ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE Mathematical Analysis of a Saint
... In the remaining part of the paper we derive the Saint-Venant equations with an energy equation taking into account the temperature dependence of transport coefficients. These equations are derived from an asymptotic study of a three dimensional incompressible model of a thin viscous sheet over a f ...
... In the remaining part of the paper we derive the Saint-Venant equations with an energy equation taking into account the temperature dependence of transport coefficients. These equations are derived from an asymptotic study of a three dimensional incompressible model of a thin viscous sheet over a f ...
Hopkins Imaging Conference Poster Contest
... the presence of axial contrast concentration gradients in obstructed arteries, but the mechanism responsible for this phenomenon is not well understood. We use computational fluid dynamics to study intracoronary contrast dispersion and the correlation of concentration gradients with intracoronary bl ...
... the presence of axial contrast concentration gradients in obstructed arteries, but the mechanism responsible for this phenomenon is not well understood. We use computational fluid dynamics to study intracoronary contrast dispersion and the correlation of concentration gradients with intracoronary bl ...
u(z + dz)
... When the wind direction turns clockwise, or anticyclonic, with height in the northern hemisphere we say that the wind veers with height. If the wind turns cyclonically with height we say it backs with height. In the southern hemisphere 'cyclonic' and 'anticyclonic' have reversed senses, but wh ...
... When the wind direction turns clockwise, or anticyclonic, with height in the northern hemisphere we say that the wind veers with height. If the wind turns cyclonically with height we say it backs with height. In the southern hemisphere 'cyclonic' and 'anticyclonic' have reversed senses, but wh ...
PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS — DAY 2 The general first
... and to parametrize S by x0 (s) = s. Transport equations play an important role in fluid dynamics and optimal transportation. The method of characteristics directly applies to the quasilinear equation V (x, u) · ∇u = c(x, u) . ...
... and to parametrize S by x0 (s) = s. Transport equations play an important role in fluid dynamics and optimal transportation. The method of characteristics directly applies to the quasilinear equation V (x, u) · ∇u = c(x, u) . ...
A simplified human birth model: Translation of a Rigid - Tulane-Math
... that point, and ε is a regularization parameter. [3] R. Cortez (2001). Method of Regularized Stokeslets, SIAM Journal of Scientific Computing. [4] R. Cortez, L. Fauci, A. Medovikov (2005). The method of regularized Stokeslets in three dimensions: analysis, validation, and application to helical swim ...
... that point, and ε is a regularization parameter. [3] R. Cortez (2001). Method of Regularized Stokeslets, SIAM Journal of Scientific Computing. [4] R. Cortez, L. Fauci, A. Medovikov (2005). The method of regularized Stokeslets in three dimensions: analysis, validation, and application to helical swim ...
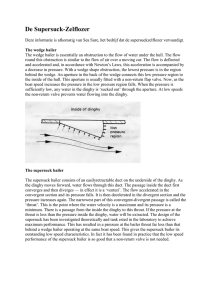
De Supersuck-Zelflozer - Twaalfvoetsjollenclub
... whereas the wedge bailer has not even started to operate! These figures are typical. They vary somewhat with the draught of the boat and with the class of boat. They may even vary slightly with different locations of the bailer in boats of the same class. ...
... whereas the wedge bailer has not even started to operate! These figures are typical. They vary somewhat with the draught of the boat and with the class of boat. They may even vary slightly with different locations of the bailer in boats of the same class. ...
COURSE EXPECTATIONS COURSE CODE: PHYS
... General and Liberal Science programs, introduces fundamental concepts and physical laws in fluid dynamics, mechanical wave, thermodynamics and their applications in modern science and technology. Topics cover: simple harmonic motion; sinusoidal wave, energy transportation by mechanical waves, sound ...
... General and Liberal Science programs, introduces fundamental concepts and physical laws in fluid dynamics, mechanical wave, thermodynamics and their applications in modern science and technology. Topics cover: simple harmonic motion; sinusoidal wave, energy transportation by mechanical waves, sound ...
Fluid Mechanics
... this phenomenon, see Fig. 8.1.1. A fluid of density ρ and viscosity μ flows through a pipe under steady state conditions. The quality of the flow is shown by injecting a thin colored fluid into the main flow. At low velocities the colored fluid is seen as a nearly straight line parallel to the axis ...
... this phenomenon, see Fig. 8.1.1. A fluid of density ρ and viscosity μ flows through a pipe under steady state conditions. The quality of the flow is shown by injecting a thin colored fluid into the main flow. At low velocities the colored fluid is seen as a nearly straight line parallel to the axis ...
CHAPTER 05
... decreasing? A.+ B.C.mass cannot change 6.When the flow is steady the assumption can be made that the mass flow in is equal to the mass flow out. True or False A.True B.False 7.The velocity of the surface of a deforming control volume is ____ at all points. YOUR ANSWER: not the same 8.Newton's second ...
... decreasing? A.+ B.C.mass cannot change 6.When the flow is steady the assumption can be made that the mass flow in is equal to the mass flow out. True or False A.True B.False 7.The velocity of the surface of a deforming control volume is ____ at all points. YOUR ANSWER: not the same 8.Newton's second ...
ENT 211 Week 1 - Introduction to Thermal-Fluid
... Solid Resist an applied shear stress by deforming. Stress proportional to strain. Fluid Deforms continuously under the influence of shear stress. Stress proportional to strain rate. ...
... Solid Resist an applied shear stress by deforming. Stress proportional to strain. Fluid Deforms continuously under the influence of shear stress. Stress proportional to strain rate. ...
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids (liquids and gases) in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Some of its principles are even used in traffic engineering, where traffic is treated as a continuous fluid, and crowd dynamics. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves calculating various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space and time.Before the twentieth century, hydrodynamics was synonymous with fluid dynamics. This is still reflected in names of some fluid dynamics topics, like magnetohydrodynamics and hydrodynamic stability, both of which can also be applied to gases.