Puredown Protein A/G-Agarose Conjugate
... Puredown Protein A/G-Agarose Conjugate Immunoprecipitation (IP) is the technique of precipitating a protein antigen out of solution using an antibody that specifically binds to that particular protein. This process can be used to isolate and concentrate a particular protein from a sample containing ...
... Puredown Protein A/G-Agarose Conjugate Immunoprecipitation (IP) is the technique of precipitating a protein antigen out of solution using an antibody that specifically binds to that particular protein. This process can be used to isolate and concentrate a particular protein from a sample containing ...
Evolution of Cell Signaling
... Evolution of Cell Signaling • The yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, has two mating types, a and • Cells of different mating types locate each other via secreted factors specific to each type • A signal transduction pathway is a series of steps by which a signal on a cell’s surface is converted int ...
... Evolution of Cell Signaling • The yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, has two mating types, a and • Cells of different mating types locate each other via secreted factors specific to each type • A signal transduction pathway is a series of steps by which a signal on a cell’s surface is converted int ...
Biologically Important Molecules - Proteins PPT
... since the peptide bonds are polar, H-bonding is possible polypeptides can form a coil-like shape called an alpha helix, or a folded fan like shape called a beta pleated sheet ...
... since the peptide bonds are polar, H-bonding is possible polypeptides can form a coil-like shape called an alpha helix, or a folded fan like shape called a beta pleated sheet ...
Mixed Lineage Kinase 7 is the Mitogen Activated Protein
... inflammation may affect systemic absorption of Stx, thus promoting systemic illness. Stxs inhibit host cell protein synthesis by cleaving a conserved adenine in the alpha-sarcin loop of the 28S ribosomal RNA. This cleavage event terminates elongation in affected ribosomes, but paradoxically up-regul ...
... inflammation may affect systemic absorption of Stx, thus promoting systemic illness. Stxs inhibit host cell protein synthesis by cleaving a conserved adenine in the alpha-sarcin loop of the 28S ribosomal RNA. This cleavage event terminates elongation in affected ribosomes, but paradoxically up-regul ...
Summary of Endomembrane
... 29. Targeting of soluble lysosomal enzymes to endosomes and lysosomes by M-6-P tag 30. The mannose 6-phosphate (M6P) pathway, the major route for targeting lysosomal enzymes to lysosomes: (1)Precursors of lysosomal enzymes migrate from the rER to the cis-Golgi where mannose residues are phosphorylat ...
... 29. Targeting of soluble lysosomal enzymes to endosomes and lysosomes by M-6-P tag 30. The mannose 6-phosphate (M6P) pathway, the major route for targeting lysosomal enzymes to lysosomes: (1)Precursors of lysosomal enzymes migrate from the rER to the cis-Golgi where mannose residues are phosphorylat ...
Aquaporin IDI Prelab
... b. What specific proteins are used as models for these new synthetic water channels? ...
... b. What specific proteins are used as models for these new synthetic water channels? ...
How does the structure of the cell membrane contribute to its function?
... •Proteins for communication •Chemicals sent from other cells must fit •Lock and key concept ...
... •Proteins for communication •Chemicals sent from other cells must fit •Lock and key concept ...
Lucky Lady Slots Online - How Does Shot Roulette Work
... 25. Complete the table below. Definition Protein Vocab ...
... 25. Complete the table below. Definition Protein Vocab ...
Cell-cell communication Cell-cell communication is distance
... Signal transduction Both receptor-enzymes and G-protein coupled receptors use second messengers learn to recognize names like cAMP, IP3, and DAG as second messengers Protein kinases are also important in phosphorylating or dephosphorylating proteins where do you think that phosphate might come from? ...
... Signal transduction Both receptor-enzymes and G-protein coupled receptors use second messengers learn to recognize names like cAMP, IP3, and DAG as second messengers Protein kinases are also important in phosphorylating or dephosphorylating proteins where do you think that phosphate might come from? ...
Protein Trafficking and Localization
... CYTOPLASMIC MEMBRANE PROTEINS CONTAIN “SIGNAL SEQUENCE” 15 - 30 HYDROPHOBIC AMINO ACID RESIDUES NEAR THE N-TERMINUS [e.g., GLYCINE, ALANINE, VALINE, LEUCINE, PHENYLALANINE] SIGNAL SEQUENCE ALLOWS PROTEIN TO BIND MEMBRANE AND BE SOLUBLE IN THE PHOSPHOLIPID MATRIX. AND TRANS-MEMBRANE-SPANNING SEQUENCE ...
