PRINCIPLES OF SENSORY TRANSDUCTION
... the stimuli. Both are generated by neural processing in the retina. (C) In the auditory system, primary neurons y single g tones. The outline of this excitatory y area is known as the tuning g curve. When the neuron is are excited by excited by a tone in this area, the introduction of a second tone ...
... the stimuli. Both are generated by neural processing in the retina. (C) In the auditory system, primary neurons y single g tones. The outline of this excitatory y area is known as the tuning g curve. When the neuron is are excited by excited by a tone in this area, the introduction of a second tone ...
NEUROTRANSMITTERS AND RECEPTORS AS THE TARGETS FOR ADDICTION TREATMENT: A
... increases in extracellular DA, an effect that seems to be dependent on the presence of α4β2 nAChRs, and is blocked by nAChR blockers such as mecamylamine. Role of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in drug dependence A direct and indirect role for nAChRs in drug dependence has been observed. For exam ...
... increases in extracellular DA, an effect that seems to be dependent on the presence of α4β2 nAChRs, and is blocked by nAChR blockers such as mecamylamine. Role of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in drug dependence A direct and indirect role for nAChRs in drug dependence has been observed. For exam ...
proposal2000a.doc
... the mature postsynaptic cell, GABA inhibitory action is different through other receptors. Through GABAB receptors, binding of GABA activates G-proteins that increase potassium and calcium channels’ permeability, so activation of these receptors results in a slow, long-lasting hyperpolarization of t ...
... the mature postsynaptic cell, GABA inhibitory action is different through other receptors. Through GABAB receptors, binding of GABA activates G-proteins that increase potassium and calcium channels’ permeability, so activation of these receptors results in a slow, long-lasting hyperpolarization of t ...
Neural Integration I: Sensory Pathways and the
... • Little specificity (i.e.: free nerve endings respond to stimulus caused by chemicals, pressure, temperature or trauma) ...
... • Little specificity (i.e.: free nerve endings respond to stimulus caused by chemicals, pressure, temperature or trauma) ...
Chapter 22 Thalamus
... Receptors; specialized cells which convert external stimulus energy into a signal that produces a neural response Each of the fundamental types of stimuli has a separate population of receptors selective for the particular form of energy Within a single sensory system are classes of receptors ...
... Receptors; specialized cells which convert external stimulus energy into a signal that produces a neural response Each of the fundamental types of stimuli has a separate population of receptors selective for the particular form of energy Within a single sensory system are classes of receptors ...
Poster
... painkillers such as OxyContin and Vicodin is largely attributed to the response they trigger in proteins such as mu opioid receptors (MOPs). This receptor activates cellular signaling pathways responsible for dulling pain; however, the protein also has the ability to stimulate cellular signaling pat ...
... painkillers such as OxyContin and Vicodin is largely attributed to the response they trigger in proteins such as mu opioid receptors (MOPs). This receptor activates cellular signaling pathways responsible for dulling pain; however, the protein also has the ability to stimulate cellular signaling pat ...
I. The direct-acting drugs
... chemical structures and mechanism of action To understand major pharmacological effects and therapeutic applications To understand major adverse reactions ...
... chemical structures and mechanism of action To understand major pharmacological effects and therapeutic applications To understand major adverse reactions ...
Opioids General - IHMC Public Cmaps (3)
... Recent information regarding the peripheral endogenous opioid system (PEOS) has presented a unique opportunity to use the powerful analgesic effect of opiates while minimizing untoward systemic effects. The PEOS includes peripheral opioid receptors (POR) and peripheral leukocyte-derived opioids (PLD ...
... Recent information regarding the peripheral endogenous opioid system (PEOS) has presented a unique opportunity to use the powerful analgesic effect of opiates while minimizing untoward systemic effects. The PEOS includes peripheral opioid receptors (POR) and peripheral leukocyte-derived opioids (PLD ...
How Do Muscles Work?
... The calcium ions cause the movement of troponin and tropomyosin on their thin (actin) filaments, which then enables the myosin molecule heads to "grab and swivel" their way along the thin filament. ...
... The calcium ions cause the movement of troponin and tropomyosin on their thin (actin) filaments, which then enables the myosin molecule heads to "grab and swivel" their way along the thin filament. ...
Altered Glutamate Receptor Function during Recovery of Bladder
... MO). The uninjured, subacute, and chronic SCI animals were randomly assigned for treatment with either NBQX (n ⫽ 8, 10, and 9, respectively) or CPP (n ⫽ 7, 9, and 9, respectively). The intrathecal catheterization was done as previously described (Storkson et al., 1996). Animals were anesthetized wit ...
