Thyrostimulin beta subunit (Glycoprotein hormone beta 5) Human E
... Human thyrostimulin ranks among the glycoprotein hormone family. These hormones consist of two subunits, the common alpha- and specific beta-subunits, which associate noncovalently to form a heterodimer. The alpha-subunit combines with four distinct beta-subunits giving rise to four biologically act ...
... Human thyrostimulin ranks among the glycoprotein hormone family. These hormones consist of two subunits, the common alpha- and specific beta-subunits, which associate noncovalently to form a heterodimer. The alpha-subunit combines with four distinct beta-subunits giving rise to four biologically act ...
Pegylation - WordPress.com
... It is a polymer of ethylene oxide, and different lengths of the polymer have different uses. For the purpose of this presentation we will stick to the name PEG, and limit our explanation to how it can be used to extend the half-life (t1 ) ...
... It is a polymer of ethylene oxide, and different lengths of the polymer have different uses. For the purpose of this presentation we will stick to the name PEG, and limit our explanation to how it can be used to extend the half-life (t1 ) ...
PowerPoint-Präsentation
... of all attending colleagues including the Professors. So, everybody learns from the others, kind of a multiplication effect. One of the powers of molecular modelling resides in its informative value in displaying molecules, in total or in portions thereof, in different formats such as wireframe, pro ...
... of all attending colleagues including the Professors. So, everybody learns from the others, kind of a multiplication effect. One of the powers of molecular modelling resides in its informative value in displaying molecules, in total or in portions thereof, in different formats such as wireframe, pro ...
AP BIO Chp 11 Cell to Cell Communication
... into body fluids, often the blood. Hormones may reach virtually all C body cells. ...
... into body fluids, often the blood. Hormones may reach virtually all C body cells. ...
Metal chelate chrom
... Metal-Chelate Affinity Chromatography (MCAC), also known as Immobilized Metal Affinity Chromatography (IMAC), was first successfully demonstrated in 1975 by Porath and collaborators for human serum proteins. ...
... Metal-Chelate Affinity Chromatography (MCAC), also known as Immobilized Metal Affinity Chromatography (IMAC), was first successfully demonstrated in 1975 by Porath and collaborators for human serum proteins. ...
ionotropic and metabotropic receptors, second messengers
... Understand the structure and function of the synapse Presynaptic release and postsynaptic receptors Knowledge of the major types of neurotransmitter/neuromodulator Basic understanding of EPSPs and IPSPs Different types of signalling - ionotropic and metabotropic receptors, second messengers Colocali ...
... Understand the structure and function of the synapse Presynaptic release and postsynaptic receptors Knowledge of the major types of neurotransmitter/neuromodulator Basic understanding of EPSPs and IPSPs Different types of signalling - ionotropic and metabotropic receptors, second messengers Colocali ...
I. Characteristics of amino acids and folding of nascent polypeptides
... I. Characteristics of amino acids and folding of nascent polypeptides You will be responsible for knowing the 3 letter code for the different amino acid residues (e.g., Trp for tryptophan), and their general characteristics, i.e, hydropholic, polar, and charged. Please see pp 59-64 for an overview o ...
... I. Characteristics of amino acids and folding of nascent polypeptides You will be responsible for knowing the 3 letter code for the different amino acid residues (e.g., Trp for tryptophan), and their general characteristics, i.e, hydropholic, polar, and charged. Please see pp 59-64 for an overview o ...
ECS 189K - UC Davis
... http://www.rcsb.org, you can locate proteins by keyword searching or by entering the PDB accession number for the structure file, like 5PTI. Details on the molecule (how the structure was determined, pertinent research articles, position of secondary structures, unusual amino acids, etc) can be fou ...
... http://www.rcsb.org, you can locate proteins by keyword searching or by entering the PDB accession number for the structure file, like 5PTI. Details on the molecule (how the structure was determined, pertinent research articles, position of secondary structures, unusual amino acids, etc) can be fou ...
