1 Protein Secretion: Targeting to the ER I. Introduction nucleus ER
... signal sequence could compete with the nascent protein's signal sequence for SRP 54 binding and thus block the arrest of translation. SRP 54 is composed of three domains, including an N-terminal GTPase. The GTPase domain acts as a timing device based on the fact that GDP remains stuck for some time ...
... signal sequence could compete with the nascent protein's signal sequence for SRP 54 binding and thus block the arrest of translation. SRP 54 is composed of three domains, including an N-terminal GTPase. The GTPase domain acts as a timing device based on the fact that GDP remains stuck for some time ...
The G protein pathway in neuroscience
... These are called “M” channels, and are now termed the KCNQ family. because they were first discovered downstream from muscarinic receptors . . . A different muscarinic receptor subtype from the one that opens K channels in heart. ...
... These are called “M” channels, and are now termed the KCNQ family. because they were first discovered downstream from muscarinic receptors . . . A different muscarinic receptor subtype from the one that opens K channels in heart. ...
Getting things where they need to go: Protein Targeting
... Neurotransmitters are stored in and secreted from vesicles. Neurotransmitter receptors are delivered to dendrite in vesicles. Could sorting and targeting problems be at the root of bipolar disorder? If sorting and targeting are the problems would you predict alteration of something like the NT rece ...
... Neurotransmitters are stored in and secreted from vesicles. Neurotransmitter receptors are delivered to dendrite in vesicles. Could sorting and targeting problems be at the root of bipolar disorder? If sorting and targeting are the problems would you predict alteration of something like the NT rece ...
Gene Section SH3GL2 (SH3-domain GRB2-like 2) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... loop of the G-protein coupled-1-adrenergic receptor. SH3GL2 overexpression increased isoproterenolinduced receptor inter-nalization by 25% and decreased coupling of receptor to the G-protein. The SH3 domain of SH3GL2 also binds to a proline rich domain within the cytoplasmic tail of metalloprotease ...
... loop of the G-protein coupled-1-adrenergic receptor. SH3GL2 overexpression increased isoproterenolinduced receptor inter-nalization by 25% and decreased coupling of receptor to the G-protein. The SH3 domain of SH3GL2 also binds to a proline rich domain within the cytoplasmic tail of metalloprotease ...
Cell signaling, endocrine and reproduction
... Cell communication II: endocrine and reproduction ...
... Cell communication II: endocrine and reproduction ...
Chapter 27: Ca2+-Sensing Receptor
... polycationic agonists of the CaSR. Aromatic amino acids and calcimimetics—drugs that activate the receptor and are used to control hyperparathyroidism—are allosteric modulators of the CaSR. The former bind to a site near a putative calcium-binding site in the receptor’s ECD, whereas the latter bind ...
... polycationic agonists of the CaSR. Aromatic amino acids and calcimimetics—drugs that activate the receptor and are used to control hyperparathyroidism—are allosteric modulators of the CaSR. The former bind to a site near a putative calcium-binding site in the receptor’s ECD, whereas the latter bind ...
Bi 12 Biological Molecules Current.pptx
... composed of C, H, O, N, and sometimes P and S ¨ generally quite large. A long polymer chain of amino acid subunits linked end to end by a ...
... composed of C, H, O, N, and sometimes P and S ¨ generally quite large. A long polymer chain of amino acid subunits linked end to end by a ...
Nerve Cells
... • How is the action of acetylcholine terminated? Serotonin? • What is Parkinson's disease, and what is the mechanism for its development? How is parkinsonism treated? • How are neurotransmitters released at the synapse? What proteins are involved? Name the calcium ion sensor • Describe the Otto Loew ...
... • How is the action of acetylcholine terminated? Serotonin? • What is Parkinson's disease, and what is the mechanism for its development? How is parkinsonism treated? • How are neurotransmitters released at the synapse? What proteins are involved? Name the calcium ion sensor • Describe the Otto Loew ...
2 Answer all the questions. 1 Knowledge of the nitrogen cycle can
... Knowledge of the nitrogen cycle can be used to make decisions about management of farmland. A farmer uses her grass meadow to raise sheep. In a separate field she grows cabbages. (a) Fig. 1.1 shows part of the nitrogen cycle. The four boxes on the bottom line of the diagram refer to substances in th ...
... Knowledge of the nitrogen cycle can be used to make decisions about management of farmland. A farmer uses her grass meadow to raise sheep. In a separate field she grows cabbages. (a) Fig. 1.1 shows part of the nitrogen cycle. The four boxes on the bottom line of the diagram refer to substances in th ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier
... phosphorylates, among other substrates, DARPP-32, which, when phosphorylated, will inhibit protein phosphatase-1. Activation of D1-family receptors will result in activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). A prominent substrate of PKA that alters gene transcription is CREB (cAMPresponse ...
... phosphorylates, among other substrates, DARPP-32, which, when phosphorylated, will inhibit protein phosphatase-1. Activation of D1-family receptors will result in activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK). A prominent substrate of PKA that alters gene transcription is CREB (cAMPresponse ...
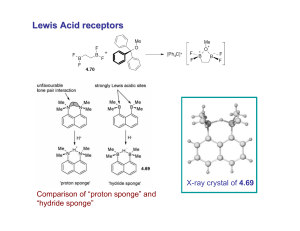
Lewis Acid receptors
... Anion receptors based on metal centers are a well established class of anion binding compound and can be classified into three broad categories: • Those in which an inert or labile metal centre plays a structural role • Those in which an inert or labile the metal is a key component of the anion bind ...
