* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Microsoft Word - SPH 3U, T2L6, Newton`s Second Law.doc
Survey
Document related concepts
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Specific impulse wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Centrifugal force wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Seismometer wikipedia , lookup
Center of mass wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
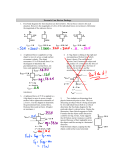
Newton’s Second Law (N2L) Lets compare force, mass, and acceleration in the following cases (starting with the middle box) F F F 2m m ½m Regular bus at double capacity a Regular bus at regular capacity Supercharged bus at regular capacity We can see that these three variables are connected. As mass increases, acceleration decreases (because of inertia). By how much will it decrease? Is it proportional? YES! As mass increases, acceleration will decrease proportionally (with a constant force): F a OR Fnet ma m This is N2L! In words; “An object will accelerate proportionally to an applied net external force, but inversely proportional to its mass.” Fnet ma where: F is force in Newtons (N) m is mass in kg a is acceleration in m/s2 Unit Analysis: Eg. A 56N net force is applied to a 26kg box. How fast will it accelerate? Activity With a partner, find an office chair (with wheels) and an accelerometer. Try to pull the person on the chair with a constant force. Does the person move at constant velocity or accelerate? Explain.