Abstract
... Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase ERK1 Abstract Protein kinases mediate most intracellular signal transduction via the reversible phosphorylation on serine, threonine, or tyrosine residue of specific protein/peptide substrates. Such phosphorylation is employed by all eukaryotes in regulation of enzym ...
... Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase ERK1 Abstract Protein kinases mediate most intracellular signal transduction via the reversible phosphorylation on serine, threonine, or tyrosine residue of specific protein/peptide substrates. Such phosphorylation is employed by all eukaryotes in regulation of enzym ...
1 Supplementary Model Description
... Phosphorylation of regulatory light chain (MLC) of myosin II plays a critical role in controlling actomyosin contractility in both smooth muscle and nonmuscle cells [11-13]. MLC phosphorylation is regulated by the balance of two enzymatic activities, i.e., Myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) and myosin ...
... Phosphorylation of regulatory light chain (MLC) of myosin II plays a critical role in controlling actomyosin contractility in both smooth muscle and nonmuscle cells [11-13]. MLC phosphorylation is regulated by the balance of two enzymatic activities, i.e., Myosin light chain kinase (MLCK) and myosin ...
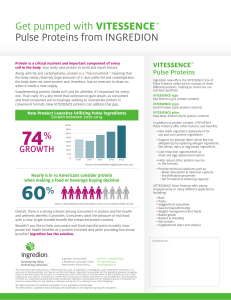
60% 74% - Ingredion
... Wouldn’t you like to help consumers and food manufacturers to easily incorporate the health benefits of a protein-enriched diet while providing functional benefits? Ingredion has the solution. ...
... Wouldn’t you like to help consumers and food manufacturers to easily incorporate the health benefits of a protein-enriched diet while providing functional benefits? Ingredion has the solution. ...
Proteins – Organic/Macromolecule #3
... Proteins – Organic/Macromolecule #3 Name:_____________________________________Date:________Per:_____ Proteins are organic molecules. They are built from the connection of many amino acids into a long chain. Proteins have many functions that can be remembered by this acronym STEM(Structure, Transport ...
... Proteins – Organic/Macromolecule #3 Name:_____________________________________Date:________Per:_____ Proteins are organic molecules. They are built from the connection of many amino acids into a long chain. Proteins have many functions that can be remembered by this acronym STEM(Structure, Transport ...
Proteins – Organic/Macromolecule #3
... Proteins – Organic/Macromolecule #3 Name:_____________________________________Date:________Per:_____ Proteins are organic molecules. They are built from the connection of many amino acids into a long chain. Proteins have many functions that can be remembered by this acronym STEM(Structure, Transport ...
... Proteins – Organic/Macromolecule #3 Name:_____________________________________Date:________Per:_____ Proteins are organic molecules. They are built from the connection of many amino acids into a long chain. Proteins have many functions that can be remembered by this acronym STEM(Structure, Transport ...
The structure of components of a multi
... The focus of the talk will be on recent results that pertain to the structure of the components, and mechanisms of a protein in the heavy metal extrusion class of RND family, as compared with other proteins in this family (1) by X-ray diffraction and hybrid methods. We seek to understand the mechani ...
... The focus of the talk will be on recent results that pertain to the structure of the components, and mechanisms of a protein in the heavy metal extrusion class of RND family, as compared with other proteins in this family (1) by X-ray diffraction and hybrid methods. We seek to understand the mechani ...
The basis of specific ligand recognition by proteins
... Interfaces of molecular complexes with proteins exhibit significant and relevant mobility, also referred to as fluctuating networks of interactions; these often involve water molecules with very short residence times. The general problem of mobility will be addressed by specifically looking at inter ...
... Interfaces of molecular complexes with proteins exhibit significant and relevant mobility, also referred to as fluctuating networks of interactions; these often involve water molecules with very short residence times. The general problem of mobility will be addressed by specifically looking at inter ...
