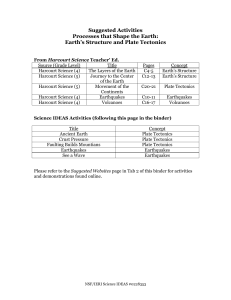
Layers of the Earth - Atlanta Public Schools
... •A rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust. •There are two kinds of crust: continental and oceanic. Yes, there is even crust under the ...
... •A rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust. •There are two kinds of crust: continental and oceanic. Yes, there is even crust under the ...
!GLG 101-Illustrated Vocabulary-Chapter 16 !Structure of the Earth
... *a portion of the Earth's crust that is thicker and less dense than oceanic crust. Consequently, this type of crust floats at a higher elevation and protrudes above sea level to form continents. !core *the innermost spherical structure of a planet; it is the densest material, probably consisting mos ...
... *a portion of the Earth's crust that is thicker and less dense than oceanic crust. Consequently, this type of crust floats at a higher elevation and protrudes above sea level to form continents. !core *the innermost spherical structure of a planet; it is the densest material, probably consisting mos ...
Changing Earth - Ms. Stinson's Science Class
... can move toward each other and converge, or collide. They also can pull apart or slide alongside one another. When the plates interact, the result of their movement is seen at the plate boundaries , as in the figure above. Movement along any plate boundary means that changes must happen at other bou ...
... can move toward each other and converge, or collide. They also can pull apart or slide alongside one another. When the plates interact, the result of their movement is seen at the plate boundaries , as in the figure above. Movement along any plate boundary means that changes must happen at other bou ...
Layers of the Earth Power Point
... •A rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust. •There are two kinds of crust: continental and oceanic. Yes, there is even crust under the ...
... •A rigid layer made up of the uppermost part of the mantle and the crust. •There are two kinds of crust: continental and oceanic. Yes, there is even crust under the ...
The African Plate: tapping 4 billion years of geodynamics and Earth
... origin of Earth’s first continents. Crustal evolution is represented throughout the 3.5 billion years by vast areas of both juvenile and reworked crust (and sediment cover) that allow detailed curves of crustal growth, geochemical changes, and impact rates to be tested. The African plate is unique i ...
... origin of Earth’s first continents. Crustal evolution is represented throughout the 3.5 billion years by vast areas of both juvenile and reworked crust (and sediment cover) that allow detailed curves of crustal growth, geochemical changes, and impact rates to be tested. The African plate is unique i ...
Name
... Rocks that are made from other rocks that have been weathered and eroded, and then compacted and cemented together. They contain small rocks, pebbles, shells and fossils. 27. What is igneous rock? Where does it most likely come from? Rocks that are made from cooled magma or lava. 28. What is metamor ...
... Rocks that are made from other rocks that have been weathered and eroded, and then compacted and cemented together. They contain small rocks, pebbles, shells and fossils. 27. What is igneous rock? Where does it most likely come from? Rocks that are made from cooled magma or lava. 28. What is metamor ...
Earth Model Project
... Earth Model Project The Earth's structure, scale and our place on it can be difficult to comprehend. Today we will use baker's clay to create a physical model of the planet. We will also use the idea of normalized data. At times it is difficult to visualize the relationships among numbers if they ar ...
... Earth Model Project The Earth's structure, scale and our place on it can be difficult to comprehend. Today we will use baker's clay to create a physical model of the planet. We will also use the idea of normalized data. At times it is difficult to visualize the relationships among numbers if they ar ...
Document
... The earth’s crust 3 layers: Crust, mantle and core. The mantle is mostly solid, but can move slowly The crust is cracked into tectonic plates How do tectonic plates move? 1. Radioactive processes occur in the core which release heat. 2. The heat travels through the mantle by convention currents. The ...
... The earth’s crust 3 layers: Crust, mantle and core. The mantle is mostly solid, but can move slowly The crust is cracked into tectonic plates How do tectonic plates move? 1. Radioactive processes occur in the core which release heat. 2. The heat travels through the mantle by convention currents. The ...
Yr9 Revision Geography 2016 June
... and all pregnancies are supposed to be planned and authorised. Because the One Child Policy is implemented and monitored by local authorities, it has been applied differently across the nation. For example, there has been stricter enforcement of the policy in urban areas than in rural areas. The pol ...
... and all pregnancies are supposed to be planned and authorised. Because the One Child Policy is implemented and monitored by local authorities, it has been applied differently across the nation. For example, there has been stricter enforcement of the policy in urban areas than in rural areas. The pol ...
