Molten rock that comes to the surface of the earth is called:
... d. determine the mineral’s chemical reactivity 30. What property of a rock determines if it will float or sink? a. Its mass b. Its volume c. Its color d. Its density 31. Which of these is most likely formed when a continental and oceanic plate collide? a. An alpine glacier b. A rain shadow desert c. ...
... d. determine the mineral’s chemical reactivity 30. What property of a rock determines if it will float or sink? a. Its mass b. Its volume c. Its color d. Its density 31. Which of these is most likely formed when a continental and oceanic plate collide? a. An alpine glacier b. A rain shadow desert c. ...
Notes Earth - Westmount High School
... found in refrigerators and air conditioners. • When the ozone layer shrinks, it cannot protect us as well from solar UV rays. • UV rays are trapped inside our atmosphere because of the greenhouse effect. ...
... found in refrigerators and air conditioners. • When the ozone layer shrinks, it cannot protect us as well from solar UV rays. • UV rays are trapped inside our atmosphere because of the greenhouse effect. ...
20130926123994
... Rotation • The earth rotates (spins) on its Axis • Axis – imaginary line that runs through the center of the earth from North Pole to South Pole • 24 hours = 1 rotation • Causes day and night ...
... Rotation • The earth rotates (spins) on its Axis • Axis – imaginary line that runs through the center of the earth from North Pole to South Pole • 24 hours = 1 rotation • Causes day and night ...
Name:
... What is the direction of movement for the San Andreas Fault (which direction do the plates move)? ...
... What is the direction of movement for the San Andreas Fault (which direction do the plates move)? ...
Isaac disasters
... A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary mass object, such as the Earth, which allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. Earth's volcanoes occur because the planet's crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter ...
... A volcano is a rupture on the crust of a planetary mass object, such as the Earth, which allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. Earth's volcanoes occur because the planet's crust is broken into 17 major, rigid tectonic plates that float on a hotter ...
Earth Science, 12e (Tarbuck/Lutgens)
... Earth Sciences I – Practice Midterm Exam 1) What are the basic differences between the disciplines of physical and historical geology? A) Physical geology is the study of fossils and sequences of rock strata; historical geology is the study of how rocks and minerals were used in the past. B) Histori ...
... Earth Sciences I – Practice Midterm Exam 1) What are the basic differences between the disciplines of physical and historical geology? A) Physical geology is the study of fossils and sequences of rock strata; historical geology is the study of how rocks and minerals were used in the past. B) Histori ...
A Living Planet Internal Forces Shaping the Earth
... a number of different natural disasters like earthquakes, tsunamis and volcanic eruptions. • There are three classifications for the plates movements. ...
... a number of different natural disasters like earthquakes, tsunamis and volcanic eruptions. • There are three classifications for the plates movements. ...
Core Case Study: Environmental Effects of Gold Mining
... Concept 14-1A Gigantic plates in the earth’s crust move very slowly atop the planet’s mantle, and wind and water move the matter from place to place across the earth’s surface. Concept 14-1B Natural geological hazards such as earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanoes, and landslides can cause considerabl ...
... Concept 14-1A Gigantic plates in the earth’s crust move very slowly atop the planet’s mantle, and wind and water move the matter from place to place across the earth’s surface. Concept 14-1B Natural geological hazards such as earthquakes, tsunamis, volcanoes, and landslides can cause considerabl ...
Slide 1
... Why is climate so variable? How old is the earth? Why do we have ocean tides? Is there really global warming? Is there really ice ages? How do we get water out of the ground? How does earth “fit” in our universe? ...
... Why is climate so variable? How old is the earth? Why do we have ocean tides? Is there really global warming? Is there really ice ages? How do we get water out of the ground? How does earth “fit” in our universe? ...
Version A - Partners4results
... Use the passage below to answer questions 11 and 12. Earth’s Early Atmosphere Early in Earth’s history, the molten outer layers of Earth released gases to form an early atmosphere. Cooling and solidification of that molten surface formed the early lithosphere approximately 4.4 billion years ago. Aro ...
... Use the passage below to answer questions 11 and 12. Earth’s Early Atmosphere Early in Earth’s history, the molten outer layers of Earth released gases to form an early atmosphere. Cooling and solidification of that molten surface formed the early lithosphere approximately 4.4 billion years ago. Aro ...
Constructive and Destructive Forces - TypePad
... affects the land. The cool nights and hot days always cause things to expand and contract. That movement can cause rocks to crack and break apart. Roots and plants also push into the rocks and break them apart. They act like wedges and push the rocks apart. Little animals also help by burrowing and ...
