CitA (citrate) and DcuS (C 4 -dicarboxylate) sensor kinases in
... CitAGt is a citrate specific sensor that is able to replace CitAEC in the heterologous system and ...
... CitAGt is a citrate specific sensor that is able to replace CitAEC in the heterologous system and ...
Structure and mechanism of ATP-dependent phospholipid transporters
... this protein family. The 12 membrane-spanning segments arrange into two bundles of six with a large cavity in between that can either be open-inwards (to the cytosol) or open-outwards (to the extracellular/ luminal side) (Fig. 1B). In the open-inwards conformation, each bundle is commonly formed by ...
... this protein family. The 12 membrane-spanning segments arrange into two bundles of six with a large cavity in between that can either be open-inwards (to the cytosol) or open-outwards (to the extracellular/ luminal side) (Fig. 1B). In the open-inwards conformation, each bundle is commonly formed by ...
The Three-dimensional Structure of 4-Hydroxybenzoyl
... moiety and the 4-hydroxybenzoyl group is cleaved by 4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA thioesterase, hereafter referred to simply as thioesterase. The genes encoding these three enzymes are organized in an operon under the positive control of 4-chlorobenzoyl-CoA (8). Presently, little is known concerning the evol ...
... moiety and the 4-hydroxybenzoyl group is cleaved by 4-hydroxybenzoyl-CoA thioesterase, hereafter referred to simply as thioesterase. The genes encoding these three enzymes are organized in an operon under the positive control of 4-chlorobenzoyl-CoA (8). Presently, little is known concerning the evol ...
Bacterial tail anchors can target to the mitochondrial outer
... translocon may not be warranted in any case, since the structural characteristics likely ...
... translocon may not be warranted in any case, since the structural characteristics likely ...
Electron microscopy in structural studies of Photosystem II
... splitted to Endoplasmic (E) and Protoplasmic plane (P) that corresponds to lumenal and stromal leaflet of the membrane, respectively. We can distinguish Fracture plane (F) and original Surface (S) referred to endoplasmic surface ES, endoplasmic fracture EF, protoplasmic surface PS, and protoplasmic ...
... splitted to Endoplasmic (E) and Protoplasmic plane (P) that corresponds to lumenal and stromal leaflet of the membrane, respectively. We can distinguish Fracture plane (F) and original Surface (S) referred to endoplasmic surface ES, endoplasmic fracture EF, protoplasmic surface PS, and protoplasmic ...
Role of Na and K in Enzyme Function
... the past decade permits a broad discussion. For brevity, we focus on enzymes characterized in both kinetic and structural detail. A brief introduction to ion homeostasis provides biological context (sect. I) and is followed by inspection of the chemical properties and coordination of M⫹s (sect. II). ...
... the past decade permits a broad discussion. For brevity, we focus on enzymes characterized in both kinetic and structural detail. A brief introduction to ion homeostasis provides biological context (sect. I) and is followed by inspection of the chemical properties and coordination of M⫹s (sect. II). ...
The Serum Proteins of the Rat During Development
... An asymmetry was found in the trailing region of the gamma-globulin fraction during all stages of development, including the adult. An asymmetry very similar in appearance and position was also found by Gurvich & Karsaevskaya (1956), but only in sera from perinatal animals. These workers have design ...
... An asymmetry was found in the trailing region of the gamma-globulin fraction during all stages of development, including the adult. An asymmetry very similar in appearance and position was also found by Gurvich & Karsaevskaya (1956), but only in sera from perinatal animals. These workers have design ...
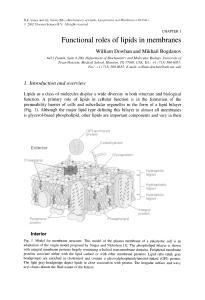
Functional Roles Of Lipids In membranes - IJS
... ionic interaction with water and therefore are energetically stable in an aqueous environment. The structural organization that a polar lipid assumes in water is determined by its concentration and the law of opposing forces, i.e. hydrophobic forces driving self-association versus steric and ionic ...
... ionic interaction with water and therefore are energetically stable in an aqueous environment. The structural organization that a polar lipid assumes in water is determined by its concentration and the law of opposing forces, i.e. hydrophobic forces driving self-association versus steric and ionic ...
Mechanisms Shaping the Membranes of Cellular Organelles
... As discussed below, some integral membrane proteins have also been proposed to generate curvature by a combination of scaffolding and hydrophobic insertion (wedging). Protein embedding alone could cause membrane curvature by the bilayer coupling effect ...
