Exam II Review: - Texas Tech University
... 2. Protein is facilitated by chaperone proteins that prevent interaction of protein with other molecules. a. HSP70 and HSP60 use ATP to bind and unbind folding protein. b. Protein folding errors cause diseases. c. Ubiquitin and proteosomes function to degrade proteins. 3. Translation can also be mod ...
... 2. Protein is facilitated by chaperone proteins that prevent interaction of protein with other molecules. a. HSP70 and HSP60 use ATP to bind and unbind folding protein. b. Protein folding errors cause diseases. c. Ubiquitin and proteosomes function to degrade proteins. 3. Translation can also be mod ...
2.4 review
... 2) Draw a condensation reaction between two amino acids. What is the name of the bond that is formed as a result? 3) Discuss why the same 20 amino organisms are used by most organisms to make proteins. 4) Distinguish between a polypeptide and a protein. 5) What is an “R” group? How many different on ...
... 2) Draw a condensation reaction between two amino acids. What is the name of the bond that is formed as a result? 3) Discuss why the same 20 amino organisms are used by most organisms to make proteins. 4) Distinguish between a polypeptide and a protein. 5) What is an “R” group? How many different on ...
„Biochemical reconstitution of protein complexes involved in
... in mitochondria, where they are synthetized by dynamic complex of interacting proteins. Until today over 20 different proteins were identified to be important in this process, but the very core of FeS cluster assembly complex is formed by molecular scaffold protein Isu1, cysteine desulfurase Nfs1(Is ...
... in mitochondria, where they are synthetized by dynamic complex of interacting proteins. Until today over 20 different proteins were identified to be important in this process, but the very core of FeS cluster assembly complex is formed by molecular scaffold protein Isu1, cysteine desulfurase Nfs1(Is ...
b-cells - APBiology2015-2016
... • The fragments will later appear on the cell surface inside a molecule because it is now a plasma cell. • T-cells help b-cells function properly by releasing chemicals that signal the b-cells to divide in multiples and attack invaders inside the cell that may interfere with the signal pathway. ...
... • The fragments will later appear on the cell surface inside a molecule because it is now a plasma cell. • T-cells help b-cells function properly by releasing chemicals that signal the b-cells to divide in multiples and attack invaders inside the cell that may interfere with the signal pathway. ...
Introduction to Protein Science Architecture, Function
... Simplest change to a protein is the substitution of a single amino acid Then, what is the effect on the protein structure and function? ...
... Simplest change to a protein is the substitution of a single amino acid Then, what is the effect on the protein structure and function? ...
Sensory receptor organs
... Sensory Receptor Organs Detect Energy or Substances • Sensory receptor organs are organs specialized to detect a certain stimulus. • Receptor cells within the organ convert the stimulus into an electrical signal a “transduction” process. ...
... Sensory Receptor Organs Detect Energy or Substances • Sensory receptor organs are organs specialized to detect a certain stimulus. • Receptor cells within the organ convert the stimulus into an electrical signal a “transduction” process. ...
Lecture 13-Effects of glycosylation on protein structure and function
... • Shielding of hydrophobic regions of a protein surface from the aqueous solvent can also ...
... • Shielding of hydrophobic regions of a protein surface from the aqueous solvent can also ...
Pharmacology for the Health Sciences
... receptors are located is crucial to understanding what actions and side effects will be produced. ...
... receptors are located is crucial to understanding what actions and side effects will be produced. ...
Anti-CCR4 antibody ab83250 Product datasheet 1 Image
... Use a concentration of 1 µg/ml. Predicted molecular weight: 41 kDa. Good results were obtained when blocked with 5% non-fat dry milk in 0.05% PBS-T. ...
... Use a concentration of 1 µg/ml. Predicted molecular weight: 41 kDa. Good results were obtained when blocked with 5% non-fat dry milk in 0.05% PBS-T. ...
Guanide and biguanide compounds synthesized by the Teintze lab have... Amanda Kelley: Chemistry & Biochemistry
... Guanide and biguanide compounds synthesized by the Teintze lab have been found to bind to the CXCR4 chemokine receptor which is used by X4 strains of HIV to enter cells and is involved in cancer metastasis. Therefore, they may be able to inhibit both HIV infection and cancer metastasis. When the che ...
... Guanide and biguanide compounds synthesized by the Teintze lab have been found to bind to the CXCR4 chemokine receptor which is used by X4 strains of HIV to enter cells and is involved in cancer metastasis. Therefore, they may be able to inhibit both HIV infection and cancer metastasis. When the che ...
5.3 G Protein-Coupled Receptors
... Representative members of the family B receptors include calcitonine receptor, glucagon receptor and parat hormone receptors. ...
... Representative members of the family B receptors include calcitonine receptor, glucagon receptor and parat hormone receptors. ...
Lh6Ch04bProt
... Amyloid Fibers Stabilized by F Different Amyloid diseases depend on organ the fibers occur ...
... Amyloid Fibers Stabilized by F Different Amyloid diseases depend on organ the fibers occur ...
Molecular Biology of the Cell
... Not Plants Too???!!! Where they are called glyoxysomes. Seeds and fatty acids. ...
... Not Plants Too???!!! Where they are called glyoxysomes. Seeds and fatty acids. ...
answers_ch07
... 4) It is possible to identify five CN fragments within the skeleton of adenine as shown below. NH2 N ...
