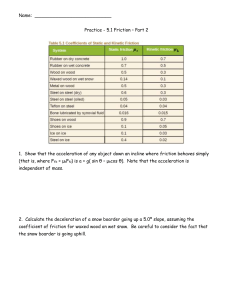
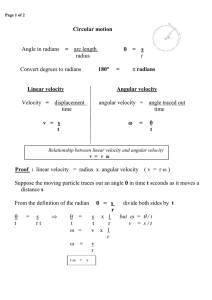
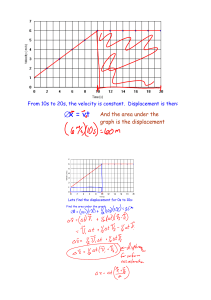
Name: Practice - 5.1 Friction – Part 2 1. Show that the acceleration of
... 2. Calculate the deceleration of a snow boarder going up a 5.0º slope, assuming the coefficient of friction for waxed wood on wet snow. Be careful to consider the fact that the snow boarder is going uphill. ...
... 2. Calculate the deceleration of a snow boarder going up a 5.0º slope, assuming the coefficient of friction for waxed wood on wet snow. Be careful to consider the fact that the snow boarder is going uphill. ...
Newton`s 2nd Law - fhssciencerocks
... One Newton is equal to 0.225 lbs. One pound is equal to 4.448 Newtons If you push an empty cart with the same force you would use to push a full cart, the empty one will have a much greater acceleration ...
... One Newton is equal to 0.225 lbs. One pound is equal to 4.448 Newtons If you push an empty cart with the same force you would use to push a full cart, the empty one will have a much greater acceleration ...
AP1 Ch. 8 Review w/answers
... 6. A ventilation fan with a moment of inertia of 0.034 kgm2 has a net torque of 0.11 Nm applied to it. What angular acceleration does it experience? ...
... 6. A ventilation fan with a moment of inertia of 0.034 kgm2 has a net torque of 0.11 Nm applied to it. What angular acceleration does it experience? ...
4.1 Forces and the Law of Inertia
... Relates the applied force, the mass, and the acceleration of an object. It states that Acceleration is directly proportional to force And, inversely proportional to mass. ...
... Relates the applied force, the mass, and the acceleration of an object. It states that Acceleration is directly proportional to force And, inversely proportional to mass. ...
Up, Up and Away
... We will consider motion the the x-y plane. Positions now have (x,y) coordinates so we need to use vectors. ...
... We will consider motion the the x-y plane. Positions now have (x,y) coordinates so we need to use vectors. ...
Acceleration - Sikeston R-6
... •IV. Force, motion and mechanical energy •A. Relative Motion •7th grade assessment •Science standards 3.1; 3.3; 4.1 •Students should be able to explain how an object’s acceleration is affected by outside forces and its mass. •View lesson before using with students. Click mouse to view sample questio ...
... •IV. Force, motion and mechanical energy •A. Relative Motion •7th grade assessment •Science standards 3.1; 3.3; 4.1 •Students should be able to explain how an object’s acceleration is affected by outside forces and its mass. •View lesson before using with students. Click mouse to view sample questio ...
Student Learning Goals
... in units of newtons. A one newton net force acting on a one-kilogram object produces an acceleration of 1 m/s2. Therefore, a newton is the same as a kilogrammeter/second2. (N = kgm/s2) 5. Use Newton's 2nd Law to qualitatively describe the relationship between m and a, F and a, m and F. (For exampl ...
... in units of newtons. A one newton net force acting on a one-kilogram object produces an acceleration of 1 m/s2. Therefore, a newton is the same as a kilogrammeter/second2. (N = kgm/s2) 5. Use Newton's 2nd Law to qualitatively describe the relationship between m and a, F and a, m and F. (For exampl ...
racing - MathinScience.info
... A frame of reference is the standard used for judging or deciding if motion has occurred in a situation. Motion can be determined by using the frame of reference to measure from point A to point B. The most common frame of reference is the horizon. ...
... A frame of reference is the standard used for judging or deciding if motion has occurred in a situation. Motion can be determined by using the frame of reference to measure from point A to point B. The most common frame of reference is the horizon. ...
Centripetal Force
... A 200. g mass hung is from a 50. cm string as a conical pendulum. The period of the pendulum in a perfect circle is 1.4 s. What is the angle of the pendulum? What is the tension on the string? ...
... A 200. g mass hung is from a 50. cm string as a conical pendulum. The period of the pendulum in a perfect circle is 1.4 s. What is the angle of the pendulum? What is the tension on the string? ...
forces
... When our mass is in kg (kilograms) and our acceleration is in m/s2 (meters per second squared) then our force’s units will be: ...
... When our mass is in kg (kilograms) and our acceleration is in m/s2 (meters per second squared) then our force’s units will be: ...
Electrostatics
... The amount of acceleration experienced by an object is proportional to the amount of force acting on it. bigger force bigger acceleration ...
... The amount of acceleration experienced by an object is proportional to the amount of force acting on it. bigger force bigger acceleration ...
Newton`s second law of motion
... I.e. To accelerate an object a force in needed, this force is proportional to the acceleration, and the constant of proportionality is m. the mass of the object. ...
... I.e. To accelerate an object a force in needed, this force is proportional to the acceleration, and the constant of proportionality is m. the mass of the object. ...
03
... 13. Find the equilibrium position and the frequency of small oscillations of a particle of mass m about the equilibrium position for the potential V (x) = − where a, b are positive constants. ...
... 13. Find the equilibrium position and the frequency of small oscillations of a particle of mass m about the equilibrium position for the potential V (x) = − where a, b are positive constants. ...
Name: Notes - 4.3 Newton`s Second Law of Motion: Concept of a
... A. What do bathroom scales measure? Mass or Weight? B. Would the bathroom scale reading change if you were on the Moon? How? 12. Suppose that the net external force (push minus friction) exerted on a lawn mower is 51 N (about 11 lb) parallel to the ground. The mass of the mower is 24 kg. What is its ...
... A. What do bathroom scales measure? Mass or Weight? B. Would the bathroom scale reading change if you were on the Moon? How? 12. Suppose that the net external force (push minus friction) exerted on a lawn mower is 51 N (about 11 lb) parallel to the ground. The mass of the mower is 24 kg. What is its ...
force-problems-old
... rope without it breaking is 600 N. Find the minimum acceleration the man can have without breaking the rope? Find the maximum acceleration the man can have? 7. A 50 kg child slides down the same rope as in problem #6. Can the child slide down the rope with a constant velocity? What is the tension in ...
... rope without it breaking is 600 N. Find the minimum acceleration the man can have without breaking the rope? Find the maximum acceleration the man can have? 7. A 50 kg child slides down the same rope as in problem #6. Can the child slide down the rope with a constant velocity? What is the tension in ...