Here we can focus directly on the input neurons, the Schaffer
... pyramidal cells. We now see on the right hand side this is the whole synaptic cell, notice we are now focusing on the post-synaptic cell. The early change for explicit memory storage is going to have a pull synaptic target rather than a p synaptic target. The Schaffer collaterals come in, they re ...
... pyramidal cells. We now see on the right hand side this is the whole synaptic cell, notice we are now focusing on the post-synaptic cell. The early change for explicit memory storage is going to have a pull synaptic target rather than a p synaptic target. The Schaffer collaterals come in, they re ...
Ren - University of Illinois Archives
... & Integrative Physiology, Univ. of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL 61801. Studies using cortical and hippocampal brain slices suggest that many young central synapses initially contain only NMDA receptors, and are thus functionally silent. The expression of AMPA receptors in the formerly si ...
... & Integrative Physiology, Univ. of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL 61801. Studies using cortical and hippocampal brain slices suggest that many young central synapses initially contain only NMDA receptors, and are thus functionally silent. The expression of AMPA receptors in the formerly si ...
Slide 1 - AccessPharmacy
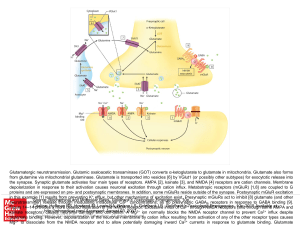
... Glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) converts α-ketoglutarate to glutamate in mitochondria. Glutamate also forms from glutamine via mitochondrial glutaminase. Glutamate is transported into vesicles [6] by VGlut1 (or possibly other subtypes) for exocytotic release ...
... Glutamatergic neurotransmission. Glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase (GOT) converts α-ketoglutarate to glutamate in mitochondria. Glutamate also forms from glutamine via mitochondrial glutaminase. Glutamate is transported into vesicles [6] by VGlut1 (or possibly other subtypes) for exocytotic release ...
Slide ()
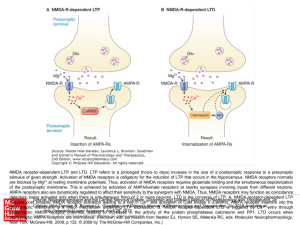
... stimulus of given strength. Activation of NMDA receptors is obligatory for the induction of LTP that occurs in the hippocampus. NMDA receptors normally are blocked by Mg2+ at resting membrane potentials. Thus, activation of NMDA receptors requires glutamate binding and the simultaneous depolarizatio ...
... stimulus of given strength. Activation of NMDA receptors is obligatory for the induction of LTP that occurs in the hippocampus. NMDA receptors normally are blocked by Mg2+ at resting membrane potentials. Thus, activation of NMDA receptors requires glutamate binding and the simultaneous depolarizatio ...
NMDA receptor

The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and ion channel protein found in nerve cells. It is activated when glutamate and glycine (or D-serine) bind to it, and when activated it allows positively charged ions to flow through the cell membrane. The NMDA receptor is very important for controlling synaptic plasticity and memory function.The NMDAR is a specific type of ionotropic glutamate receptor. The NMDA receptor is named this because the agonist molecule N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) binds selectively to it, and not to other glutamate receptors. Activation of NMDA receptors results in the opening of an ion channel that is nonselective to cations with a reversal potential near 0 mV. A property of the NMDA receptor is its voltage-dependent activation, a result of ion channel block by extracellular Mg2+ & Zn2+ ions. This allows the flow of Na+ and small amounts of Ca2+ ions into the cell and K+ out of the cell to be voltage-dependent.Calcium flux through NMDARs is thought to be critical in synaptic plasticity, a cellular mechanism for learning and memory. The NMDA receptor is distinct in two ways: first, it is both ligand-gated and voltage-dependent; second, it requires co-activation by two ligands: glutamate and either D-serine or glycine.The activity of the NMDA receptor is affected by many psychoactive drugs such as phencyclidine (PCP), alcohol (ethanol) and dextromethorphan (DXM). The anaesthetic effects of the drugs ketamine and nitrous oxide are partially because of their effects on NMDA receptor activity.