Chapter 5 PowerPoint
... 5-2 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion Newton F=ma Object moving in a circle must be acted on by a force Fr=mar=mv2/r Net force must be directed toward the center of the circle. Centripetal force - force directed towards center of circle ...
... 5-2 Dynamics of Uniform Circular Motion Newton F=ma Object moving in a circle must be acted on by a force Fr=mar=mv2/r Net force must be directed toward the center of the circle. Centripetal force - force directed towards center of circle ...
Forces and Motion Study Guide
... Formulas S= D/T Speed = Distance/ Time ; Momentum= mv; a= Vf - Vi / t (acceleration) ...
... Formulas S= D/T Speed = Distance/ Time ; Momentum= mv; a= Vf - Vi / t (acceleration) ...
Force and motion 1
... * know some different types of forces * know and be able to apply Newton’s second law to simple examples of objects moving in a straight line * understands the idea of equilibrium. ...
... * know some different types of forces * know and be able to apply Newton’s second law to simple examples of objects moving in a straight line * understands the idea of equilibrium. ...
Mass and Motion
... • 1 atomic mass unit (about the mass of one hydrogen atom) = 1.66 x 10-27 kg ...
... • 1 atomic mass unit (about the mass of one hydrogen atom) = 1.66 x 10-27 kg ...
Natural Order Gravitation Assignment Solutions
... The astronauts feel weightless because they are in ’freefall’. That is, they are accelerating toward the planet at a rate equal to the acceleration of gravity at that point. (Note: The sensation of weight is actually the normal force of a surface acting on your body in order to limit your accelerati ...
... The astronauts feel weightless because they are in ’freefall’. That is, they are accelerating toward the planet at a rate equal to the acceleration of gravity at that point. (Note: The sensation of weight is actually the normal force of a surface acting on your body in order to limit your accelerati ...
Newton's Laws powerpoint - South Webster High School
... acceleration (change in speed or direction (acceleration) speeding up Deceleration is negative acceleration or slowing down Centripetal acceleration changing direction ...
... acceleration (change in speed or direction (acceleration) speeding up Deceleration is negative acceleration or slowing down Centripetal acceleration changing direction ...
1) You push your lawnmower (mass = 15 kg) across
... 11) The figure shows two blocks connected by a cord that passes over a massless, frictionless pulley. The lighter block has a mass m = 1.3 kg and the heavier block has a m = 2.8 kg. Find the magnitudes of the accelerations of the two blocks and the magnitude T of the force on each block from the cor ...
... 11) The figure shows two blocks connected by a cord that passes over a massless, frictionless pulley. The lighter block has a mass m = 1.3 kg and the heavier block has a m = 2.8 kg. Find the magnitudes of the accelerations of the two blocks and the magnitude T of the force on each block from the cor ...
The Gravitron! 1.1 Observe and Reason 1) Roll a bowling ball along
... If a 40.0 g stone is whirled horizontally on the end of a 0.60 m string at a speed of 2.2 m/s, what is the force the string exerts on the stone? 1.8 Represent and Reason A bowling ball has a mass of 7.3 kg. If you move it around a circle with a radius of 0.75 m and a velocity of 2.5 m/s, what force ...
... If a 40.0 g stone is whirled horizontally on the end of a 0.60 m string at a speed of 2.2 m/s, what is the force the string exerts on the stone? 1.8 Represent and Reason A bowling ball has a mass of 7.3 kg. If you move it around a circle with a radius of 0.75 m and a velocity of 2.5 m/s, what force ...
1. A sphere with a radius of 1.7 cm has a volume of: A) 2.1 × 10–5 m
... 3. How far does a car travel in 6 s if its initial velocity is 2 m/s and its acceleration is 2 m/s2 in the forward direction? A) 12 m B) 14 m C) 24 m D) 36 m E) 48 m 4. A baseball is thrown vertically into the air. The acceleration of the ball at its highest point is: A) zero B) g, down C) g, up D) ...