Cell Membrane Structure & Function
... – 4.May be non polar helix beta-pleated sheets of non polar amino acids – 5.Non polar portion held within interior of bilayer – 6.Polar ends protrude from both sides of membrane B. Enzymes – 1. Chemical reactions carried out on interior surface of membrane ...
... – 4.May be non polar helix beta-pleated sheets of non polar amino acids – 5.Non polar portion held within interior of bilayer – 6.Polar ends protrude from both sides of membrane B. Enzymes – 1. Chemical reactions carried out on interior surface of membrane ...
Recombinant Human Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4
... and induces chromatin condensation followed by internucleosomal DNA fragmentation. Key component of the Hippo signaling pathway which plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. The core of this pathway is composed of a kina ...
... and induces chromatin condensation followed by internucleosomal DNA fragmentation. Key component of the Hippo signaling pathway which plays a pivotal role in organ size control and tumor suppression by restricting proliferation and promoting apoptosis. The core of this pathway is composed of a kina ...
ß-arrestin signaling and regulation of transcription
... suggests that the interaction of -arrestin and TRAF6 is regulated by IL1R independently of GPCR stimulation. arrestin 1 and -arrestin 2 mutants that can bind to TRAF6 but not IB␣ inhibit the IL1R signaling as well as their wild-type counterparts do. This suggests that the interaction with TRAF6 ...
... suggests that the interaction of -arrestin and TRAF6 is regulated by IL1R independently of GPCR stimulation. arrestin 1 and -arrestin 2 mutants that can bind to TRAF6 but not IB␣ inhibit the IL1R signaling as well as their wild-type counterparts do. This suggests that the interaction with TRAF6 ...
charge-to-mass ratio. The electrophoretic mobility is defined as the
... similarity between the above equation and that used for gel filtration. For example, if hemoglobin were run as a standard, it would result in a band on the gel at a mobility corresponding to Mr = 16 kDa, i.e. its monomer molecular weight and myoglobin (Mr = 17 kDa) would be nearby because it is a si ...
... similarity between the above equation and that used for gel filtration. For example, if hemoglobin were run as a standard, it would result in a band on the gel at a mobility corresponding to Mr = 16 kDa, i.e. its monomer molecular weight and myoglobin (Mr = 17 kDa) would be nearby because it is a si ...
Importance of Protein sorting Cell organization depend on sorting
... 3. Genetic approach to identify essential players ...
... 3. Genetic approach to identify essential players ...
(2e Communication within multicellular organisms)
... Why is thyroxine not classified as a carbohydrate, lipid or protein? ...
... Why is thyroxine not classified as a carbohydrate, lipid or protein? ...
Answers-to-exam-in-protein-chemistry-20130315-
... Residues at position a and d are hydrophobic. By interacting with neighbouring hydrophobic residues helices are forced to coil around each other forming a coil-coil. The interleaving of side chains has been known as knobs-on-holes packing. b) Collagen has a repetitive primary sequence in which every ...
... Residues at position a and d are hydrophobic. By interacting with neighbouring hydrophobic residues helices are forced to coil around each other forming a coil-coil. The interleaving of side chains has been known as knobs-on-holes packing. b) Collagen has a repetitive primary sequence in which every ...
Leukaemia Section t(1;9)(p34;q34) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... recombination. The SFPQ/NONO heterodimer enhances DNA strand break rejoining. SFPQ has homologous recombination and non-homologous end joining activities. SFPQ is associated with the RAD51 protein complex. Role in transcriptional regulation: SFPQ and PTK6 (protein tyrosine kinase 6, also called BRK) ...
... recombination. The SFPQ/NONO heterodimer enhances DNA strand break rejoining. SFPQ has homologous recombination and non-homologous end joining activities. SFPQ is associated with the RAD51 protein complex. Role in transcriptional regulation: SFPQ and PTK6 (protein tyrosine kinase 6, also called BRK) ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).