... Anion receptors based on metal centers are a well established class of anion binding compound and can be classified into three broad categories: • Those in which an inert or labile metal centre plays a structural role • Those in which an inert or labile the metal is a key component of the anion bind ...
distinct format
... proteins of which 714 proteins were identified in asexual blood stages (left panel), 931 in gametocytes (right panel) and 645 in gametes. The last two groups provide insights into the biology of the sexual stages of the parasite, and include conserved, stage-specific, secreted and membrane-associate ...
... proteins of which 714 proteins were identified in asexual blood stages (left panel), 931 in gametocytes (right panel) and 645 in gametes. The last two groups provide insights into the biology of the sexual stages of the parasite, and include conserved, stage-specific, secreted and membrane-associate ...
here - BioGeometry
... of pure protein yield information about the protein’s structure. The results of their interdisciplinary collaboration will not only be useful new software for biologists, but also new talent. “Part of the success of this project will be the education of postdoctoral students in this interdisciplinar ...
... of pure protein yield information about the protein’s structure. The results of their interdisciplinary collaboration will not only be useful new software for biologists, but also new talent. “Part of the success of this project will be the education of postdoctoral students in this interdisciplinar ...
Chapter 6 Crossword Puzzle
... disassembled into amino acids Increased dietary protein intake can lead to increased excretion of the mineral _____. Amino acids can be used to make glucose if insufficient dietary _____ are consumed. What the body uses to assemble its own proteins Proteins that act to defend the body from disease P ...
... disassembled into amino acids Increased dietary protein intake can lead to increased excretion of the mineral _____. Amino acids can be used to make glucose if insufficient dietary _____ are consumed. What the body uses to assemble its own proteins Proteins that act to defend the body from disease P ...
The Cell Study Guide Vocabulary: Cell theory Cytoplasm Organelle
... Summarize the functions of organelles in plant and animal cells. Know how organelles can work together as a system. For example, ribosomes are made in the nucleolus, they exit through the pores in the nucleus and are found in the RER. Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis, where amino acids ar ...
... Summarize the functions of organelles in plant and animal cells. Know how organelles can work together as a system. For example, ribosomes are made in the nucleolus, they exit through the pores in the nucleus and are found in the RER. Ribosomes are the site of protein synthesis, where amino acids ar ...
How Do Molecules Cross the Plasma Membrane? 1. Indicate the
... 1. Indicate the types of molecules that can diffuse through the lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane, then explain why this can occur. ...
... 1. Indicate the types of molecules that can diffuse through the lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane, then explain why this can occur. ...
Distinguish between these 3 root types: - mvhs
... translation takes place. Catalyzes the formation of __________ bonds between amino acids to form the polypeptide chain. Made of ________ and rRNA. ...
... translation takes place. Catalyzes the formation of __________ bonds between amino acids to form the polypeptide chain. Made of ________ and rRNA. ...
Spectroscopy of Proteins
... • Exert all the biological functions of the organism: enzymes, antibodies, cytoskeletons, hormones, receptors ...
... • Exert all the biological functions of the organism: enzymes, antibodies, cytoskeletons, hormones, receptors ...
Summer 2011 Proposal for UNCA Undergraduate Research
... Heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide binding proteins (G proteins) are important cell signaling proteins that mediate a wide variety of cellular responses via signal transduction across the plasma membrane. They do so by interacting with a number of downstream target proteins to drive various signaling ...
... Heterotrimeric guanine nucleotide binding proteins (G proteins) are important cell signaling proteins that mediate a wide variety of cellular responses via signal transduction across the plasma membrane. They do so by interacting with a number of downstream target proteins to drive various signaling ...
A1987J365500002
... Chou P Y. Welts M & Fasmimu G 0. Conformational studies on copolymcrs of hydroxypropyl-L.glatamine and L-leucine. Circutar-dichroism studies. Biochemistry—USA t 1:3028-343. 1972. Ch,tu P V & Fasman G 0. Structural and functional rote of leucine residues in proteins, J. Mo), Rio!. 74:263-81. 972. - C ...
... Chou P Y. Welts M & Fasmimu G 0. Conformational studies on copolymcrs of hydroxypropyl-L.glatamine and L-leucine. Circutar-dichroism studies. Biochemistry—USA t 1:3028-343. 1972. Ch,tu P V & Fasman G 0. Structural and functional rote of leucine residues in proteins, J. Mo), Rio!. 74:263-81. 972. - C ...
CSM 101 Fall 2010 Timeline
... the enzyme’s shape and activity. Once activated, the enzyme can trigger the next step leading to a cellular response. Binding of signaling molecules is reversible. The activating changes in the GPCR, as well as the changes in the G protein and enzyme, are only temporary; these molecules soon become ...
... the enzyme’s shape and activity. Once activated, the enzyme can trigger the next step leading to a cellular response. Binding of signaling molecules is reversible. The activating changes in the GPCR, as well as the changes in the G protein and enzyme, are only temporary; these molecules soon become ...
Endocrine System: Overview
... Lipid insoluble hormone molecules cannot penetrate cellular plasma membranes like lipid soluble hormones can. How then, do they affect cellular activity? ...
... Lipid insoluble hormone molecules cannot penetrate cellular plasma membranes like lipid soluble hormones can. How then, do they affect cellular activity? ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).