... CYTOPLASMIC MEMBRANE PROTEINS CONTAIN “SIGNAL SEQUENCE” 15 - 30 HYDROPHOBIC AMINO ACID RESIDUES NEAR THE N-TERMINUS [e.g., GLYCINE, ALANINE, VALINE, LEUCINE, PHENYLALANINE] SIGNAL SEQUENCE ALLOWS PROTEIN TO BIND MEMBRANE AND BE SOLUBLE IN THE PHOSPHOLIPID MATRIX. AND TRANS-MEMBRANE-SPANNING SEQUENCE ...
Lecture 1
... When genes are expressed, the genetic information (base sequence) on DNA is first transcribed (copied) to a molecule of messenger RNA in a process similar to DNA replication. The mRNA molecules then leave the cell nucleus and enter the cytoplasm, where triplets of (codons) forming the genetic code ...
... When genes are expressed, the genetic information (base sequence) on DNA is first transcribed (copied) to a molecule of messenger RNA in a process similar to DNA replication. The mRNA molecules then leave the cell nucleus and enter the cytoplasm, where triplets of (codons) forming the genetic code ...
Enzymes: Principles of Catalysis
... In eukaryotic cells, proteins can be targeted to specific locales: ER, Golgi, Nucleus, mitochondrion or secreted Specific signal sequences interact with other proteins at the target site KDEL: Endoplasmic reticulum KRKR: Nucleus Hydrophobic residues: Secretion (Golgi) (Why?) Signal sequences are not ...
... In eukaryotic cells, proteins can be targeted to specific locales: ER, Golgi, Nucleus, mitochondrion or secreted Specific signal sequences interact with other proteins at the target site KDEL: Endoplasmic reticulum KRKR: Nucleus Hydrophobic residues: Secretion (Golgi) (Why?) Signal sequences are not ...
Gene Section NTRK3 (neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor,
... expression of TrkC catalytic and noncatalytic isoforms suggests that they act independently or in association. J Comp ...
... expression of TrkC catalytic and noncatalytic isoforms suggests that they act independently or in association. J Comp ...
TIM barrel proteins (ie
... TIM barrel proteins (ie. the aldo-keto reductase family represented by pdb entry code 2ACQ) consist of a repeated -strand-loop--helix-loop motif, most often containing eight repeats, with the parallel -strands forming the interior of an open barrel, and the -helices forming the outer belt of the ...
... TIM barrel proteins (ie. the aldo-keto reductase family represented by pdb entry code 2ACQ) consist of a repeated -strand-loop--helix-loop motif, most often containing eight repeats, with the parallel -strands forming the interior of an open barrel, and the -helices forming the outer belt of the ...
Protein classification
... • Biological properties of proteins result from interactions with other molecules – Antibodies, enzymes, structure, etc ...
... • Biological properties of proteins result from interactions with other molecules – Antibodies, enzymes, structure, etc ...
Membranes
... • Mosaic = diverse proteins embedded in phospholipids • Fluid = proteins can drift laterally within bi-layer ...
... • Mosaic = diverse proteins embedded in phospholipids • Fluid = proteins can drift laterally within bi-layer ...
Document
... to reveal the monoglucosylated species recognized by the lectin sites of calnexin/calreticulin. In their ATP-bound state, calnexin bind to the monoglucosylated oligosaccharide and hydrophobic segments of the unfolded glycoprotein (via their polypeptide binding or chaperone sites). Glycoprotein disso ...
... to reveal the monoglucosylated species recognized by the lectin sites of calnexin/calreticulin. In their ATP-bound state, calnexin bind to the monoglucosylated oligosaccharide and hydrophobic segments of the unfolded glycoprotein (via their polypeptide binding or chaperone sites). Glycoprotein disso ...
Ultrafast Solvation: Investigating Molecular Forces in Protein Folding November 12, 2010
... the cooperative behavior of these interactions drives the spontaneous folding and unfolding of large macromolecules. The ability to manipulate these large-scale conformational changes will require a complete understanding of solvent-protein interactions. We investigate solvent-protein interactions b ...
