2015 department of medicine research day
... Design: This is an open-label, safety, pharmacokinetic (PK), dose-escalation, multicenter study. Rationale: KD019 was originally developed for a solid tumor indication, and is currently being investigated as a cancer treatment. In non-clinical studies, KD019 selectively inhibited key kinases and val ...
... Design: This is an open-label, safety, pharmacokinetic (PK), dose-escalation, multicenter study. Rationale: KD019 was originally developed for a solid tumor indication, and is currently being investigated as a cancer treatment. In non-clinical studies, KD019 selectively inhibited key kinases and val ...
Synapses and Neurotransmitters Notes
... Norepinephrine is strongly associated with bringing our nervous systems into "high alert." It is prevalent in the sympathetic nervous system, and it increases our heart rate and our blood pressure. Our adrenal glands release it into the blood stream, along with its close relative epinephrine (aka ad ...
... Norepinephrine is strongly associated with bringing our nervous systems into "high alert." It is prevalent in the sympathetic nervous system, and it increases our heart rate and our blood pressure. Our adrenal glands release it into the blood stream, along with its close relative epinephrine (aka ad ...
Presentation
... Put the spotlight on segments that can be a part of the best path and extend them. The best path is close to a diagonal n ...
... Put the spotlight on segments that can be a part of the best path and extend them. The best path is close to a diagonal n ...
The Nerve Impulse - hrsbstaff.ednet.ns.ca
... Many poisons and drugs affect the activity of chemical neurotransmitters at the synapses. Nerve gas, curare, botulin toxin, and some poisonous insecticides can interfere with the functioning of acetylcholine and cause muscle paralysis (death for respiratory paralysis). Stimulants cause a feeling of ...
... Many poisons and drugs affect the activity of chemical neurotransmitters at the synapses. Nerve gas, curare, botulin toxin, and some poisonous insecticides can interfere with the functioning of acetylcholine and cause muscle paralysis (death for respiratory paralysis). Stimulants cause a feeling of ...
Human Anatomy, First Edition McKinley&O'Loughlin
... Is the entire area through which the sensitive ends of the receptor cell are distributed. There is an inverse relationship between the size of the receptive field and our ability to identify the exact location of a stimulus. If the receptive field is small, precise localization and sensitivity are e ...
... Is the entire area through which the sensitive ends of the receptor cell are distributed. There is an inverse relationship between the size of the receptive field and our ability to identify the exact location of a stimulus. If the receptive field is small, precise localization and sensitivity are e ...
File
... A. An Action Potential (AP) is a self-propagating electrical signal caused by membrane depolarization resulting in the flow of sodium (Na+) ions into the cell and the flow of potassium (K+) ions out of the cell. B. Action Potentials occur on the axon portion of the neuron. ...
... A. An Action Potential (AP) is a self-propagating electrical signal caused by membrane depolarization resulting in the flow of sodium (Na+) ions into the cell and the flow of potassium (K+) ions out of the cell. B. Action Potentials occur on the axon portion of the neuron. ...
What Is the Role of Neurotransmitter Systems in Cortical Seizures?
... antiepileptic drugs (Jones-Davis and Macdonald 2003, Rogawski and Loscher 2004, Meldrum and Rogawski 2007, White et al. 2007). Sites of action of individual drugs are different, major mechanisms of action are presented in Figure 1. Opposite way, i.e. suppression of excitatory transmission using anta ...
... antiepileptic drugs (Jones-Davis and Macdonald 2003, Rogawski and Loscher 2004, Meldrum and Rogawski 2007, White et al. 2007). Sites of action of individual drugs are different, major mechanisms of action are presented in Figure 1. Opposite way, i.e. suppression of excitatory transmission using anta ...
File - Wk 1-2
... Inverse Agonist: a drug capable of reducing the constitutive activation (have negative efficacy) ...
... Inverse Agonist: a drug capable of reducing the constitutive activation (have negative efficacy) ...
Drugs Of Abuse: A Pharmacological Perspective
... Used medically and recreationally since 5000 BC Sap contains the opiates morphine, codeine and thebaine Opioids: compounds binding to the opiate receptors (agonists) Heroin and other opioids synthesized from morphine ...
... Used medically and recreationally since 5000 BC Sap contains the opiates morphine, codeine and thebaine Opioids: compounds binding to the opiate receptors (agonists) Heroin and other opioids synthesized from morphine ...
