supplemental materials
... these regions contain fragmented density (not shown) indicating local conformational heterogeneity. Some regions of poor correlation are due to the incompleteness of the atomic model. For example, density is present in the cryo-EM map that probably corresponds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence at the 5 ...
... these regions contain fragmented density (not shown) indicating local conformational heterogeneity. Some regions of poor correlation are due to the incompleteness of the atomic model. For example, density is present in the cryo-EM map that probably corresponds to the Shine-Dalgarno sequence at the 5 ...
Crosstalk in NF-κB signaling pathways
... of IRF3 (ref. 28). The relative contribution to this process of TRAFs and other E3 ligases needs further investigation under physiological conditions. Furthermore, it remains unclear whether the requirement for TRAF3 in interferon production likewise depends on its E3 ligase activity. As it would se ...
... of IRF3 (ref. 28). The relative contribution to this process of TRAFs and other E3 ligases needs further investigation under physiological conditions. Furthermore, it remains unclear whether the requirement for TRAF3 in interferon production likewise depends on its E3 ligase activity. As it would se ...
Molecular Recognition of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins by
... of methyl viologen (MV), and the resulting Q8•MV complex binds to 2,6dihydroxynaphthalene (HN). Binding of HN produces a new visible charge-transfer absorbance and the quenching of HN fluorescence. A crystal structure shows that the two aromatic groups are stacked face-to-face in the cavity of Q8. I ...
... of methyl viologen (MV), and the resulting Q8•MV complex binds to 2,6dihydroxynaphthalene (HN). Binding of HN produces a new visible charge-transfer absorbance and the quenching of HN fluorescence. A crystal structure shows that the two aromatic groups are stacked face-to-face in the cavity of Q8. I ...
Darnell, JC, Warren, ST and Darnell, RB: The fragile X mental retardation protein, FMRP, recognizes G-quartets. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews 10:49-52 (2004).
... hnRNP-K, and a less well-defined element consisting of repeats of the amino acid element RGG (the RGG-box). Initial work on hnRNP-K had revealed a role for this protein in the regulation of translational control of a specific RNA target, the 15-lipoxygenase mRNA expressed in erythrocytes [Ostareck et ...
... hnRNP-K, and a less well-defined element consisting of repeats of the amino acid element RGG (the RGG-box). Initial work on hnRNP-K had revealed a role for this protein in the regulation of translational control of a specific RNA target, the 15-lipoxygenase mRNA expressed in erythrocytes [Ostareck et ...
Sample & Assay Technologies QIAgenes E. coli
... express lysozyme (a natural inhibitor of T7 RNA polymerase) and provide an additional level of regulation. Lysozyme inhibits T7 RNA polymerase potentially generated by “leaky” repression prior to induction. Tight regulation is of special importance if proteins toxic to E. coli are produced. Tighter ...
... express lysozyme (a natural inhibitor of T7 RNA polymerase) and provide an additional level of regulation. Lysozyme inhibits T7 RNA polymerase potentially generated by “leaky” repression prior to induction. Tight regulation is of special importance if proteins toxic to E. coli are produced. Tighter ...
In Silico Prediction of the Peroxisomal Proteome in Fungi, Plants
... method to scan the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ORFs for potential peroxisomal proteins. Including both PTS1 and PTS2 motifs in their search, they found 18 new potential peroxisomal proteins. GFP fusions allowed them to confirm that about half of these proteins were truly located in the peroxisome. Anot ...
... method to scan the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ORFs for potential peroxisomal proteins. Including both PTS1 and PTS2 motifs in their search, they found 18 new potential peroxisomal proteins. GFP fusions allowed them to confirm that about half of these proteins were truly located in the peroxisome. Anot ...
TETHERING: Fragment-Based Drug Discovery
... NON-TETHERING METHODS Detecting fragments that bind a target can be challenging. Traditional high-throughput screening (HTS) typically relies on inhibition assays. But high concentrations of compound may be needed to find weak inhibitors. For example, an inhibitor with an IC50 of 1 mM produces less ...
... NON-TETHERING METHODS Detecting fragments that bind a target can be challenging. Traditional high-throughput screening (HTS) typically relies on inhibition assays. But high concentrations of compound may be needed to find weak inhibitors. For example, an inhibitor with an IC50 of 1 mM produces less ...
12 Insights into the mechanisms underlying CFTR channel activity
... The role of the R domain in channel gating In addition to the structural features shared with other ABC proteins, CFTR also contains a unique 241‑residue R domain in the linker region that joins the two halves of the protein [35] and is essential for its activity [36]. The highly charged R domain po ...
... The role of the R domain in channel gating In addition to the structural features shared with other ABC proteins, CFTR also contains a unique 241‑residue R domain in the linker region that joins the two halves of the protein [35] and is essential for its activity [36]. The highly charged R domain po ...