Notes - Sayre Geography Class
... Forces Inside the Earth What is the Earth made of? ____________________________________ ____________________________________. Continents are unique, in part because of their landforms, which include mountains, hills, plateaus, and plains. ...
... Forces Inside the Earth What is the Earth made of? ____________________________________ ____________________________________. Continents are unique, in part because of their landforms, which include mountains, hills, plateaus, and plains. ...
Museum of Natural History field trip - e
... Map of the HALL OF PLANET EARTH on Floor 1 of the American Museum of Natural History (AMNH). ...
... Map of the HALL OF PLANET EARTH on Floor 1 of the American Museum of Natural History (AMNH). ...
Yr 7 Rocks and Fossils Unit Overview
... identify a range of common rock types using a key based on observable physical and chemical properties Give a basic explanation of fossils are formed and how they can be used to learn about earth’s past ...
... identify a range of common rock types using a key based on observable physical and chemical properties Give a basic explanation of fossils are formed and how they can be used to learn about earth’s past ...
plate tectonics post-test
... Which has the greatest mass (most space)? Which is least dense? 3. 5 mechanical/physical layers: Lost Ants March On Ice Which is the strong, lower layer of the mantle? Which is rigid? Which is rock that slowly flows (stretchy)? Which is solid iron and nickel? Which is liquid? 4. Be abl ...
... Which has the greatest mass (most space)? Which is least dense? 3. 5 mechanical/physical layers: Lost Ants March On Ice Which is the strong, lower layer of the mantle? Which is rigid? Which is rock that slowly flows (stretchy)? Which is solid iron and nickel? Which is liquid? 4. Be abl ...
- Aboriginal Access to Engineering
... On the Great Plains, Lakota Elders have long known of Tunka-shila, Grandfather Rock. They tell that before the beginning, everything existed as spirits in the mind of the Creator. Looking for a place to begin life, the spirits travelled through space, first to the sun, which was too hot, then to the ...
... On the Great Plains, Lakota Elders have long known of Tunka-shila, Grandfather Rock. They tell that before the beginning, everything existed as spirits in the mind of the Creator. Looking for a place to begin life, the spirits travelled through space, first to the sun, which was too hot, then to the ...
Chapter 19 Study Notes: The Ocean Basins
... • Scientists use ______ to calculate the ______ of the ocean floor. – sonar – depth ...
... • Scientists use ______ to calculate the ______ of the ocean floor. – sonar – depth ...
Plate Tectonics - St John Brebeuf
... Wegener realized that the puzzlelike fit of the continents were more than a coincidence, but he couldn't correctly explain what powered their movement. • Geologists now know that the Earth's outermost layer, the lithosphere, is divided into independently moving plates into which the continents are e ...
... Wegener realized that the puzzlelike fit of the continents were more than a coincidence, but he couldn't correctly explain what powered their movement. • Geologists now know that the Earth's outermost layer, the lithosphere, is divided into independently moving plates into which the continents are e ...
Plate Tectonics Background CDSU
... plates are solid rock and can be 80 to 400km thick. They vary in shape and size and have borders that cut through continents and oceans. There are nine large plates and several smaller plates. Of the major plates, six are mostly comprised of land (continental plates) and the other three are under th ...
... plates are solid rock and can be 80 to 400km thick. They vary in shape and size and have borders that cut through continents and oceans. There are nine large plates and several smaller plates. Of the major plates, six are mostly comprised of land (continental plates) and the other three are under th ...
The Earth`s Layers Foldable
... 3. Now you may cut out the layers! Also cut out the four squares and the 12 labels. Remember to cut out The Earth's Layers title. 4. Set one piece of blue paper in front of you. Closely trim the title. Paste The Earth's Layers title in the top left corner of the paper. 5. Paste the Crust right below ...
... 3. Now you may cut out the layers! Also cut out the four squares and the 12 labels. Remember to cut out The Earth's Layers title. 4. Set one piece of blue paper in front of you. Closely trim the title. Paste The Earth's Layers title in the top left corner of the paper. 5. Paste the Crust right below ...
Plate Tectonics - bvsd.k12.pa.us
... 3. The crust and upper mantle together are called the ____________________. 4. Beneath this layer is the plasticlike ____________________. 5. Scientists suggest that differences in density cause hot, plasticlike rock to be forced upward toward the surface, cool, and sink. This cycle is called a ____ ...
... 3. The crust and upper mantle together are called the ____________________. 4. Beneath this layer is the plasticlike ____________________. 5. Scientists suggest that differences in density cause hot, plasticlike rock to be forced upward toward the surface, cool, and sink. This cycle is called a ____ ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.