... the cooperative behavior of these interactions drives the spontaneous folding and unfolding of large macromolecules. The ability to manipulate these large-scale conformational changes will require a complete understanding of solvent-protein interactions. We investigate solvent-protein interactions b ...
Protein folding
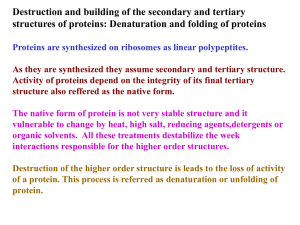
... Destruction and building of the secondary and tertiary structures of proteins: Denaturation and folding of proteins Proteins are synthesized on ribosomes as linear polypeptites. As they are synthesized they assume secondary and tertiary structure. Activity of proteins depend on the integrity of its ...
... Destruction and building of the secondary and tertiary structures of proteins: Denaturation and folding of proteins Proteins are synthesized on ribosomes as linear polypeptites. As they are synthesized they assume secondary and tertiary structure. Activity of proteins depend on the integrity of its ...
Document
... The G-Protein Coupled Receptor(GPCR) Superfamily All G-protein receptors are homologous, this has become clear from DNA sequencing experiments. ...
... The G-Protein Coupled Receptor(GPCR) Superfamily All G-protein receptors are homologous, this has become clear from DNA sequencing experiments. ...
PowerPoint - Center for Biological Physics
... protein folding. Concerned primarily with chemical interaction of amino acid side chains. ♦ Recognize areas of rigidity and flexibility in proteins. Flexible areas interact with other molecules to undergo chemical reactions. Great potential for combating disease as proteins could be manufactured for ...
... protein folding. Concerned primarily with chemical interaction of amino acid side chains. ♦ Recognize areas of rigidity and flexibility in proteins. Flexible areas interact with other molecules to undergo chemical reactions. Great potential for combating disease as proteins could be manufactured for ...
Center for Biological Physics* Math and Science Teachers Fellows
... protein folding. Concerned primarily with chemical interaction of amino acid side chains. Recognize areas of rigidity and flexibility in proteins. Flexible areas interact with other molecules to undergo chemical reactions. Great potential for combating disease as proteins could be manufactured for u ...
... protein folding. Concerned primarily with chemical interaction of amino acid side chains. Recognize areas of rigidity and flexibility in proteins. Flexible areas interact with other molecules to undergo chemical reactions. Great potential for combating disease as proteins could be manufactured for u ...
Protein Structure and Bioinformatics
... • They occur over and over again in natural proteins. • Some combinations of secondary structures are so common they are called “folds” (e.g., the SCOP database of protein folds). ...
... • They occur over and over again in natural proteins. • Some combinations of secondary structures are so common they are called “folds” (e.g., the SCOP database of protein folds). ...
G protein–coupled receptor

G protein–coupled receptors (GPCRs), also known as seven-transmembrane domain receptors, 7TM receptors, heptahelical receptors, serpentine receptor, and G protein–linked receptors (GPLR), constitute a large protein family of receptors that sense molecules outside the cell and activate inside signal transduction pathways and, ultimately, cellular responses. Coupling with G proteins, they are called seven-transmembrane receptors because they pass through the cell membrane seven times.G protein–coupled receptors are found only in eukaryotes, including yeast, choanoflagellates, and animals. The ligands that bind and activate these receptors include light-sensitive compounds, odors, pheromones, hormones, and neurotransmitters, and vary in size from small molecules to peptides to large proteins. G protein–coupled receptors are involved in many diseases, and are also the target of approximately 40% of all modern medicinal drugs. Two of the United States's top five selling drugs (Hydrocodone and Lisinopril) act by targeting a G protein–coupled receptor. The 2012 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Brian Kobilka and Robert Lefkowitz for their work that was ""crucial for understanding how G protein–coupled receptors function."". There have been at least seven other Nobel Prizes awarded for some aspect of G protein–mediated signaling.There are two principal signal transduction pathways involving the G protein–coupled receptors: the cAMP signal pathway and the phosphatidylinositol signal pathway. When a ligand binds to the GPCR it causes a conformational change in the GPCR, which allows it to act as a guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF). The GPCR can then activate an associated G protein by exchanging its bound GDP for a GTP. The G protein's α subunit, together with the bound GTP, can then dissociate from the β and γ subunits to further affect intracellular signaling proteins or target functional proteins directly depending on the α subunit type (Gαs, Gαi/o, Gαq/11, Gα12/13).