... As discussed below, some integral membrane proteins have also been proposed to generate curvature by a combination of scaffolding and hydrophobic insertion (wedging). Protein embedding alone could cause membrane curvature by the bilayer coupling effect ...
Plant Wnt: deciphering a novel signalling pathway
... cascade, the non-canonical pathway does not bank on catenin to carry out downstream signalling, hence is known as -catenin independent Wnt signalling. PCP signalling is involved mainly in the regulation of cell polarity during morphogenesis by activating JNK-dependent transcription factors via sma ...
... cascade, the non-canonical pathway does not bank on catenin to carry out downstream signalling, hence is known as -catenin independent Wnt signalling. PCP signalling is involved mainly in the regulation of cell polarity during morphogenesis by activating JNK-dependent transcription factors via sma ...
Expression of biologically active mouse ciliary neutrophic factor
... and gp130 [40, 41]. CNTFRa is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) - anchored protein, which can also be found in a soluble form (sCNTFRa) [42]. The binding of CNTF to membrane bound or soluble forms of CNTFRa leads to the recruitment and activation of two signal transducing receptor subunits, LIFRb ...
... and gp130 [40, 41]. CNTFRa is a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) - anchored protein, which can also be found in a soluble form (sCNTFRa) [42]. The binding of CNTF to membrane bound or soluble forms of CNTFRa leads to the recruitment and activation of two signal transducing receptor subunits, LIFRb ...
Comparison of the Structure of the Extrinsic 33 kDa Protein from
... free form, among different plant species. The cleavage sites of the 33 kDa protein by protease were reported to be different between higher plant and cyanobacterium. The higher plant 33 kDa protein was cleaved at 16Y by chymotrypsin and at 18E by V8 protease (Eaton-Rye and Murata 1989), while the cy ...
... free form, among different plant species. The cleavage sites of the 33 kDa protein by protease were reported to be different between higher plant and cyanobacterium. The higher plant 33 kDa protein was cleaved at 16Y by chymotrypsin and at 18E by V8 protease (Eaton-Rye and Murata 1989), while the cy ...
A Guide to the Analysis and Purification of Proteins and
... protein therapeutic products and to analyze these for product identity and impurities. Reversed-phase HPLC plays a vital role in the separation of peptides from digested proteomes prior to protein identification by mass spectrometry. It is also used to purify many proteins and peptides during invest ...
... protein therapeutic products and to analyze these for product identity and impurities. Reversed-phase HPLC plays a vital role in the separation of peptides from digested proteomes prior to protein identification by mass spectrometry. It is also used to purify many proteins and peptides during invest ...
"Genetic Methods of Polymer Synthesis". In: Encyclopedia of
... which is characteristic of the fibrous proteins (eg, silk, collagen, and elastin) that serve a mechanical or structural function; globular proteins that serve catalytic or molecular recognition functions do not contain such repetitive sequences. The exact nature of the repetitive amino acid sequence ...
... which is characteristic of the fibrous proteins (eg, silk, collagen, and elastin) that serve a mechanical or structural function; globular proteins that serve catalytic or molecular recognition functions do not contain such repetitive sequences. The exact nature of the repetitive amino acid sequence ...
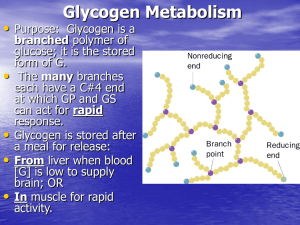
Glycogen Metabolism - http://www.utm.edu
... without the accumulation of glucose. It is said that “GP is the glucose sensor”: a) In the phospho (active) form, the P’s on GP are “buried” where PP1 can’t get at them. b) When G binds to active GP-P, its conformation changes, “exposing” the P’s so PP1 can “clip them” off. c) PP1 binds strongly to ...
... without the accumulation of glucose. It is said that “GP is the glucose sensor”: a) In the phospho (active) form, the P’s on GP are “buried” where PP1 can’t get at them. b) When G binds to active GP-P, its conformation changes, “exposing” the P’s so PP1 can “clip them” off. c) PP1 binds strongly to ...
Role of Dietary Soy Protein in Obesity
... the dietary proteins, soy protein is considered a complete protein in that it contains ample amounts of all the essential amino acids plus several other macronutrients with a nutritional value roughly equivalent to that of animal protein of high biological value. Soy protein is unique among the plan ...
... the dietary proteins, soy protein is considered a complete protein in that it contains ample amounts of all the essential amino acids plus several other macronutrients with a nutritional value roughly equivalent to that of animal protein of high biological value. Soy protein is unique among the plan ...