... MO). The uninjured, subacute, and chronic SCI animals were randomly assigned for treatment with either NBQX (n ⫽ 8, 10, and 9, respectively) or CPP (n ⫽ 7, 9, and 9, respectively). The intrathecal catheterization was done as previously described (Storkson et al., 1996). Animals were anesthetized wit ...
FYI information about sensory perception
... is much larger. In order for a person to feel two points, two separate central neuronal populations must be activated by stimulation of their respective receptive fields. When this happens, two points are reported. To summarize, two-point discrimination depends on activating two separate populations ...
... is much larger. In order for a person to feel two points, two separate central neuronal populations must be activated by stimulation of their respective receptive fields. When this happens, two points are reported. To summarize, two-point discrimination depends on activating two separate populations ...
Gene Section ESRRG (estrogen-related receptor gamma) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... as coactivators or corepressors. Coactivators and corepressors bind directly to nuclear receptors, most often within the carboxyl-terminal activation function-2 (AF2) domain that participates in ligand-binding but some can exert their effects by binding to the aminoterminal AF1 domain or the flexibl ...
... as coactivators or corepressors. Coactivators and corepressors bind directly to nuclear receptors, most often within the carboxyl-terminal activation function-2 (AF2) domain that participates in ligand-binding but some can exert their effects by binding to the aminoterminal AF1 domain or the flexibl ...
Love at First Smell — The 2004 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
... must locate and evaluate sources of food and avoid becoming food for predators. They must identify mating partners so that they can pass on their genes. Evolutionary pressure has thus produced elaborate olfactory systems that contribute to the survival of both the individual and the species. In the ...
... must locate and evaluate sources of food and avoid becoming food for predators. They must identify mating partners so that they can pass on their genes. Evolutionary pressure has thus produced elaborate olfactory systems that contribute to the survival of both the individual and the species. In the ...
No Slide Title
... Note the “propeller” in the b subunit which caps the a subunit, preventing either subunit from interacting with the effector (There is no effector in this structure): ...
... Note the “propeller” in the b subunit which caps the a subunit, preventing either subunit from interacting with the effector (There is no effector in this structure): ...
Post-pubertal Emergence of Prefrontal Cortical Up
... activation of D1 and NMDA receptors in PFC pyramidal neurons may reflect the activity of a local neuronal network. D1--NMDA-mediated Plateau Depolarizations Involve Intracellular Ca2+, L-type Ca2+ Channels, Protein Kinase A and Voltage-gated Na+ Channels Several cellular mechanisms may also contribut ...
... activation of D1 and NMDA receptors in PFC pyramidal neurons may reflect the activity of a local neuronal network. D1--NMDA-mediated Plateau Depolarizations Involve Intracellular Ca2+, L-type Ca2+ Channels, Protein Kinase A and Voltage-gated Na+ Channels Several cellular mechanisms may also contribut ...
Unit 3-2 Nervous System Pt 2 Notes File
... •Mechanoreceptors – respond to touch, pressure, vibration, stretch, and itch •Thermoreceptors – sensitive to changes in temperature •Photoreceptors – respond to light energy (e.g., retina) •Chemoreceptors – respond to chemicals (e.g., smell, taste, changes in blood chemistry) •Nociceptors – sensitiv ...
... •Mechanoreceptors – respond to touch, pressure, vibration, stretch, and itch •Thermoreceptors – sensitive to changes in temperature •Photoreceptors – respond to light energy (e.g., retina) •Chemoreceptors – respond to chemicals (e.g., smell, taste, changes in blood chemistry) •Nociceptors – sensitiv ...
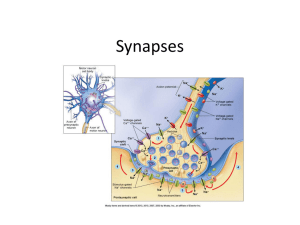
4. Nervous System: Synapses
... several working together or “rapid fire” of repeated stimulation= summation • Does all sensory information received by sensory neurons get transmitted to conscious part of brain? ...
... several working together or “rapid fire” of repeated stimulation= summation • Does all sensory information received by sensory neurons get transmitted to conscious part of brain? ...
Recitation 16 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... Ions can move across membranes through pumps and channels. Integral membrane proteins like these cross the membrane via transmembrane domains. Pumps are ATPases that set up the concentration gradients of ions across cell membranes, such that K+ is high inside cells and other ions (such as Cl–, Na+, ...
... Ions can move across membranes through pumps and channels. Integral membrane proteins like these cross the membrane via transmembrane domains. Pumps are ATPases that set up the concentration gradients of ions across cell membranes, such that K+ is high inside cells and other ions (such as Cl–, Na+, ...