... affects the land. The cool nights and hot days always cause things to expand and contract. That movement can cause rocks to crack and break apart. Roots and plants also push into the rocks and break them apart. They act like wedges and push the rocks apart. Little animals also help by burrowing and ...
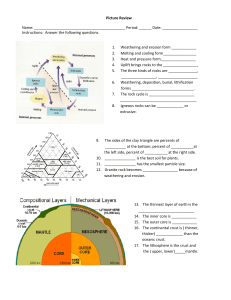
Picture Review Name
... 14. The inner core is ____________ 15. The outer core is ____________ 16. The continental crust is ( thinner, thicker) _____________ than the oceanic crust. 17. The lithosphere is the crust and the ( upper, lower)_____mantle. ...
... 14. The inner core is ____________ 15. The outer core is ____________ 16. The continental crust is ( thinner, thicker) _____________ than the oceanic crust. 17. The lithosphere is the crust and the ( upper, lower)_____mantle. ...
Prelude :: Just What is Geology?
... Hot spot tracks: why are they useful for understanding plate tectonics? Was the motion of the pacific plate constant through time? How do we know? Why is Iceland geologically unique? ...
... Hot spot tracks: why are they useful for understanding plate tectonics? Was the motion of the pacific plate constant through time? How do we know? Why is Iceland geologically unique? ...
File
... In an earthquake, energy is released in the form of waves. These are called seismic waves. The waves spread out from the focus. The strongest waves are found near the centre of the earthquake. This means that the most severe damage caused by an earthquake will happen close to the epicentre. ...
... In an earthquake, energy is released in the form of waves. These are called seismic waves. The waves spread out from the focus. The strongest waves are found near the centre of the earthquake. This means that the most severe damage caused by an earthquake will happen close to the epicentre. ...
File
... Describe how magnetic rocks on the seafloor provide evidence for tectonic theory • Earth has a magnetic field • Polarity of field reverses every 100 million years • When new rock forms at plate boundary at the oceanic ridge, the rock cools and solidifies and magnetic minerals in the rock (magnetite ...
... Describe how magnetic rocks on the seafloor provide evidence for tectonic theory • Earth has a magnetic field • Polarity of field reverses every 100 million years • When new rock forms at plate boundary at the oceanic ridge, the rock cools and solidifies and magnetic minerals in the rock (magnetite ...
ExamView - Earth Science Study Guide Final.tst
... 2. Evidence for sea-floor spreading has come from a. fossils in South America and Africa. c. b. magnetic minerals on the ocean floor. d. ...
... 2. Evidence for sea-floor spreading has come from a. fossils in South America and Africa. c. b. magnetic minerals on the ocean floor. d. ...
Grade 7 Science Unit 4: The Earth`s Crust
... Theory of Continental Drift which suggests that the continents change position slowly by a few cm a year. ...
... Theory of Continental Drift which suggests that the continents change position slowly by a few cm a year. ...
Grade 7 Science Unit 4: The Earth`s Crust
... Theory of Continental Drift which suggests that the continents change position slowly by a few cm a year. ...
... Theory of Continental Drift which suggests that the continents change position slowly by a few cm a year. ...
abstract
... variation of ISTFs and perform global noise reduction using estimated magnetic fields by ISTF at the sites. Usually FFT is used for estimating transfer function but wavelet transform is applied in this paper. We analyzed data observed at Boso stations. Near the Boso stations, there are two slow eart ...
... variation of ISTFs and perform global noise reduction using estimated magnetic fields by ISTF at the sites. Usually FFT is used for estimating transfer function but wavelet transform is applied in this paper. We analyzed data observed at Boso stations. Near the Boso stations, there are two slow eart ...
Plate Tectonics PowerPoint
... – TRANSFORM: Where two plates slide past each other, moving in opposite directions. ...
... – TRANSFORM: Where two plates slide past each other, moving in opposite directions. ...
key terms
... Characterized by a high frequency of earthquakes and are thought to be the zones along which folded mountain ranges or deep-sea trenches may develop. dip (170): The angle of inclination of the tilted layer also measured from the horizontal plane. discontinuity (seismic) (164): Boundaries where seism ...
... Characterized by a high frequency of earthquakes and are thought to be the zones along which folded mountain ranges or deep-sea trenches may develop. dip (170): The angle of inclination of the tilted layer also measured from the horizontal plane. discontinuity (seismic) (164): Boundaries where seism ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.