Solids, Liquids, and Gases oh my!!! - super
... Liter (L), and other units. Formula to find volume is length x width x height. Temperature-the measure of the average energy of random motion of the particles of a substance. Pressure- the number of times particles hit the surface of a substance. The formula to find the pressure of an object i ...
... Liter (L), and other units. Formula to find volume is length x width x height. Temperature-the measure of the average energy of random motion of the particles of a substance. Pressure- the number of times particles hit the surface of a substance. The formula to find the pressure of an object i ...
COVER PAGE - PSU MNE - Penn State University
... Reynolds numbers of about 1 105 and 3 106. In cases where a turbulent boundary layer is desired, but the Reynolds number is not quite high enough to achieve a naturally turbulent boundary layer, roughness or other disturbances on the plate (trip wires, vortex generators, etc.) can be used to cau ...
... Reynolds numbers of about 1 105 and 3 106. In cases where a turbulent boundary layer is desired, but the Reynolds number is not quite high enough to achieve a naturally turbulent boundary layer, roughness or other disturbances on the plate (trip wires, vortex generators, etc.) can be used to cau ...
v` mf - EngineeringDuniya.com
... affected by them, the process is called free settling. • If the motion of the particle is impeded by other particles, which will happen when the particles are near each other even though they may not actually be colliding, the process is called hindered settling. ...
... affected by them, the process is called free settling. • If the motion of the particle is impeded by other particles, which will happen when the particles are near each other even though they may not actually be colliding, the process is called hindered settling. ...
Newton`s Laws of Motion
... What would the net force be if two players kick a soccer ball from opposite directions according to the diagram? 1. 60 N, to the left 2. 60 N, to the right 3. 0 N ...
... What would the net force be if two players kick a soccer ball from opposite directions according to the diagram? 1. 60 N, to the left 2. 60 N, to the right 3. 0 N ...
momentum principle
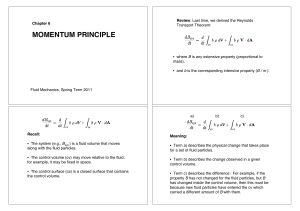
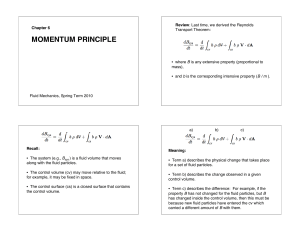
... • Term a) describes the physical change that takes place for a set of fluid particles. • Term b) describes the change observed in a given control volume. • Term c) describes the difference: For example, if the property B has not changed for the fluid particles, but B has changed inside the control v ...
... • Term a) describes the physical change that takes place for a set of fluid particles. • Term b) describes the change observed in a given control volume. • Term c) describes the difference: For example, if the property B has not changed for the fluid particles, but B has changed inside the control v ...
phys1441-120610
... In what ways do you think fluid exerts stress on the object submerged in it? Fluid cannot exert shearing or tensile stress. Thus, the only force the fluid exerts on an object immersed in it is the force perpendicular to the surface of the object. This force by the fluid on an object usually is expre ...
... In what ways do you think fluid exerts stress on the object submerged in it? Fluid cannot exert shearing or tensile stress. Thus, the only force the fluid exerts on an object immersed in it is the force perpendicular to the surface of the object. This force by the fluid on an object usually is expre ...
Pulmpnary
... infants, a standard (20-27 kcal/oz) formula is given along with supplemental enzymes. Hydrolyzed formula with MCT oil may also be used. ...
... infants, a standard (20-27 kcal/oz) formula is given along with supplemental enzymes. Hydrolyzed formula with MCT oil may also be used. ...
Document
... Boyle’s Law • Pressure depends on density of the gas. • Pressure is just the force per unit area exerted by the molecules as they collide with the walls of the container. • Double the density, double the number of collisions with the wall and this doubles the ...
... Boyle’s Law • Pressure depends on density of the gas. • Pressure is just the force per unit area exerted by the molecules as they collide with the walls of the container. • Double the density, double the number of collisions with the wall and this doubles the ...
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids (liquids and gases) in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Some of its principles are even used in traffic engineering, where traffic is treated as a continuous fluid, and crowd dynamics. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves calculating various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space and time.Before the twentieth century, hydrodynamics was synonymous with fluid dynamics. This is still reflected in names of some fluid dynamics topics, like magnetohydrodynamics and hydrodynamic stability, both of which can also be applied to gases.