ME33: Fluid Flow Lecture 1: Information and Introduction
... analysis are highly accurate, but they are typically time consuming and expensive. Finite control volume approach: described in this chapter is remarkably fast and simple and usually gives answers that are sufficiently accurate for most engineering purposes. ...
... analysis are highly accurate, but they are typically time consuming and expensive. Finite control volume approach: described in this chapter is remarkably fast and simple and usually gives answers that are sufficiently accurate for most engineering purposes. ...
Plasma
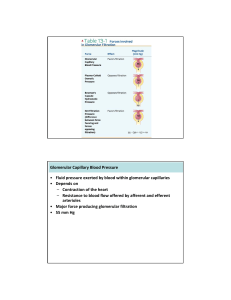
... Vasopressin‐controlled, variable water reabsorption occurs in the final tubular segments. 65 percent of water reabsorption is obligatory in the proximal tubule. In the distal tubule and collecting duct it is variable, based on the secretion of ADH. The secretion of vasopressin increases the permea ...
... Vasopressin‐controlled, variable water reabsorption occurs in the final tubular segments. 65 percent of water reabsorption is obligatory in the proximal tubule. In the distal tubule and collecting duct it is variable, based on the secretion of ADH. The secretion of vasopressin increases the permea ...
Fluid Mechanics Lab
... the new weight and the flow rate. 7. Reduce the flow rate in steps; adjust the weights on the platform to return to its initial position with each move. 8. Install the flat target and repeat the procedure. 9. Install the concave target and repeat the procedure. 10. Install the 8mm nozzle and repeat ...
... the new weight and the flow rate. 7. Reduce the flow rate in steps; adjust the weights on the platform to return to its initial position with each move. 8. Install the flat target and repeat the procedure. 9. Install the concave target and repeat the procedure. 10. Install the 8mm nozzle and repeat ...
Chapter 3
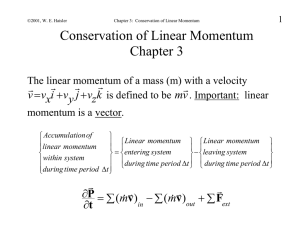
... mass flow in the x direction only. We can write similar momentum terms for mass flow in the y and z directions. Similarly, we can define the forces on the volume due to tractions on the y and z faces. Now, the change in momentum with respect to time: ...
... mass flow in the x direction only. We can write similar momentum terms for mass flow in the y and z directions. Similarly, we can define the forces on the volume due to tractions on the y and z faces. Now, the change in momentum with respect to time: ...
Fluid Flow Notes - The University of Manchester
... its original position. (A viscoelastic material is in between – it will flow to some extent on application of a shear force, and will bounce back to some extent, but not completely, on removal of the applied force. Blu-tack and bread doughs are both examples of viscoelastic materials.) Fluids may be ...
... its original position. (A viscoelastic material is in between – it will flow to some extent on application of a shear force, and will bounce back to some extent, but not completely, on removal of the applied force. Blu-tack and bread doughs are both examples of viscoelastic materials.) Fluids may be ...
NICaN Nurses Guide Infusor System FINAL
... elastomeric balloon pre-filled with a chemotherapy drug that is encased inside a plastic bottle. This method of delivery is a convenient way of administering chemotherapy to avoid long stays in hospital and to keep life as normal as possible for the patient. Delivering treatment in this way is calle ...
... elastomeric balloon pre-filled with a chemotherapy drug that is encased inside a plastic bottle. This method of delivery is a convenient way of administering chemotherapy to avoid long stays in hospital and to keep life as normal as possible for the patient. Delivering treatment in this way is calle ...
Presentation
... • Expansion waves are created by the interaction of multiple shock waves and convex corners • They cause a continuous change in the supersonic flow of the air. • Density, pressure and temperature ratios decrease through the expansion wave while the Mach number increases • Act like gradient index len ...
... • Expansion waves are created by the interaction of multiple shock waves and convex corners • They cause a continuous change in the supersonic flow of the air. • Density, pressure and temperature ratios decrease through the expansion wave while the Mach number increases • Act like gradient index len ...
On the Lorentz-force driven flow around an insulating sphere
... outside of its center. Even though this component is relatively small, it induces noticeable Lorentzforces at the edges of the electrolysis cell. Therefore, the observed flow cannot be uniquely attributed to the influence of the sphere. For this reason, the glass sphere was replaced by an axially ma ...
... outside of its center. Even though this component is relatively small, it induces noticeable Lorentzforces at the edges of the electrolysis cell. Therefore, the observed flow cannot be uniquely attributed to the influence of the sphere. For this reason, the glass sphere was replaced by an axially ma ...
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids (liquids and gases) in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Some of its principles are even used in traffic engineering, where traffic is treated as a continuous fluid, and crowd dynamics. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves calculating various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space and time.Before the twentieth century, hydrodynamics was synonymous with fluid dynamics. This is still reflected in names of some fluid dynamics topics, like magnetohydrodynamics and hydrodynamic stability, both of which can also be applied to gases.