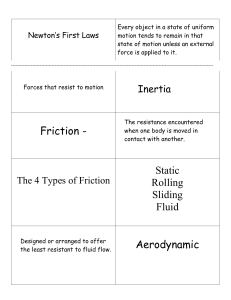
Cut squares along dotted line then fold in half to make flashcard
... Every object in a state of uniform motion tends to remain in that state of motion unless an external force is applied to it. ...
... Every object in a state of uniform motion tends to remain in that state of motion unless an external force is applied to it. ...
Algebra - Militant Grammarian
... SHM. If the frequency is 10.0 vibrations per second and the amplitude is 4.0 mm, what is the velocity when the displacement of the free end is 2.0 mm? 10. A particle which is performing simple harmonic motion passes through two points 20.0 cm apart with the same velocity, taking 1.0 seconds to get f ...
... SHM. If the frequency is 10.0 vibrations per second and the amplitude is 4.0 mm, what is the velocity when the displacement of the free end is 2.0 mm? 10. A particle which is performing simple harmonic motion passes through two points 20.0 cm apart with the same velocity, taking 1.0 seconds to get f ...
DiffLinearMotion
... • Your speed is 100 km/h and you’ve been driving for 5 hours. How far have you driven? ...
... • Your speed is 100 km/h and you’ve been driving for 5 hours. How far have you driven? ...
Math Practice for Test!! Make Sure you can do these problems
... 4. What is the average acceleration of a car that goes from 0 m/s to 25 m/s in 8.0 sec? 5. A cheetah can accelerate at up to 6.0 m/s squared. How long does it take for a cheetah to speed up from 10.5 m/s to 12.2 m/s? 6. What unbalanced force is needed to give a 976 kg vehicle an acceleration of 2.5 ...
... 4. What is the average acceleration of a car that goes from 0 m/s to 25 m/s in 8.0 sec? 5. A cheetah can accelerate at up to 6.0 m/s squared. How long does it take for a cheetah to speed up from 10.5 m/s to 12.2 m/s? 6. What unbalanced force is needed to give a 976 kg vehicle an acceleration of 2.5 ...
Lesson 25 – PowerPoint
... A car is travelling with a starting velocity of 90m/s and then after 10s its velocity changes to a final velocity of 50m/s. ...
... A car is travelling with a starting velocity of 90m/s and then after 10s its velocity changes to a final velocity of 50m/s. ...
Newton’s Second Law of Motion Force & Acceleration
... How fast is an object moving in free fall? • The increase in speed per second is the • Let’s consider the acceleration which in following data table: this case is 10 m/s/s. Elapsed time Instantaneous (sec) speed (m/sec) • The instantaneous speed of an object that is ...
... How fast is an object moving in free fall? • The increase in speed per second is the • Let’s consider the acceleration which in following data table: this case is 10 m/s/s. Elapsed time Instantaneous (sec) speed (m/sec) • The instantaneous speed of an object that is ...
Exam 2 Physics 125 Fall 2008 Name:
... 13. The diagram shows three blocks on a frictionless table connected together with two identical strings, which can be subject to a maximum tension of 50.0N before breaking. The masses of the blocks are indicated, and the assembly is pulled by a horizontal force P. What is the maximum acceleration t ...
... 13. The diagram shows three blocks on a frictionless table connected together with two identical strings, which can be subject to a maximum tension of 50.0N before breaking. The masses of the blocks are indicated, and the assembly is pulled by a horizontal force P. What is the maximum acceleration t ...
Lesson 20 - Acceleration
... the y-axis (m/s) and time (s) on the x-axis Plot your three points on the velocity time graph; what do you notice? ...
... the y-axis (m/s) and time (s) on the x-axis Plot your three points on the velocity time graph; what do you notice? ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Air bags act to increase the time of impact, reducing the acceleration (and reducing the force of your body’s impact). Crumple zones work in the same way: parts of a car are designed to collaspe during an impact, increasing the time it takes to come to a complete stop (they also ‘absorb’ energy) ...
... Air bags act to increase the time of impact, reducing the acceleration (and reducing the force of your body’s impact). Crumple zones work in the same way: parts of a car are designed to collaspe during an impact, increasing the time it takes to come to a complete stop (they also ‘absorb’ energy) ...
FOPS UNIT 3 – Newton`s Laws of Motion Review Worksheet
... the opposite direction. Why wont the box move? (use the word equilibrium) ...
... the opposite direction. Why wont the box move? (use the word equilibrium) ...
Physics ~ Fall Final Review
... the car slows from 15.0 m/s to 0.0 m/s. What is the car’s average acceleration? 7. Define force, static friction, kinetic friction, acceleration due to gravity, WEIGHT 8. Draw a free body diagram for the following situations: a) a rock on the ground; b) a thrown ball as it flies through the air; c) ...
... the car slows from 15.0 m/s to 0.0 m/s. What is the car’s average acceleration? 7. Define force, static friction, kinetic friction, acceleration due to gravity, WEIGHT 8. Draw a free body diagram for the following situations: a) a rock on the ground; b) a thrown ball as it flies through the air; c) ...
ppt
... • Motion of a body when only the force of gravity is acting on the body • The acceleration of an object in free fall is called the acceleration due to gravity, or free fall accleration • Free fall acceleration is denoted by the symbol g ...
... • Motion of a body when only the force of gravity is acting on the body • The acceleration of an object in free fall is called the acceleration due to gravity, or free fall accleration • Free fall acceleration is denoted by the symbol g ...
Matter and Forces in Motion (2a-2c)
... 26.A real car moving at 10 km/h has more momentum than a toy car moving at the same speed because the real car has greater mass 27.In the equation p = m v, the p represents momentum. 28.The statement "to every action there is an equal and opposite reaction" is Newton’s third law of motion. 29.The ...
... 26.A real car moving at 10 km/h has more momentum than a toy car moving at the same speed because the real car has greater mass 27.In the equation p = m v, the p represents momentum. 28.The statement "to every action there is an equal and opposite reaction" is Newton’s third law of motion. 29.The ...
Sects. 12.3 through 12.4
... undergoes simple harmonic oscillations. Find (a) the force constant of the spring, (b) the frequency of the oscillations, and (c) the maximum speed of the object. Where does this maximum speed occur? (d) Find the maximum acceleration of the object. Where does it occur? (e) Find the total energy of t ...
... undergoes simple harmonic oscillations. Find (a) the force constant of the spring, (b) the frequency of the oscillations, and (c) the maximum speed of the object. Where does this maximum speed occur? (d) Find the maximum acceleration of the object. Where does it occur? (e) Find the total energy of t ...























