* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics Review
Relativistic mechanics wikipedia , lookup
Mitsubishi AWC wikipedia , lookup
Equations of motion wikipedia , lookup
Modified Newtonian dynamics wikipedia , lookup
Rolling resistance wikipedia , lookup
Newton's laws of motion wikipedia , lookup
Faster-than-light wikipedia , lookup
Coriolis force wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum operator wikipedia , lookup
Differential (mechanical device) wikipedia , lookup
Fictitious force wikipedia , lookup
Angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Rotating locomotion in living systems wikipedia , lookup
Speeds and feeds wikipedia , lookup
Newton's theorem of revolving orbits wikipedia , lookup
Work (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Relativistic angular momentum wikipedia , lookup
Variable speed of light wikipedia , lookup
Jerk (physics) wikipedia , lookup
Classical central-force problem wikipedia , lookup
Rigid body dynamics wikipedia , lookup
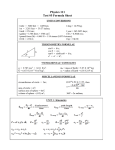
Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics Review 1. The Earth takes slightly less than one day to complete one rotation about the axis passing through its poles. The actual time is 8.616 × 104 s. Given this information, what is the angular speed of the Earth about its axis? 2. A wheel with a 0.10-m radius is rotating at 35 rev/s. It then slows uniformly to 15 rev/s over a 3.0-s interval. What is the angular acceleration of a point on the wheel? 3. A fan rotating with an initial angular velocity of 1000 rev/min is switched off. In 2 seconds, the angular velocity decreases to 200 rev/min. Assuming the angular acceleration is constant, how many revolutions does the blade undergo during this time? 4. A wheel, originally rotating at 126 rad/s undergoes a constant angular deceleration of 5.00 rad/s2. What is its angular speed after it has turned through an angle of 628 radians? Page 1 5. On an amusement park ride, passengers are seated in a horizontal circle of radius 7.5 m. The seats begin from rest and are uniformly accelerated for 21 seconds to a maximum rotational speed of 1.4 rad/s. What is the tangential acceleration of the passengers during the first 21 s of the ride? What is the instantaneous tangential speed of the passengers 15 s after the acceleration begins? 6. A ball attached to a string starts at rest and undergoes a constant angular acceleration as it travels in a horizontal circle of radius 0.30 m. After 0.65 sec, the angular speed of the ball is 9.7 rad/s. What is the tangential acceleration of the ball? 7. A bicycle has tires of radius 0.35 meters. If the bicycle is traveling at a constant speed of 7.8 m/s, at approximately what angular speed are the tires rotating? Page 2 8. A wrench is used to tighten a nut as shown in the figure. A 12-N force is applied 7.0 cm from the axis of rotation. What is the magnitude of the torque due to the applied force? 9. A string is tied to a doorknob 0.72 m from the hinge as illustrated in the figure. At the instant shown, the force applied to the string is 5.0 N. What is the magnitude of the torque on the door? Page 3 10. One end of a rope is tied to the handle of a horizontally-oriented and uniform door. A force F is applied to the other end of the rope as shown in the drawing. The door has a weight of 145 N and is hinged on the right. What is the maximum magnitude of F for which the door will remain at rest? 11. Consider four point masses located as shown in the sketch. The acceleration due to gravity is the same everywhere. What is the x coordinate of the center of gravity for this system? Page 4 12. A 66-N m torque acts on a wheel with a moment of inertia 175 kg m2. If the wheel starts from rest, how long will it take the wheel to make one revolution? 13. Three children are pulling on a rotatable platform on a playground. The platform has a radius of 3.80 m. In the picture, two children are pulling with equal forces of 40.0 N in an attempt to make the platform rotate clockwise. The third child applies a force of 60 N as shown. What is the net torque on the platform? Note: “ccw” is counterclockwise and “cw” is clockwise. Page 5 Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics Review 14. A rider on a motorcycle that has a mass of 195 kg is traveling with a speed of 24 m/s. Each of the two wheels of the motorcycle has a radius of 0.29 m and a moment of inertia of 0.46 kg m2. What is the approximate total rotational kinetic energy of the wheels? 15. In an amusement park ride, a child stands against the wall of a cylindrical room that is then made to rotate. The floor drops downward and the child remains pinned against the wall. If the radius of the room is 2.15 m and the relevant coefficient of friction between the child and the wall is 0.600, with what minimum speed is the child moving if he is to remain pinned against the wall? Page 1 16. A 0.300-kg mass, attached to the end of a 0.750-m string, is whirled around in a smooth level table. If the maximum tension that the string can withstand is 250 N, then what maximum linear speed can the mass have if the string is not to break? 17. A car is negotiating a flat curve of radius 50 m with a speed of 20 m/s. The centripetal force provided by friction is 1.2 × 104 N. What is the mass of the car? 18. A car enters a horizontal, curved roadbed of radius 50 m. The coefficient of static friction between the tires and the roadbed is 0.20. What is the maximum speed with which the car can safely negotiate the unbanked curve? Page 2