Submembraneous microtubule cytoskeleton: biochemical and
... which becomes especially apparent under microtubules depolymerising conditions such as presence of nocodazol or increased Ca2+ concentrations [28]. TRPV1 channels are nonselective cation channels. Therefore, the role of increased concentration of Ca2+ on the properties of TRPV1–tubulin and ⁄ or TRPV ...
... which becomes especially apparent under microtubules depolymerising conditions such as presence of nocodazol or increased Ca2+ concentrations [28]. TRPV1 channels are nonselective cation channels. Therefore, the role of increased concentration of Ca2+ on the properties of TRPV1–tubulin and ⁄ or TRPV ...
THE INFLUENCE OF BODY MASS INDEX (BMI)
... no longer produce the required amino acid or not produce sufficient amounts to meet demand, the amino acid becomes conditionally essential. Peptide bonds bind amino acids to one another and can be thought of as the glue that holds them together (1). The peptide bond connects the acid end of one amin ...
... no longer produce the required amino acid or not produce sufficient amounts to meet demand, the amino acid becomes conditionally essential. Peptide bonds bind amino acids to one another and can be thought of as the glue that holds them together (1). The peptide bond connects the acid end of one amin ...
A CBS domain-containing pyrophosphatase of Moorella
... PPase: soluble and integral membrane-bound. Soluble PPases are subdivided further into families I and II, which are not homologous [7,8]. Family I PPases are found in all kingdoms of life and are among the best-characterized phosphoryl transfer enzymes [9,10]. Family II PPases, which were discovered ...
... PPase: soluble and integral membrane-bound. Soluble PPases are subdivided further into families I and II, which are not homologous [7,8]. Family I PPases are found in all kingdoms of life and are among the best-characterized phosphoryl transfer enzymes [9,10]. Family II PPases, which were discovered ...
proposal-aug25
... Requested: $137775 short conserved segments that fall within disordered regions, but do not match any known protein domains. To estimate the expected number of false positives identified in the cluster analysis we will repeat the clustering on the motifs identified in simulated disordered proteins. ...
... Requested: $137775 short conserved segments that fall within disordered regions, but do not match any known protein domains. To estimate the expected number of false positives identified in the cluster analysis we will repeat the clustering on the motifs identified in simulated disordered proteins. ...
Introduction to Protein Structure
... •are amino acid sidechain dihedral angles, numbered 1, 2, 3,... going outward from C atom •different numbers of -angles depending on amino acid type •are usually defined as low energy side-chain conformations. •the use of a library of rotamers allows the modeling of a structure while trying the ...
... •are amino acid sidechain dihedral angles, numbered 1, 2, 3,... going outward from C atom •different numbers of -angles depending on amino acid type •are usually defined as low energy side-chain conformations. •the use of a library of rotamers allows the modeling of a structure while trying the ...
Detection of proteins and intact microorganisms using
... resonators coated with affinity ligand reagents (ALRs) deposited onto individual sensors with a microdroplet applicator. Because the size of an individual sensor element is very small, many sensors—each targeted at a different analyte— can be integrated within a single small silicon chip. This enabl ...
... resonators coated with affinity ligand reagents (ALRs) deposited onto individual sensors with a microdroplet applicator. Because the size of an individual sensor element is very small, many sensors—each targeted at a different analyte— can be integrated within a single small silicon chip. This enabl ...
Structure and mechanism of action of a novel
... (Chander et al., 1998). These latter organisms include members of Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species, some of which are important human pathogens. Consequently, it is possible that iPGMs could be a target for rational design of a novel antibiotic. Interestingly, some bacteria have genes for bo ...
... (Chander et al., 1998). These latter organisms include members of Staphylococcus and Streptococcus species, some of which are important human pathogens. Consequently, it is possible that iPGMs could be a target for rational design of a novel antibiotic. Interestingly, some bacteria have genes for bo ...
Role of Dietary Protein in Post-Exercise Muscle Reconditioning
... and range between 0.04 and 0.14% per hour. The latter largely depends on food intake and habitual physical activity, the two main anabolic stimuli. Food intake, or rather protein ingestion, directly elevates muscle protein synthesis rates. Following protein digestion and absorption, the rise in plas ...
... and range between 0.04 and 0.14% per hour. The latter largely depends on food intake and habitual physical activity, the two main anabolic stimuli. Food intake, or rather protein ingestion, directly elevates muscle protein synthesis rates. Following protein digestion and absorption, the rise in plas ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).