drug Action
... Cellular Sites of Drug Action Antibiotics inhibit bacterial but not host functions. ...
... Cellular Sites of Drug Action Antibiotics inhibit bacterial but not host functions. ...
SYNAPTIC TRANSMISSION
... The synaptic gap contains enzymes that will destroy the neurotransmitters, thus returning the synapse to its original condition prior to the arrival of the impulse STEP 9: The calcium ions are returned to the synaptic gap by active transport. Because only the axon bulb has the neurotr ...
... The synaptic gap contains enzymes that will destroy the neurotransmitters, thus returning the synapse to its original condition prior to the arrival of the impulse STEP 9: The calcium ions are returned to the synaptic gap by active transport. Because only the axon bulb has the neurotr ...
Savage Science AP Biology
... Many sensory receptors are very sensitive: they are able to detect the smallest physical unit of stimulus – For example, most light receptors can detect a photon of light ...
... Many sensory receptors are very sensitive: they are able to detect the smallest physical unit of stimulus – For example, most light receptors can detect a photon of light ...
Local anesthetics
... twoα1,two β2 and one γ2 subunits. GABA A receptor, which functions as a chloride ion channel, is activated by the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA . ...
... twoα1,two β2 and one γ2 subunits. GABA A receptor, which functions as a chloride ion channel, is activated by the inhibitory neurotransmitter GABA . ...
Direct cholinergic agonists
... The control of localized bleeding and the prolongation of the action of local anesthetics. Norepinephrine has a relatively low affinity for b2 receptors. The main effect of al stimulation (with an agonist such as phenylephrine) is vasoconstriction. Local application of a vasoconstrictor to the nasal ...
... The control of localized bleeding and the prolongation of the action of local anesthetics. Norepinephrine has a relatively low affinity for b2 receptors. The main effect of al stimulation (with an agonist such as phenylephrine) is vasoconstriction. Local application of a vasoconstrictor to the nasal ...
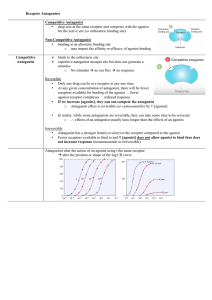
Receptor Antagonists Competitive Antagonist • drug acts at the
... • If a full agonist requires occupation of only 5% of the available receptors in order to produce a maximal response, then 95% of receptors are spare receptors for that agonist. ⇒ there is a receptor reserve of 95% for that agonist. Drugs acting on the same receptor but producing d ...
... • If a full agonist requires occupation of only 5% of the available receptors in order to produce a maximal response, then 95% of receptors are spare receptors for that agonist. ⇒ there is a receptor reserve of 95% for that agonist. Drugs acting on the same receptor but producing d ...
NEUROTRANSMITTERS IN THE CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM
... is considered to be the Rosetta stone of chemical transmission concept and has provided the first evidence that nerves do not influence the heart directly, but liberate specific chemical substances from their terminals. Today, when neurotransmitters are inseparable part of theories of how our brain ...
... is considered to be the Rosetta stone of chemical transmission concept and has provided the first evidence that nerves do not influence the heart directly, but liberate specific chemical substances from their terminals. Today, when neurotransmitters are inseparable part of theories of how our brain ...
Neurons Communicate by Neurotransmission
... Neurons communicate using both electrical signals and chemical messages. Information in the form of an electrical impulse is carried away from the neuron’s cell body along the axon of a presynaptic neuron toward the axon terminals. When the electrical signal reaches the terminal, it cannot cross the ...
... Neurons communicate using both electrical signals and chemical messages. Information in the form of an electrical impulse is carried away from the neuron’s cell body along the axon of a presynaptic neuron toward the axon terminals. When the electrical signal reaches the terminal, it cannot cross the ...
The role of synaptic ion channels in synaptic
... postsynaptic depolarization. Notably, unlike NMDA receptors, nAChRs are not blocked by Mg2+ at negative resting potentials; therefore, postsynaptic nAChR activity might assist the removal of the Mg2+ block from NMDA receptors and facilitate LTP ( Ji et al, 2001). The function of nAChRs at presynapti ...
... postsynaptic depolarization. Notably, unlike NMDA receptors, nAChRs are not blocked by Mg2+ at negative resting potentials; therefore, postsynaptic nAChR activity might assist the removal of the Mg2+ block from NMDA receptors and facilitate LTP ( Ji et al, 2001). The function of nAChRs at presynapti ...
Minerals on the Go
... Rules to Consider Rule: Whereas macrominerals (Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, Cl- etc.) travel in the blood and access cells primarily as free ions, the micronutrients (Cu2+, Zn2+, Fe2+, Mn2,, Se) rely on proteins and other ligands for transport and delivery Rule: Targeting microminerals to select organs and lo ...
... Rules to Consider Rule: Whereas macrominerals (Ca2+, Mg2+, Na+, Cl- etc.) travel in the blood and access cells primarily as free ions, the micronutrients (Cu2+, Zn2+, Fe2+, Mn2,, Se) rely on proteins and other ligands for transport and delivery Rule: Targeting microminerals to select organs and lo ...
NMDA receptor

The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and ion channel protein found in nerve cells. It is activated when glutamate and glycine (or D-serine) bind to it, and when activated it allows positively charged ions to flow through the cell membrane. The NMDA receptor is very important for controlling synaptic plasticity and memory function.The NMDAR is a specific type of ionotropic glutamate receptor. The NMDA receptor is named this because the agonist molecule N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) binds selectively to it, and not to other glutamate receptors. Activation of NMDA receptors results in the opening of an ion channel that is nonselective to cations with a reversal potential near 0 mV. A property of the NMDA receptor is its voltage-dependent activation, a result of ion channel block by extracellular Mg2+ & Zn2+ ions. This allows the flow of Na+ and small amounts of Ca2+ ions into the cell and K+ out of the cell to be voltage-dependent.Calcium flux through NMDARs is thought to be critical in synaptic plasticity, a cellular mechanism for learning and memory. The NMDA receptor is distinct in two ways: first, it is both ligand-gated and voltage-dependent; second, it requires co-activation by two ligands: glutamate and either D-serine or glycine.The activity of the NMDA receptor is affected by many psychoactive drugs such as phencyclidine (PCP), alcohol (ethanol) and dextromethorphan (DXM). The anaesthetic effects of the drugs ketamine and nitrous oxide are partially because of their effects on NMDA receptor activity.