No Slide Title
... the most important being: 1. Glutamate: Also known as glutamic acid and is found throughout the brain. It produces EPSP's in the postsynaptic membrane but also directly affects axons by lowering their threshold of excitation, thus increasing the rate at which action potentials occur. Some Orient ...
... the most important being: 1. Glutamate: Also known as glutamic acid and is found throughout the brain. It produces EPSP's in the postsynaptic membrane but also directly affects axons by lowering their threshold of excitation, thus increasing the rate at which action potentials occur. Some Orient ...
Zoology Assignment - Wikimedia Commons
... Compound eyes consist of a few to many distinct units called ommatidia (ommato, eye+ium, little) (figure. 4c). Although compound eyes occur in some annelids and bivalve molluscs, they are best developed and understood in arthropods. A compound eye may contain thousands of ommatidia, each oriented in ...
... Compound eyes consist of a few to many distinct units called ommatidia (ommato, eye+ium, little) (figure. 4c). Although compound eyes occur in some annelids and bivalve molluscs, they are best developed and understood in arthropods. A compound eye may contain thousands of ommatidia, each oriented in ...
Autonomic Nervous System ANS - Anderson School District One
... • α1 & β1 produce excitation when activated • α2 & β2 receptors cause inhibition of effector tissues • β3 found only on cells of brown adipose where activation causes thermogenesis (heat production) ...
... • α1 & β1 produce excitation when activated • α2 & β2 receptors cause inhibition of effector tissues • β3 found only on cells of brown adipose where activation causes thermogenesis (heat production) ...
Document
... Wild type receptors can be mutated via a PCR based site-directed mutagenesis protocol. We have also demonstrated that high transient expression levels can be obtained using a lipid based transfection protocol. ...
... Wild type receptors can be mutated via a PCR based site-directed mutagenesis protocol. We have also demonstrated that high transient expression levels can be obtained using a lipid based transfection protocol. ...
Review notes
... Therapeutic dose: promotes excretion and inhibits reabsorption of uric acid Sub-therapeutic dose: inhibits both excretion and reabsorption ...
... Therapeutic dose: promotes excretion and inhibits reabsorption of uric acid Sub-therapeutic dose: inhibits both excretion and reabsorption ...
C1 Effects of piperine, the pungent ingredient of black pepper, at the
... resiniferatoxin (100 nM, 3.16 ± 0.08 fold, n = 5). These data are consistent with a mechanism in which protons mediate a distinct agonist-independent effect on TRPV1 function rather than by altering agonist potency. In further experiments, we noted that the degree of potentiation by protons was rela ...
... resiniferatoxin (100 nM, 3.16 ± 0.08 fold, n = 5). These data are consistent with a mechanism in which protons mediate a distinct agonist-independent effect on TRPV1 function rather than by altering agonist potency. In further experiments, we noted that the degree of potentiation by protons was rela ...
MOTM SALVINORIN A MAGIC MINT
... It's also a more powerful hallucinogen than LSD”. Its effects seem qualitatively different from other hallucinogens. People taking it sometimes report feelings of madness but some effects seem frequent, involving distortion of perception, such as moving in a particular direction like spinning or str ...
... It's also a more powerful hallucinogen than LSD”. Its effects seem qualitatively different from other hallucinogens. People taking it sometimes report feelings of madness but some effects seem frequent, involving distortion of perception, such as moving in a particular direction like spinning or str ...
2 receptor
... An unpleasant sensory or emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Pain is always subjective. Each individual learns the application of the word through experiences related to injury in early life. It is unquestionably a sensation i ...
... An unpleasant sensory or emotional experience associated with actual or potential tissue damage, or described in terms of such damage. Pain is always subjective. Each individual learns the application of the word through experiences related to injury in early life. It is unquestionably a sensation i ...
The Glutamate Uptake Inhibitor L- Trans
... Sodium-dependent high-affinity uptake of glutamate is thought to play a major role in the maintenance of very low extracellular concentrations of excitatory amino acids (EAA), and may modulate the actions of released transmitter at G-protein-coupled receptors and extrasynaptic receptors that are act ...
... Sodium-dependent high-affinity uptake of glutamate is thought to play a major role in the maintenance of very low extracellular concentrations of excitatory amino acids (EAA), and may modulate the actions of released transmitter at G-protein-coupled receptors and extrasynaptic receptors that are act ...