5-HT receptor - Pharmatutor
... The serotonin receptors also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors or 5-HT receptors are a group of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs) found in the central and peripheral nervous systems.[1][2] They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The ...
... The serotonin receptors also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine receptors or 5-HT receptors are a group of G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs) found in the central and peripheral nervous systems.[1][2] They mediate both excitatory and inhibitory neurotransmission. The ...
Slide 1
... medulla and peripheral adrenergic nerve endings. 2. direct blockade of CA receptors. 3. antiarrhythmic properties related to calcium channel antagonism. An initial bolus dose of 40-60mg/kg IV followed by 2g/hr has been a suggested regimen ...
... medulla and peripheral adrenergic nerve endings. 2. direct blockade of CA receptors. 3. antiarrhythmic properties related to calcium channel antagonism. An initial bolus dose of 40-60mg/kg IV followed by 2g/hr has been a suggested regimen ...
Drug-drug interactions in inpatient and outpatient settings in Iran: a
... There are two types of neurotransmitter receptors [9]: 1- ligand-gated receptors or ionotropic receptors 2- G protein-coupled receptors or metabotropic receptors. Ligand-gated receptors These receptors are a group of trans-membrane ion channel proteins that are opened or closed in response to the bi ...
... There are two types of neurotransmitter receptors [9]: 1- ligand-gated receptors or ionotropic receptors 2- G protein-coupled receptors or metabotropic receptors. Ligand-gated receptors These receptors are a group of trans-membrane ion channel proteins that are opened or closed in response to the bi ...
Neuron Structure and Function
... In mammals a combination of the T1R2/T1R3 receptors have a response to sugars and sweeteners These receptors stimulate a G protein (Gp) which in this case activates phosopholipase C (PLC) PLC breaks down PIP2 (phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate) into IP3 (inositol triphosphosphate) and DAG ...
... In mammals a combination of the T1R2/T1R3 receptors have a response to sugars and sweeteners These receptors stimulate a G protein (Gp) which in this case activates phosopholipase C (PLC) PLC breaks down PIP2 (phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate) into IP3 (inositol triphosphosphate) and DAG ...
AP Biology - wlhs.wlwv.k12.or.us
... **NOTE: This chapter is often considered difficult as you have not covered it in your general biology course. Plan on reading this chapter slowly!! I would suggest that you read the key concepts in bold first and then for each concept, look at the headings, then the figures and then READ for detail… ...
... **NOTE: This chapter is often considered difficult as you have not covered it in your general biology course. Plan on reading this chapter slowly!! I would suggest that you read the key concepts in bold first and then for each concept, look at the headings, then the figures and then READ for detail… ...
here - York University
... that are used to bind the vesicles to the membrane and then facilitate their fusion causing the release of the neurotransmitters. When an action potential invades an axonal terminal, voltage-gated calcium channels open causing an increase in calcium in the cytoplasm. Higher concentration of calcium ...
... that are used to bind the vesicles to the membrane and then facilitate their fusion causing the release of the neurotransmitters. When an action potential invades an axonal terminal, voltage-gated calcium channels open causing an increase in calcium in the cytoplasm. Higher concentration of calcium ...
NMDA receptor

The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor (also known as the NMDA receptor or NMDAR), is a glutamate receptor and ion channel protein found in nerve cells. It is activated when glutamate and glycine (or D-serine) bind to it, and when activated it allows positively charged ions to flow through the cell membrane. The NMDA receptor is very important for controlling synaptic plasticity and memory function.The NMDAR is a specific type of ionotropic glutamate receptor. The NMDA receptor is named this because the agonist molecule N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) binds selectively to it, and not to other glutamate receptors. Activation of NMDA receptors results in the opening of an ion channel that is nonselective to cations with a reversal potential near 0 mV. A property of the NMDA receptor is its voltage-dependent activation, a result of ion channel block by extracellular Mg2+ & Zn2+ ions. This allows the flow of Na+ and small amounts of Ca2+ ions into the cell and K+ out of the cell to be voltage-dependent.Calcium flux through NMDARs is thought to be critical in synaptic plasticity, a cellular mechanism for learning and memory. The NMDA receptor is distinct in two ways: first, it is both ligand-gated and voltage-dependent; second, it requires co-activation by two ligands: glutamate and either D-serine or glycine.The activity of the NMDA receptor is affected by many psychoactive drugs such as phencyclidine (PCP), alcohol (ethanol) and dextromethorphan (DXM). The anaesthetic effects of the drugs ketamine and nitrous oxide are partially because of their effects on NMDA receptor activity.