Jeopardy - Fair Lawn Schools
... The total momentum in a system cannot change as long as all the forces act only between the objects in the system. ...
... The total momentum in a system cannot change as long as all the forces act only between the objects in the system. ...
Document
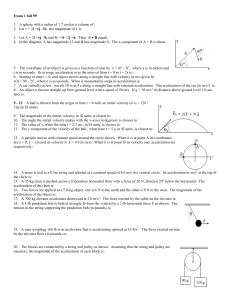
... 5. The coordinate of an object is given as a function of time by x = 4t 2 - 3t3 , where x is in meters and t is in seconds. Its average acceleration over the interval from t = 0 to t = 2s is: 6. Starting at time t = 0, and object moves along a straight line with velocity in m/s given by v(t) = 98 - ...
... 5. The coordinate of an object is given as a function of time by x = 4t 2 - 3t3 , where x is in meters and t is in seconds. Its average acceleration over the interval from t = 0 to t = 2s is: 6. Starting at time t = 0, and object moves along a straight line with velocity in m/s given by v(t) = 98 - ...
Physics 220 – Exam #1
... 11. In class we did a demonstration involving two people on flat carts. One exerted a force on one end of a rope while the other would just hang on. Which of the following principles or ideas was this demonstration designed to illustrate? (a) Newton’s second law: F = ma. (b) Some motion can be frict ...
... 11. In class we did a demonstration involving two people on flat carts. One exerted a force on one end of a rope while the other would just hang on. Which of the following principles or ideas was this demonstration designed to illustrate? (a) Newton’s second law: F = ma. (b) Some motion can be frict ...
Topics covered in PH111 - Rose
... Scalars and vectors, decomposition of vectors into components, addition of vectors, cross and dot products, unit vectors. Kinematics: Position, displacement, average and instantaneous velocity and acceleration, derivation of the equations of motion at constant acceleration from velocity-time graph, ...
... Scalars and vectors, decomposition of vectors into components, addition of vectors, cross and dot products, unit vectors. Kinematics: Position, displacement, average and instantaneous velocity and acceleration, derivation of the equations of motion at constant acceleration from velocity-time graph, ...
EFFECT OF CENTRIFUGAL AND CORIOLIS FORCES DUE TO
... Here r is position vector of the particle and the other terms have their usual meaning. When a particle is at rest on the surface of earth which rotates with constant angular velocity ω about its polar axis, then: ...
... Here r is position vector of the particle and the other terms have their usual meaning. When a particle is at rest on the surface of earth which rotates with constant angular velocity ω about its polar axis, then: ...
Rotational Motion
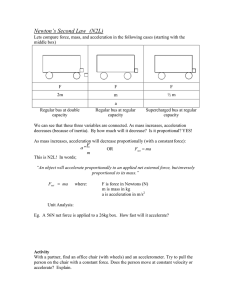
... A tangential force on a mass creates an acceleration. • Tangential force: Ft = m at • Tangential acceleration: at = r ...
... A tangential force on a mass creates an acceleration. • Tangential force: Ft = m at • Tangential acceleration: at = r ...
Physics 103 : Quiz 10
... 1. A ball dropped from a height of 4.00 m makes a perfectly elastic collision with the ground. Assuming no mechanical energy is lost due to air resistance, (a) show that the motion is periodic and (b) determine the period of the motion. (c) Is the motion simple harmonic? Explain. ...
... 1. A ball dropped from a height of 4.00 m makes a perfectly elastic collision with the ground. Assuming no mechanical energy is lost due to air resistance, (a) show that the motion is periodic and (b) determine the period of the motion. (c) Is the motion simple harmonic? Explain. ...
11.2 Questions Force and Mass Determine Acceleration 1. What 3
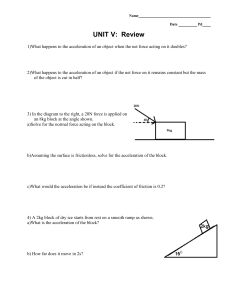
... 8. A mass is 2kg. What other information do you need to calculate acceleration? 2. Look at the picture on page 354. What do the arrows in the diagrams show? 9. If an object moves at a constant speed, but it accelerates, what changes? 3. What happens to the acceleration of an object when the force on ...
... 8. A mass is 2kg. What other information do you need to calculate acceleration? 2. Look at the picture on page 354. What do the arrows in the diagrams show? 9. If an object moves at a constant speed, but it accelerates, what changes? 3. What happens to the acceleration of an object when the force on ...
Ch. 2-3
... 3. During free fall an object accelerates toward the Earth at this rate: __________ 4. Velocity differs from speed in that velocity has a ___________. 5. Newton’s Second Law states the acceleration is ___________________ to the mass of an object in motion. 6. Weight equals ___________ times the ____ ...
... 3. During free fall an object accelerates toward the Earth at this rate: __________ 4. Velocity differs from speed in that velocity has a ___________. 5. Newton’s Second Law states the acceleration is ___________________ to the mass of an object in motion. 6. Weight equals ___________ times the ____ ...