Isolation and Characterization of Foaming Proteins of
... "Foaming proteins" that retained the full foaming capacity of the original beer were isolated by ultrafiltration followed by ammonium sulfate precipitation and ion-exchange chromatography on diethylaminoethylcellulose. Because the content of foaming proteins correlated well with head formation of ma ...
... "Foaming proteins" that retained the full foaming capacity of the original beer were isolated by ultrafiltration followed by ammonium sulfate precipitation and ion-exchange chromatography on diethylaminoethylcellulose. Because the content of foaming proteins correlated well with head formation of ma ...
a curated database for protein phosphorylation sites in prokaryotes
... its critical roles in various cellular processes such as signal transduction. Thus, an integrative data resource of the prokaryotic phosphorylation will be useful for further analysis. In this study, we presented a curated database of phosphorylation sites in prokaryotes (dbPSP, Database URL: http:/ ...
... its critical roles in various cellular processes such as signal transduction. Thus, an integrative data resource of the prokaryotic phosphorylation will be useful for further analysis. In this study, we presented a curated database of phosphorylation sites in prokaryotes (dbPSP, Database URL: http:/ ...
IndelFR: a database of indels in protein structures and their flanking
... D512–D518 Nucleic Acids Research, 2012, Vol. 40, Database issue ...
... D512–D518 Nucleic Acids Research, 2012, Vol. 40, Database issue ...
Apolipophorins and insects immune response
... Insect lipoproteins, called lipophorins, are non-covalent assemblies of lipids and proteins serving as lipid transport vehicles. The protein moiety of lipophorin comprises two glycosylated apolipoproteins, apolipophorin I (apoLp-I) and apolipophorin II (apoLp-II), constantly present in a lipophorin ...
... Insect lipoproteins, called lipophorins, are non-covalent assemblies of lipids and proteins serving as lipid transport vehicles. The protein moiety of lipophorin comprises two glycosylated apolipoproteins, apolipophorin I (apoLp-I) and apolipophorin II (apoLp-II), constantly present in a lipophorin ...
and gender-specific hallmarks
... signalling/metabolism, protein levels must be assessed. We have extensively analysed visceral adipose tissue from age-, T2DM- and gender-matched obese patients using high-throughput proteomics and systems biology methods to identify new biomarkers for the onset of T2DM in obesity, as well as to gain ...
... signalling/metabolism, protein levels must be assessed. We have extensively analysed visceral adipose tissue from age-, T2DM- and gender-matched obese patients using high-throughput proteomics and systems biology methods to identify new biomarkers for the onset of T2DM in obesity, as well as to gain ...
Glial inhibition of CNS axon regeneration
... glycoprotein (MAG)22,23, Nogo-A14–16, oligodendrocyte myelin glycoprotein (OMgp)24, ephrin B3 (REF. 26) and the transmembrane semaphorin 4D (Sema4D)25. Although the topology of Nogo-A remains unclear, both the 66 amino acid loop (Nogo-66) and the amino-terminal domain (amino-Nogo) are known to be in ...
... glycoprotein (MAG)22,23, Nogo-A14–16, oligodendrocyte myelin glycoprotein (OMgp)24, ephrin B3 (REF. 26) and the transmembrane semaphorin 4D (Sema4D)25. Although the topology of Nogo-A remains unclear, both the 66 amino acid loop (Nogo-66) and the amino-terminal domain (amino-Nogo) are known to be in ...
The Multiple Personalities of the Regulatory Subunit of Protein
... proliferation and survival [3, 4]. Genetic studies in organisms such as yeast and slime mould have revealed that CK2 is essential for viability [5, 6]. Recent studies of molecular clock machinery in Drosophila and Arabidopsis have also provided evidence for the involvement of CK2 in circadian oscill ...
... proliferation and survival [3, 4]. Genetic studies in organisms such as yeast and slime mould have revealed that CK2 is essential for viability [5, 6]. Recent studies of molecular clock machinery in Drosophila and Arabidopsis have also provided evidence for the involvement of CK2 in circadian oscill ...
Screening for increased protein thiol oxidation in oxidatively
... variety of antioxidant systems to remove reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated from a variety of sources. Disruption of this oxidative balance, often referred to as oxidative stress, is evident in many chronic disease states including muscle wasting conditions and may contribute to the pathology [ ...
... variety of antioxidant systems to remove reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated from a variety of sources. Disruption of this oxidative balance, often referred to as oxidative stress, is evident in many chronic disease states including muscle wasting conditions and may contribute to the pathology [ ...
fulltekst
... the spliceosome to create different mRNAs, giving the ability for one gene to encode for many different proteins. Both transcription and splicing are regulated by cellular as well as viral proteins. The activity of these regulatory proteins is often regulated by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation ...
... the spliceosome to create different mRNAs, giving the ability for one gene to encode for many different proteins. Both transcription and splicing are regulated by cellular as well as viral proteins. The activity of these regulatory proteins is often regulated by phosphorylation and dephosphorylation ...