Spare Receptors
... only on the affinity of the receptor for binding an agonist (KD) but also on the degree of spareness, i.e. the total number of receptors compared to the number actually needed to elicit a maximal biologic response The KD of the agonist-receptor interaction determines what fraction (B/Bmax) of total ...
... only on the affinity of the receptor for binding an agonist (KD) but also on the degree of spareness, i.e. the total number of receptors compared to the number actually needed to elicit a maximal biologic response The KD of the agonist-receptor interaction determines what fraction (B/Bmax) of total ...
Receptor-drug interaction
... CNS: - Sympathetic - Parasympathetic - Signals move through [polarization-depolarization] mechanism Liver: - Detoxification process - Storage device Hormones: - From where they produced - How they work To understand all this you have to understand the molecular level of body organization ...
... CNS: - Sympathetic - Parasympathetic - Signals move through [polarization-depolarization] mechanism Liver: - Detoxification process - Storage device Hormones: - From where they produced - How they work To understand all this you have to understand the molecular level of body organization ...
Slide () - Access Emergency Medicine
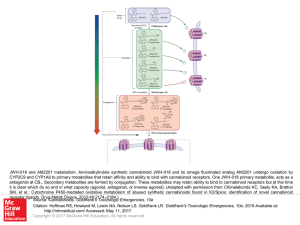
... CYP2C9 and CYP1A9 to primary metabolites that retain affinity and ability to bind with cannabinoid receptors. One JWH-018 primary metabolite, acts as a antagonist at CB1. Secondary metabolites are formed by conjugation. These metabolites may retain ability to bind to cannabinoid receptors but at thi ...
... CYP2C9 and CYP1A9 to primary metabolites that retain affinity and ability to bind with cannabinoid receptors. One JWH-018 primary metabolite, acts as a antagonist at CB1. Secondary metabolites are formed by conjugation. These metabolites may retain ability to bind to cannabinoid receptors but at thi ...
File - NorthStar Mental Wellness
... North American Center for Continuing Medical Education, LLC (NACCME) is approved by the American Psychological Association to sponsor continuing education for psychologists. NACCME maintains responsibility for this program and its content. Physician assistants, nurse practitioners and nurses may par ...
... North American Center for Continuing Medical Education, LLC (NACCME) is approved by the American Psychological Association to sponsor continuing education for psychologists. NACCME maintains responsibility for this program and its content. Physician assistants, nurse practitioners and nurses may par ...
The TNF and TNFR superfamilies
... Tumor-necrosis factor (TNF) was discovered as a serum factor that was able to kill cancer cells in mice. The TNF receptor (TNFR) led to the discovery of a superfamily of transmembrane proteins. There are 18 ligands and 28 receptors many of which are being targeted for therapeutic purposes. TNFR sig ...
... Tumor-necrosis factor (TNF) was discovered as a serum factor that was able to kill cancer cells in mice. The TNF receptor (TNFR) led to the discovery of a superfamily of transmembrane proteins. There are 18 ligands and 28 receptors many of which are being targeted for therapeutic purposes. TNFR sig ...
NMDA receptor

The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and ion channel protein found in nerve cells. It is activated when glutamate and glycine (or D-serine) bind to it, and when activated it allows positively charged ions to flow through the cell membrane. The NMDA receptor is very important for controlling synaptic plasticity and memory function.The NMDAR is a specific type of ionotropic glutamate receptor. The NMDA receptor is named this because the agonist molecule N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) binds selectively to it, and not to other glutamate receptors. Activation of NMDA receptors results in the opening of an ion channel that is nonselective to cations with a reversal potential near 0 mV. A property of the NMDA receptor is its voltage-dependent activation, a result of ion channel block by extracellular Mg2+ & Zn2+ ions. This allows the flow of Na+ and small amounts of Ca2+ ions into the cell and K+ out of the cell to be voltage-dependent.Calcium flux through NMDARs is thought to be critical in synaptic plasticity, a cellular mechanism for learning and memory. The NMDA receptor is distinct in two ways: first, it is both ligand-gated and voltage-dependent; second, it requires co-activation by two ligands: glutamate and either D-serine or glycine.The activity of the NMDA receptor is affected by many psychoactive drugs such as phencyclidine (PCP), alcohol (ethanol) and dextromethorphan (DXM). The anaesthetic effects of the drugs ketamine and nitrous oxide are partially because of their effects on NMDA receptor activity.