Force Per Unit Mass of Friction in Fluids
... toward the interface rather than away from it) leads to collisions with molecules of fluid on the other side of the interface, thereby exerting a force on the fluid there. The collective z-component of the force of many such molecular collisions, per unit area of the interface, is what we call press ...
... toward the interface rather than away from it) leads to collisions with molecules of fluid on the other side of the interface, thereby exerting a force on the fluid there. The collective z-component of the force of many such molecular collisions, per unit area of the interface, is what we call press ...
Fluids (Chapter 3,13) The term `fluids` is used to describe both gases
... while liquids in the presence of gravity deform to fill the bottom part of the container and form a sharp , usually flat, surface at the top. ...
... while liquids in the presence of gravity deform to fill the bottom part of the container and form a sharp , usually flat, surface at the top. ...
Reaction coefficient of molecular fluorine at wall coated with
... model the unstable regime. Nonetheless, the estimation of the reaction coefficient corresponding to the very beginning of the process can still be used as a first approximation. The measurement of the reaction coefficient during the stable regime can be performed within the limits of these equations ...
... model the unstable regime. Nonetheless, the estimation of the reaction coefficient corresponding to the very beginning of the process can still be used as a first approximation. The measurement of the reaction coefficient during the stable regime can be performed within the limits of these equations ...
Load Duration Curves (LDCs)
... NA indicates not applicable, because most low flows were zero flow. ...
... NA indicates not applicable, because most low flows were zero flow. ...
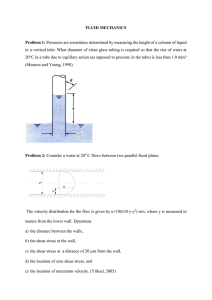
Fluid Mechanics Problems
... a) When the water level is at the top of the gate, determine the magnitude of the fluid force on the rectangular portion of the gate above the shaft and the magnitude of the fluid force on the semicircular portion of the gate below the shaft. b) For this same fluid depth determine the moment of the ...
... a) When the water level is at the top of the gate, determine the magnitude of the fluid force on the rectangular portion of the gate above the shaft and the magnitude of the fluid force on the semicircular portion of the gate below the shaft. b) For this same fluid depth determine the moment of the ...
Chapter 2: Pressure Distribution in a Fluid
... Pressure and pressure gradient In fluid statics, as well as in fluid dynamics, the forces acting on a portion of fluid (C.V.) bounded by a C.S. are of two kinds: body forces and surface forces. Body Forces: act on the entire body of the fluid (force per unit volume). Surface Forces: act at the C.S. ...
... Pressure and pressure gradient In fluid statics, as well as in fluid dynamics, the forces acting on a portion of fluid (C.V.) bounded by a C.S. are of two kinds: body forces and surface forces. Body Forces: act on the entire body of the fluid (force per unit volume). Surface Forces: act at the C.S. ...
Ch2Fall2012
... In fluid statics, as well as in fluid dynamics, the forces acting on a portion of fluid, control volume (C.V.), bounded by a control surface (C.S.) are of two kinds: body forces and surface forces. Body Forces: act on the entire body of the fluid (force per unit volume). Surface Forces: act at the C ...
... In fluid statics, as well as in fluid dynamics, the forces acting on a portion of fluid, control volume (C.V.), bounded by a control surface (C.S.) are of two kinds: body forces and surface forces. Body Forces: act on the entire body of the fluid (force per unit volume). Surface Forces: act at the C ...
Fluidized Bed Characteristics
... 5. Using log-log scale, plot the left side of Eq.(1) versus [(1 - ε)/NRe]. ...
... 5. Using log-log scale, plot the left side of Eq.(1) versus [(1 - ε)/NRe]. ...
Fluids and Viscosity Chapter 7 Particle Theory of Matter (PTM)
... difficulty getting them to stay on our food. Also, if peanut butter were kept in the fridge, the cold temperature would keep it too hard to spread. That is why we keep peanut butter on the shelf when the warmer temperature makes it easier to use! - Motor oils are needed to keep cars lubricated. We n ...