Cellular control of cholesterol
... membrane. Cholesterol helps to restrict the passage of molecules by increasing the packing of phospholipids. Cholesterol can fit into spaces between phospholipids and prevent water-soluble molecules from diffusing across the membrane. THe hydrophilic hydroxyl group of cholesterol interacts with aque ...
... membrane. Cholesterol helps to restrict the passage of molecules by increasing the packing of phospholipids. Cholesterol can fit into spaces between phospholipids and prevent water-soluble molecules from diffusing across the membrane. THe hydrophilic hydroxyl group of cholesterol interacts with aque ...
Lewis lung carcinoma regulation of mechanical stretch - AJP-Cell
... stimulation can occur independent of Akt, and there is evidence that signaling involving phospholipase D (25, 73) and extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) (34, 38) is involved in the process. Mechanical stimuli can activate muscle ERK1/2 and p38 signaling (37, 44), which can both indu ...
... stimulation can occur independent of Akt, and there is evidence that signaling involving phospholipase D (25, 73) and extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) (34, 38) is involved in the process. Mechanical stimuli can activate muscle ERK1/2 and p38 signaling (37, 44), which can both indu ...
scf and cullin/ring h2-based
... likely to be direct. Skowyra et al (1997) and Feldman et al (1997) next demonstrated that Cdc4, Cdc53, and ySkp1 expressed in insect cells assemble into a complex and that the purified complex functions as a ubiquitin ligase, promoting ubiquitination of phosphorylated Sic1 by the yCdc34 ubiquitin-co ...
... likely to be direct. Skowyra et al (1997) and Feldman et al (1997) next demonstrated that Cdc4, Cdc53, and ySkp1 expressed in insect cells assemble into a complex and that the purified complex functions as a ubiquitin ligase, promoting ubiquitination of phosphorylated Sic1 by the yCdc34 ubiquitin-co ...
Glycerolipid transfer for the building of membranes in plant cells.
... Xu et al. identified another chloroplastic ABC type protein (TGD1) (At1g19800) that is likely dedicated to the import of phosphatidate from the ER to the chloroplast for the synthesis of eukaryotic galactoglycerolipids [36, 37]. The so-called prokaryotic and eukaryotic types of galactoglycerolipid s ...
... Xu et al. identified another chloroplastic ABC type protein (TGD1) (At1g19800) that is likely dedicated to the import of phosphatidate from the ER to the chloroplast for the synthesis of eukaryotic galactoglycerolipids [36, 37]. The so-called prokaryotic and eukaryotic types of galactoglycerolipid s ...
E-mail: - HAL
... the numerous attempts to depict the connecting regions more precisely.12-16 Many research groups have designed fragment libraries or structural alphabets to try to describe the local structural features of known protein structures more accurately.17-29 These libraries or alphabets correspond to fini ...
... the numerous attempts to depict the connecting regions more precisely.12-16 Many research groups have designed fragment libraries or structural alphabets to try to describe the local structural features of known protein structures more accurately.17-29 These libraries or alphabets correspond to fini ...
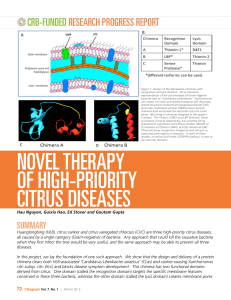
novel therapy of high-priority citrus diseases
... category, thereby allowing us to choose the chimera with the highest anti-bacterial activity. Thionin1-D4E1 chimera was the first one that we started working on three years ago. At that time, the sequence of the citrus genome was not completed, and hence complete screening of citrus Thionins was not ...
... category, thereby allowing us to choose the chimera with the highest anti-bacterial activity. Thionin1-D4E1 chimera was the first one that we started working on three years ago. At that time, the sequence of the citrus genome was not completed, and hence complete screening of citrus Thionins was not ...
View PDF - CiteSeerX
... Introduction Steroid hormones are cholesterol derivatives that serve as signaling molecules to coordinate the expression of complex gene programs in higher eukaryotes. These molecules exert their effects by diffusing into cells and interacting with specific intracellular receptors. Receptors for eac ...
... Introduction Steroid hormones are cholesterol derivatives that serve as signaling molecules to coordinate the expression of complex gene programs in higher eukaryotes. These molecules exert their effects by diffusing into cells and interacting with specific intracellular receptors. Receptors for eac ...
The Glutamate Uptake Inhibitor L- Trans
... Sodium-dependent high-affinity uptake of glutamate is thought to play a major role in the maintenance of very low extracellular concentrations of excitatory amino acids (EAA), and may modulate the actions of released transmitter at G-protein-coupled receptors and extrasynaptic receptors that are act ...
... Sodium-dependent high-affinity uptake of glutamate is thought to play a major role in the maintenance of very low extracellular concentrations of excitatory amino acids (EAA), and may modulate the actions of released transmitter at G-protein-coupled receptors and extrasynaptic receptors that are act ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).