... 4) It is possible to identify five CN fragments within the skeleton of adenine as shown below. NH2 N ...
aliphatic amino acid structures
... Locating disulfide bond • Do the same thing except breaking disulfide bond • See which peptide fragments are missing or which peptide fragment (longer) appears ...
... Locating disulfide bond • Do the same thing except breaking disulfide bond • See which peptide fragments are missing or which peptide fragment (longer) appears ...
Getting things where they need to go: Protein Targeting
... Sorting places proteins in membrane and in lumen of organelles PM (and other) proteins use Sec or SRP mediated translocation to become inserted into the ER (and only the ER) After insertion non-ER proteins are sorted and delivered sorting lumenal vs membrane proteins –how? ...
... Sorting places proteins in membrane and in lumen of organelles PM (and other) proteins use Sec or SRP mediated translocation to become inserted into the ER (and only the ER) After insertion non-ER proteins are sorted and delivered sorting lumenal vs membrane proteins –how? ...
PEPTIDE HORMONES
... Sizes, origins and fate: Due to the force of custom, “peptide hormones” is a collective name that has been applied to peptides, polypeptides and proteins that all function as hormones. The name “factor” has also been given to some of these peptides and originates from a time when their peptide/prot ...
... Sizes, origins and fate: Due to the force of custom, “peptide hormones” is a collective name that has been applied to peptides, polypeptides and proteins that all function as hormones. The name “factor” has also been given to some of these peptides and originates from a time when their peptide/prot ...
Slide 1 - ParklandNatSciWiki
... 1. Signal amplification – Binding of signal to single receptor can cause the synthesis of many cAMP that activate PKA, each PKA can phosphorylate many proteins ...
... 1. Signal amplification – Binding of signal to single receptor can cause the synthesis of many cAMP that activate PKA, each PKA can phosphorylate many proteins ...
How to build a glycinergic postsynaptic ...
... clonal antibodies (Pfeiffer et al. 1984) indicates that this polypeptide decorates the cytoplasmic face of the glyciner gic postsynaptic membrane (Triller et al. 1985; Altschuler et al. 1986). Moreover, in biochemical studies the 93 x 103Mr protein behaves as a typical peripheral mem brane compone ...
... clonal antibodies (Pfeiffer et al. 1984) indicates that this polypeptide decorates the cytoplasmic face of the glyciner gic postsynaptic membrane (Triller et al. 1985; Altschuler et al. 1986). Moreover, in biochemical studies the 93 x 103Mr protein behaves as a typical peripheral mem brane compone ...
Lectures 1-3: Review of forces and elementary statistical
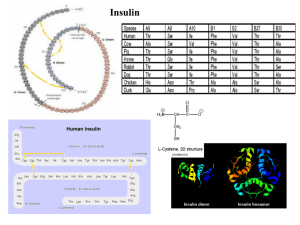
... As described above, human insulin consists of 51 amino acids, divided into two chains, commonly labeled A and B, with 21 and 30 amino acids respectively. The chains are linked by three disulfide bridges, two forming inter-chain cystine at A7-B7 and A20-B19, and one forming an intra-chain cystine at ...
... As described above, human insulin consists of 51 amino acids, divided into two chains, commonly labeled A and B, with 21 and 30 amino acids respectively. The chains are linked by three disulfide bridges, two forming inter-chain cystine at A7-B7 and A20-B19, and one forming an intra-chain cystine at ...
Save as PDF
... Drugs available to help individuals quit an addictive habit often have undesirable side effects or are ineffective. Researchers at the University of Florida have developed a variety of nicotinic receptor agonists (activators) based on a marine natural product named anabaseine that selectively stimul ...
... Drugs available to help individuals quit an addictive habit often have undesirable side effects or are ineffective. Researchers at the University of Florida have developed a variety of nicotinic receptor agonists (activators) based on a marine natural product named anabaseine that selectively stimul ...
P014 Using Simulation Cell Theory to Calculate the Thermody
... upon binding are difficult to estimate and are often neglected. Here we apply our recently developed method, simulation cell theory, to evaluate the entropy of a ligand when bound to a protein and when free in solution. In this approach the average magnitudes of the forces and torques acting on the ...
... upon binding are difficult to estimate and are often neglected. Here we apply our recently developed method, simulation cell theory, to evaluate the entropy of a ligand when bound to a protein and when free in solution. In this approach the average magnitudes of the forces and torques acting on the ...
Crystal Structure of an Anthrax Toxin –Host Cell Receptor Complex
... using data collected at beamline 9.1 at SSRL. Both proteins are largely unchanged upon complex formation. Asp683 of PA binds the MIDAS site, thus mimicking the mechanism of binding by physiological ligands. A large additional interaction surface provided by domain IV explains in part the ligand spec ...
... using data collected at beamline 9.1 at SSRL. Both proteins are largely unchanged upon complex formation. Asp683 of PA binds the MIDAS site, thus mimicking the mechanism of binding by physiological ligands. A large additional interaction surface provided by domain IV explains in part the ligand spec ...
Biochemistry Jeopardy C.P. Bio.
... is formed by chemically bonding two of these monosaccharides. ...
... is formed by chemically bonding two of these monosaccharides. ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).