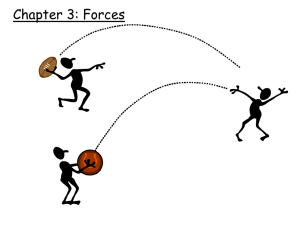
Newton`s Second Law
... Friction: a force that occurs when two touching objects move past each other. Frictional force is always in the opposite direction to the motion. ...
... Friction: a force that occurs when two touching objects move past each other. Frictional force is always in the opposite direction to the motion. ...
A baseball is thrown vertically upward
... 3) Make a force diagram for the ball after being thrown but still on the way up. ...
... 3) Make a force diagram for the ball after being thrown but still on the way up. ...
Chapter 2 Outline
... 2. Frame of Reference – the background motion is measured against 3. Distance – how far an object has moved 4. Displacement – distance and direction in a straight line from starting point to ending point B. Speed - how quickly an object changes position 1. distance traveled per unit of time 2. s = d ...
... 2. Frame of Reference – the background motion is measured against 3. Distance – how far an object has moved 4. Displacement – distance and direction in a straight line from starting point to ending point B. Speed - how quickly an object changes position 1. distance traveled per unit of time 2. s = d ...
How much force is required to inflate a high pressure
... During your travels through deep space you discover a new solar system. You land on the outermost planet and determine that the acceleration due to gravity is 2.7 m/s^2. If your mass back on Earth is 72 kg, what force would you exert on a scale in pounds while standing on the planet's surface? The ...
... During your travels through deep space you discover a new solar system. You land on the outermost planet and determine that the acceleration due to gravity is 2.7 m/s^2. If your mass back on Earth is 72 kg, what force would you exert on a scale in pounds while standing on the planet's surface? The ...
Ferris Wheel Physics
... stood 79.2 metres high with the diameter of the wheel being 75 metres. Since then many have been built and they are a very popular ride at most amusement parks worldwide. Compared to the original Ferris wheel, the model at Luna Park is a baby. It stands about 20 metres high and has a diameter of 18. ...
... stood 79.2 metres high with the diameter of the wheel being 75 metres. Since then many have been built and they are a very popular ride at most amusement parks worldwide. Compared to the original Ferris wheel, the model at Luna Park is a baby. It stands about 20 metres high and has a diameter of 18. ...
Laws of Motion
... Or, the acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force on the object and inversely proportional to the object’s mass: acceleration = force ÷ mass a=F÷m ...
... Or, the acceleration of an object is proportional to the net force on the object and inversely proportional to the object’s mass: acceleration = force ÷ mass a=F÷m ...
Unit 5 plan motion
... * SWBAT categorize as scalar or vector quantities * SWBAT draw and add vectors and find both magnitude and direction of the resultant * SWBAT describe effects of balanced forces and unbalanced forces on motion * SWBAT apply Newton’s 1st law of motion and inertia to everyday objects * SWBAT calculate ...
... * SWBAT categorize as scalar or vector quantities * SWBAT draw and add vectors and find both magnitude and direction of the resultant * SWBAT describe effects of balanced forces and unbalanced forces on motion * SWBAT apply Newton’s 1st law of motion and inertia to everyday objects * SWBAT calculate ...
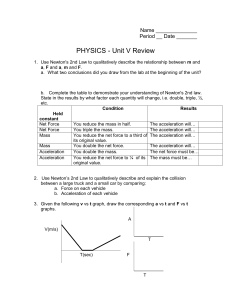
Unit V review
... You reduce the net force to ¼ of its The mass must be… original value. 2. Use Newton’s 2nd Law to qualitatively describe and explain the collision between a large truck and a small car by comparing: a. Force on each vehicle b. Acceleration of each vehicle 3. Given the following v vs t graph, draw th ...
... You reduce the net force to ¼ of its The mass must be… original value. 2. Use Newton’s 2nd Law to qualitatively describe and explain the collision between a large truck and a small car by comparing: a. Force on each vehicle b. Acceleration of each vehicle 3. Given the following v vs t graph, draw th ...
Skill Phases for
... Chaining angular momentum is transferred in the body from one set of muscle groups to another Lever action for speed or force ...
... Chaining angular momentum is transferred in the body from one set of muscle groups to another Lever action for speed or force ...
Regular Physics Mid-Term Review Packet
... 31. The acceleration of an object acted upon by a force is directly proportional to the applied force and inversely proportional to the mass. 32. Based on Newton’s 2nd law, if mass of an object doubles, for the same applied force, what happens to its acceleration? 33. For the same mass if the force ...
... 31. The acceleration of an object acted upon by a force is directly proportional to the applied force and inversely proportional to the mass. 32. Based on Newton’s 2nd law, if mass of an object doubles, for the same applied force, what happens to its acceleration? 33. For the same mass if the force ...
Physics 109 Test 1 February 17, 2011 Answer all questions on the
... 7. The value of the average velocity for any round trip is equal to (A) zero. (B) total distance traveled divided by total trip time. (C) the final acceleration multiplied by trip time (D) the person’s speed halfway through the path. 8. Suppose you have a car traveling down the road at constant spe ...
... 7. The value of the average velocity for any round trip is equal to (A) zero. (B) total distance traveled divided by total trip time. (C) the final acceleration multiplied by trip time (D) the person’s speed halfway through the path. 8. Suppose you have a car traveling down the road at constant spe ...