... difficulty getting them to stay on our food. Also, if peanut butter were kept in the fridge, the cold temperature would keep it too hard to spread. That is why we keep peanut butter on the shelf when the warmer temperature makes it easier to use! - Motor oils are needed to keep cars lubricated. We n ...
Turbulent Horizontal Convection and the Global Thermohaline
... must be a slow, possibly basin-wide, upwelling to the surface to match the poleward mass flux, with the loop closed by an inferred zonal average return flow toward the equator at depths below the thermocline. The density structure and heat transport must depend on the rate of vertical diffusion of h ...
... must be a slow, possibly basin-wide, upwelling to the surface to match the poleward mass flux, with the loop closed by an inferred zonal average return flow toward the equator at depths below the thermocline. The density structure and heat transport must depend on the rate of vertical diffusion of h ...
MOMENTUM TRANSPORT
... "angular momentum" and "force" by "torque". To describe the angular momentum and torque we have to select an origin of coordinates "O", and the locations of the midpoints at plane 1 and 2 with respect to this origin are given by the position vectors r1 and r2. ...
... "angular momentum" and "force" by "torque". To describe the angular momentum and torque we have to select an origin of coordinates "O", and the locations of the midpoints at plane 1 and 2 with respect to this origin are given by the position vectors r1 and r2. ...
17-3 Neur Neurosurgical Implants - Sterile, single
... requirement (pass/fail) criteria, results of testing may be required with clearly defined pass/pass criteria. 2. The standard prescribes a test method for determining functional range (pressure/flow characteristics of shunt). Because there is no specific pressure/flow characteristic (pass/fail) crit ...
... requirement (pass/fail) criteria, results of testing may be required with clearly defined pass/pass criteria. 2. The standard prescribes a test method for determining functional range (pressure/flow characteristics of shunt). Because there is no specific pressure/flow characteristic (pass/fail) crit ...
1.Electromagnetic Blood Flow Meters
... direction of the flow of the blood. • Voltage induced in the moving blood column is measured with stationary electrodes located on opposite sides of the blood vessel and perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field. BME 312-BMI II-L3-ALİ IŞIN 2015 ...
... direction of the flow of the blood. • Voltage induced in the moving blood column is measured with stationary electrodes located on opposite sides of the blood vessel and perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field. BME 312-BMI II-L3-ALİ IŞIN 2015 ...
ME33: Fluid Flow Lecture 1: Information and
... OF FLUID IN PIPELINE Not is steady flow state, consider a control mass comprising the whole of the water in the pipe. By Newton’s Second Law: ...
... OF FLUID IN PIPELINE Not is steady flow state, consider a control mass comprising the whole of the water in the pipe. By Newton’s Second Law: ...
Conditions of Linear Motion
... If the linear velocity of the perimeter of a ball with top spin is greater than the relative velocity of the center of mass of the ball and rebound surface, the horizontal velocity of the center of mass of the ball will be greater after rebound. This will result in an angle of reflection greater tha ...
... If the linear velocity of the perimeter of a ball with top spin is greater than the relative velocity of the center of mass of the ball and rebound surface, the horizontal velocity of the center of mass of the ball will be greater after rebound. This will result in an angle of reflection greater tha ...
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a subdiscipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids (liquids and gases) in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics (the study of air and other gases in motion) and hydrodynamics (the study of liquids in motion). Fluid dynamics has a wide range of applications, including calculating forces and moments on aircraft, determining the mass flow rate of petroleum through pipelines, predicting weather patterns, understanding nebulae in interstellar space and modelling fission weapon detonation. Some of its principles are even used in traffic engineering, where traffic is treated as a continuous fluid, and crowd dynamics. Fluid dynamics offers a systematic structure—which underlies these practical disciplines—that embraces empirical and semi-empirical laws derived from flow measurement and used to solve practical problems. The solution to a fluid dynamics problem typically involves calculating various properties of the fluid, such as flow velocity, pressure, density, and temperature, as functions of space and time.Before the twentieth century, hydrodynamics was synonymous with fluid dynamics. This is still reflected in names of some fluid dynamics topics, like magnetohydrodynamics and hydrodynamic stability, both of which can also be applied to gases.