... 3. How far does a car travel in 6 s if its initial velocity is 2 m/s and its acceleration is 2 m/s2 in the forward direction? A) 12 m B) 14 m C) 24 m D) 36 m E) 48 m 4. A baseball is thrown vertically into the air. The acceleration of the ball at its highest point is: A) zero B) g, down C) g, up D) ...
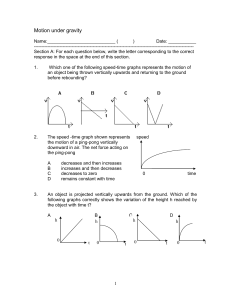
Quiz on Motion under gravity
... The acceleration of the object decreases as the object rises up; The acceleration is positive for the upward motion and negative for the downward motion; At maximum height, the velocity of the object is zero; If air resistance is negligible, the time for the upward motion is equal to the time for th ...
... The acceleration of the object decreases as the object rises up; The acceleration is positive for the upward motion and negative for the downward motion; At maximum height, the velocity of the object is zero; If air resistance is negligible, the time for the upward motion is equal to the time for th ...
Objective 1: Evaluate the following problems using the “kinematic
... Objective 2: Evaluate the following force problems. Draw a free body diagram for the following situations and then solve for the net force: F (Remember, since a net objects only have net forces on them if they are m accelerating!!!) 1. If an object is moving at a constant velocity, what is the ne ...
... Objective 2: Evaluate the following force problems. Draw a free body diagram for the following situations and then solve for the net force: F (Remember, since a net objects only have net forces on them if they are m accelerating!!!) 1. If an object is moving at a constant velocity, what is the ne ...
Review for Intro. Physics Part A Final Exam
... bicycle goes from rest to 5km/h which has a a) car greater b) bike acceleration? c) same same d) I don’t know ...
... bicycle goes from rest to 5km/h which has a a) car greater b) bike acceleration? c) same same d) I don’t know ...
Speed up Slow down Change direction 2 m/s 2 Ball rolling down a
... •Slows things down The fluid friction due to air. ...
... •Slows things down The fluid friction due to air. ...
template - charlestuttle
... 11. An 800. kg Geo Metro can go from rest to a speed of 36 m/s in 9.0s. What average net force acts on the car? ...
... 11. An 800. kg Geo Metro can go from rest to a speed of 36 m/s in 9.0s. What average net force acts on the car? ...
Exam 1 with answer
... (a) vf cos θ î + vf sin θ ĵ (b) vf cos θ î − vf sin θ ĵ ← (c) −gt ĵ (d) vf cos θ î + (vf sin θ − gt)ĵ (e) vf cos θ î − (vf sin θ + gt)ĵ 12. In the figure above, we know that h =20 m and d = 30 m. The ball’s speed when the ball reaches its highest point is 10 m/s. How long does the ball take ...
... (a) vf cos θ î + vf sin θ ĵ (b) vf cos θ î − vf sin θ ĵ ← (c) −gt ĵ (d) vf cos θ î + (vf sin θ − gt)ĵ (e) vf cos θ î − (vf sin θ + gt)ĵ 12. In the figure above, we know that h =20 m and d = 30 m. The ball’s speed when the ball reaches its highest point is 10 m/s. How long does the ball take ...
45 m/s - Madison Public Schools
... is assumed to be stationary when compared to a moving object. ...
... is assumed to be stationary when compared to a moving object. ...
Physics 103-02 Exam IV 4 Dec
... is perpendicular to the plane of the disk, through its center. The coefficient of friction between the pad and the disk is = 0.4. The spinning disk has mass of M = 15 kg, a radius of R = 0.5 m, and a moment of inertia I = 15.0 kgm2 . What is the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the disk a ...
... is perpendicular to the plane of the disk, through its center. The coefficient of friction between the pad and the disk is = 0.4. The spinning disk has mass of M = 15 kg, a radius of R = 0.5 m, and a moment of inertia I = 15.0 kgm2 . What is the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the disk a ...